Ever scratch your head and wonder, how does blockchain work? You’re not alone. We’ll dive deep and clear the mist around this tech buzzword that’s reshaping our digital world. It’s not just for crypto lovers; it’s the backbone of trust in online deals. Forget the jargon and the tech babble; I’m here to break it down into bite-size pieces. From ensuring safe transactions to laying new paths for how we interact online, blockchain is the unsung hero of the internet age. Stick around as we explore its inner workings and why being in the know is a game-changer.
Demystifying Blockchain: The Foundation of Decentralized Technology
Understanding Blockchain Technology Fundamentals
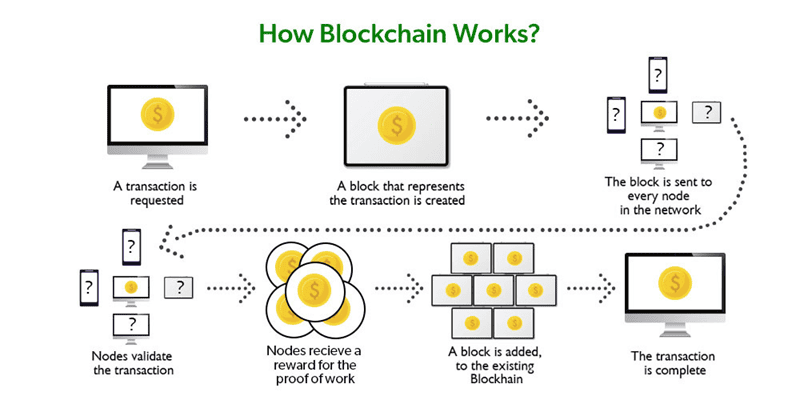
At its heart, blockchain is a list of records. These records are blocks, linked by code. Each block contains a ton of info like data, time stamps, and transaction details. Think of it as a digital ledger. But, instead of a bank or single company in charge, everyone in the network can have a copy. So, it’s like a shared, public notebook that everyone agrees on.
Exploring Decentralized and Distributed Ledger Technology
Decentralized means no single point of power. It’s a team effort to agree on data in the ledger. Distributed means the ledger is copied across a bunch of computers. This setup helps keep info the same across the network.
Let’s dive into the nuts and bolts of blockchain tech.
Imagine your friend sends you a digital coin. This transaction isn’t just between you two. It joins a pool of other trades. Then, a group of users, called nodes, use their computers to confirm these deals. They check everything matches up with the blockchain’s history. This is validating blockchain transactions.
Blockchain uses a special math puzzle for security. This is hashing. Every time a transaction happens, it’s turned into a bit of code. This code is unique. It’s like a digital fingerprint for that deal. This keeps tampering away because changing just one letter in the transaction record would change the whole fingerprint.
There’s also something called a Merkle tree in the mix. It’s a way to put many fingerprints into one. This makes checking the ledger faster and saves space.
Now, how do we decide when to add a block of transactions to the chain? For this, blockchain uses consensus mechanisms. This is just a fancy way to say ‘how we all agree’. One common way is proof of work. It’s like a race to solve a very hard math problem. The winner gets to add the block and earns a reward like new coins.
But some think proof of work eats up too much power. So, they like proof of stake. Here, users put up some of their coins as a pledge to play fair. If they try any funny business, they lose their stake. This uses less energy and can be faster too.
Nodes keep the network up and running. They help check and pass on info. This helps the whole blockchain stay strong against hacks or failures.
The beauty of blockchain is it creates trust in a trustless space. No need to trust a person or a company. Just trust the math and the code. That’s why this tech matters so much. It could change how we do everything from buying homes to voting.
Blockchain’s got its challenges, too. It needs to handle more actions without slowing down. But smart folks are working on this daily. They’re finding new ways to grow without losing that trust and security we all dig.
This tech isn’t magic. But it sure is smart. And we’re just scratching the surface. The more we explore, the more we’ll find ways to use this game-changing tool.
Securing Transactions on the Blockchain
Ensuring Integrity with Hash Functions
Hash functions are the secret sauce in blockchain. They make data secure. Think of them like unique digital fingerprints for info. Each block in the chain has its own hash. If one letter in a block changes, so does its hash. Now, because each block also holds the hash of the one before it, one change messes up the whole chain. This is good. It means we can’t have foul play. If someone tries to change a block, everyone can see it.
This hash linking forms a secure chain of blocks. Even the smartest hackers can’t mess with it easy. Plus, everyone who has the blockchain can check it. So, no one cheats unnoticed. That’s what we call transparency!
Smart Contracts Operation and Their Role in Trust
Smart contracts are like regular contracts. But instead of paper, they’re digital. And instead of lawyers, we have code.
Here’s how they work. Two people make a deal. Instead of writing it down, they put it in a smart contract. This contract lives on the blockchain. It watches everything that happens. When the deal’s conditions are met, the contract acts on its own. No need for a middleman!
This builds trust. With smart contracts, no one can say they didn’t get paid or that they didn’t get what they were promised. The blockchain oversees it all. If you did your part, you get what’s yours. Clear and fair!
Smart contracts are the future. They could change how we do almost everything. Buying a house, getting paid for work, even voting – it could all be done with smart contracts. And with blockchain, it’s all out in the open. Everyone can see the deal’s details. But your personal stuff stays safe. That’s because we have rules that protect your identity.
So, what’s the big deal with blockchain? It’s a game-changer. It keeps transactions safe without needing banks or courts. It’s like having a bodyguard for your data. That’s why businesses and even regular folks are excited about blockchain. It saves time, cuts costs, and adds a huge layer of trust in ways we’ve never seen before!
Architectures of Trust: Consensus Mechanisms and Blockchain Types
The Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake Debate
Blockchains are like trust machines. They let people agree on info without knowing each other. This trust comes from rules called consensus mechanisms. There are two big types: proof of work (PoW) and proof of stake (PoS).
Proof of work is like a math race. Computers solve puzzles to add new blocks to the chain. The first one to solve it wins a reward. This reward is often a coin, like bitcoin. But PoW uses a lot of power, which can harm our planet.
Proof of stake is different. Instead of racing, people “stake” their coins. By doing this, they get a chance to add the next block and earn more coins. It’s like a lottery where putting in more coins gives you more tickets. PoS uses less power and is kinder to Earth.
Distinguishing Between Public and Private Blockchains
Now, let’s talk about another big choice in blockchains. There are two main kinds: public and private. Public blockchains let anyone join and see what’s happening. They are open books. Bitcoin and Ethereum are public. They are secure because so many eyes are watching.
Private blockchains are just for some people, like a company or group. They decide who can join. It’s not for everyone. This kind of blockchain gives more control to the group that runs it. A private blockchain might be used by a bank to keep track of money moving around.
So, public or private? It depends on what you need. Public is good for an open, trustless system. Private is better if you need control and privacy.
Beyond the Chain: Scalability, Interoperability, and Future Trends
Addressing Scaling Challenges in Blockchain Networks
Blockchains are like digital ledgers. They store data in blocks. Each block holds a bunch of transactions. When it’s full, a new block is made. They all link together in a chain. But sometimes, blockchains face a big issue: They can get too slow as more people use them. It’s like a road getting jammed with too many cars.
To fix this, we look at “scaling.” Scaling means making the blockchain handle more stuff without slowing down. It’s vital for blockchain to work fast and well for everyone. Some folks came up with smart ideas to scale blockchains. They make new layers that sit on top of the existing blockchain. It’s like adding express lanes to our road analogy. These layers handle lots of transactions quickly. Then, they update the main blockchain afterwards. It’s a clever fix that helps keep things zipping along.
Another cool way to scale is by making the blocks big. Bigger blocks can hold more transactions. It’s like upgrading to a bigger mailbox. It means less back and forth because you can fit more inside. But here’s the thing – not all folks agree with this plan. Some worry it could lead to other problems, like making it harder for everyone to have a say in the network.
Exploring the Interoperability of Blockchains and Decentralized Applications (dApps)
Okay, so blockchains are neat on their own. But what if they could talk to each other? That’s where “interoperability” comes in. It means different blockchains can share info smoothly. Imagine two puzzle pieces from different puzzles that still fit together. That’s pretty cool, right?
Interoperability lets different blockchains pass transactions and data around without a hitch. It helps us use dApps — apps that run on a blockchain — from different blockchains without a hassle. It kind of gives superpowers to dApps, making them work across various chains.
This is huge because it opens up a ton of chances for new services and products. It’s like having a universal remote for your TV, Blu-ray, and sound system all at once. Before, you may have needed a separate remote for each chain or dApp. But with interoperability, it’s much simpler. You get to use one mega remote for everything!
The future of blockchains is bold and bright. With scaling solutions and interoperability, they could change how we do stuff on the internet. From buying things with crypto to voting in elections, blockchains could be everywhere. It sounds like a lot, but remember, a little while ago, the internet was a new thing too. Blockchains could be the start of something just as big. So, let’s keep an eye on where this wild tech goes next!
In this post, we’ve broken down blockchain, revealing the nuts and bolts of decentralized tech. From the basics of distributed ledgers to securing deals with hash functions and smart contracts, we covered the essentials that build trust in this digital space. We looked at the power struggle between Proof of Work and Proof of Stake and learned how public and private blockchains differ. Finally, we touched on the future: tackling scale woes and linking different blockchains and apps. My final thought? Blockchain is more than just tech buzz; it’s a growing field that’s reshaping trust and teamwork across the net. Keep your eyes on this space – it’s evolving fast and holds great promise for tomorrow.
Q&A :
How is a blockchain transaction processed?
A blockchain transaction undergoes several steps to ensure complete validation and security. Initially, a transaction is created and signed by the initiator, then broadcast to a network of peer-to-peer computers, known as nodes. Nodes validate the transaction using agreed-upon algorithms. Once verified, the transaction is combined with other transactions to create a new block of data for the ledger. This block is then added to the existing blockchain, in a way that is permanent and unchangeable, thus completing the transaction process.
What ensures the security and integrity of blockchain?
Blockchain’s security and integrity are maintained through cryptography, decentralization, and consensus mechanisms. Each block contains a complex mathematical puzzle with a unique solution, ensuring that changing any aspect of the block is extremely difficult. Additionally, since every participant has a copy of the entire blockchain, data is secured against tampering. Consensus algorithms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) require network participants to agree on the validity of transactions, making fraudulent activities unfeasible.
Can blockchain transactions be reversed?
Typically, blockchain transactions are irreversible. Once a transaction is added to a block and the block is appended to the blockchain, it is computationally impractical to alter it due to the cryptographic hash links between blocks. This irreversibility is a core feature that ensures trust and security within the blockchain but also means that users must be cautious as transaction errors cannot be easily rectified.
What role do nodes play in a blockchain network?
Nodes are essentially the individual computers that participate in a blockchain network. Each node has a full copy of the blockchain and works to maintain its integrity and accuracy. Nodes validate new transactions, add them to the block they are building, and share the completed blocks with other nodes. Through a collective consensus mechanism, they agree upon the verified transactions and the state of the blockchain, thus ensuring a decentralized and secure network.
How does blockchain differ from traditional banking systems?
Blockchain operates on a decentralized network structure, which contrasts sharply with the centralized model of traditional banking systems. Blockchain technology allows for peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries such as banks. It offers increased transparency with a public ledger, reduced transaction times, and enhanced security through immutable record-keeping. In contrast, traditional banking systems rely on central authorities, which can lead to longer transaction times and increased vulnerability to centralized data breaches.

RELATED POSTS
The Unique Characteristics of Blockchain Technology – A Guide to Its Power and Potential
The unique characteristics of blockchain...
Top 3 Secrets behind Bitcoin Peak that you must know
The rise and fall of...
How to protect your crypto private key: Unbreakable Security Tips
Learn how to protect your...
Evolution of Smart Contract Technology: Unlocking the Future of Digital Agreements
Discover the Evolution of smart...
What is Distributed Ledger Technology in Blockchain?
Discover the fundamentals of distributed...
Gala Airdrop and 6 Tips to Maximize Gala Game Rewards
To maximize rewards from the...
Humanity Protocol Airdrop: Step-by-step guide to participate
Humanity Protocol is an innovative...
Is Ledger Nano X Safe? Ledger Nano X vs Ledger Nano S
The Ledger Nano X is...
Grass Airdrop Stage 2 is almost here – Don’t miss out!
Successfully navigating the Grass Airdrop...
Wormhole Airdrop – Take Advantage of 3 Valuable Investment Opportunities
Wormhole Airdrop is not only...
The Evolution of Cryptocurrency and Blockchain Technology – 7 Things to Look Forward To
Cryptocurrency and Blockchain Technology have...
Can blockchain track pharmaceuticals throughout the supply chain?
Can blockchain track pharmaceuticals throughout...
Unveiling the Future: Benefits of blockchain transparency
Enhance trust & transparency with...
HTX Airdrop – Tips for Optimizing Digital Asset Investment
HTX Airdrop is not just...
Challenges of Blockchain: Can It Truly Prevent Voter Fraud?
Challenges of using blockchain for...
Blockchain Security Audits: What’s Under the Microscope?
What do Blockchain Security Audits...