Comparison of consensus mechanisms in blockchain doesn’t just compare tech jargon; it unlocks the core of blockchain’s trust. It’s the hidden muscle that makes digital cash jump and smart contracts run without a trip. Here, we will peel back the layers of this tech wizardry. Each click and transaction owes its life to these unsung heroes. So from PoW’s gritty gears to PoS’s sleek design, let’s dive into a world where every byte counts. This isn’t just a geek squad rally; it’s the tour you need to grasp blockchain’s rulebook. Strap in and get ready to see blockchain’s gatekeepers unveiled.
Understanding the Basics of Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms
Deciphering the Role of Consensus in Blockchain Operation
Imagine a group of kids choosing a game to play. They must agree, or no game happens. This is what we call consensus. It’s making sure everyone has the same info and agrees with it. In blockchain, consensus is like the kids agreeing, but for transactions and their order. It makes sure everyone follows the rules.
Consensus in blockchain means all computers, called nodes, agree on the list of transactions. Imagine a ledger that everyone has a copy of. This ledger says who owns what and moves what around. Consensus is like saying, “Yes, we all see the same thing”. It is key for trust in the system.
Blockchain can’t work without everyone agreeing. It would be like trying to build a tower with different blueprint copies. It would fall! Consensus keeps the tower strong. It uses rules, called a protocol, to make sure everyone plays fair and the same.
Analyzing the Components of a Consensus Protocol
Let’s peek into the box of consensus protocols. It has several pieces that fit together. The main parts are:
- Agreement on Truth: Like nodding heads in a meeting, all nodes must see the same transaction history to agree.
- Block Creator Selection: It’s like picking who will be ‘It’ in a game of tag. The protocol chooses who gets to add the next block of transactions.
- Validation Process: This is like double-checking your math homework. Nodes check to make sure the new block follows the rules.
- Incentives: The kid who finds the others in hide and seek gets a high five. In blockchain, nodes get rewards, like cryptocurrency, for helping out.
- Security Measures: Like a secret clubhouse password, these keep the blockchain safe from unwanted changes or attacks.
Let’s talk “hashing”. Think of it as a secret code for transactions that’s really hard to guess. It locks in the data. Miners or validators are like the locksmiths, solving complex puzzles to seal the deals onto the blockchain.
In the world of cryptocurrency, staking is putting up tokens as a pledge to be a good validator, almost like a security deposit. If you’re a validator and you break the rules, you might lose your tokens.
And then there’s Byzantine fault tolerance, which is a fancy way of saying the system can handle some mischief and not break down. It spots any attempts to mess with the ledger and stops them.
So, consensus is a mix of rules and tools that make sure the digital world plays nice. It’s the heart of the blockchain, pumping trust through the tech with every beat. Whether it’s proof of work with miners chipping away at puzzles, or staking where you put something on the line to take part, it all comes down to keeping the blockchain beating strong.
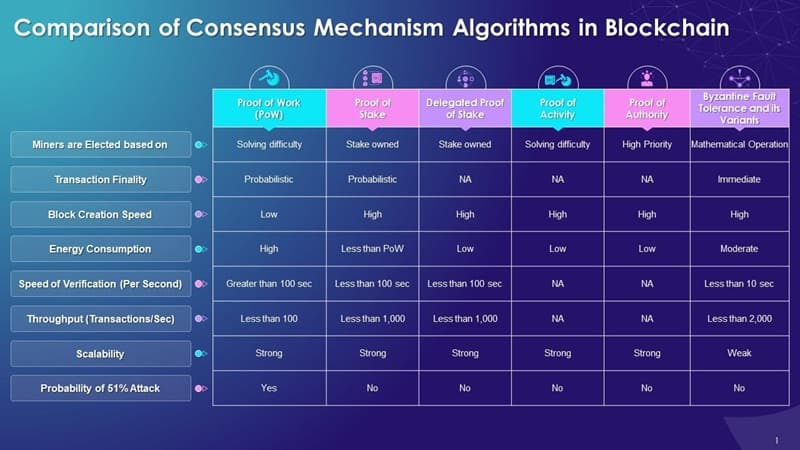
Delving into Prominent Consensus Models: PoW, PoS, and DPoS
Proof of Work (PoW): Operating Principles and Implications
Proof of Work stands as the pioneer among blockchain consensus protocols. It’s all about solving puzzles. Complex puzzles. Miners across the globe race to solve these puzzles first. The reward? New coins and transaction fees. PoW keeps the network safe from fraud and attacks. But it’s like a power-hungry giant. It consumes lots of electricity. So, we worry about its environmental impact. Yes, it offers top-notch security but at a cost to our planet.
Mining defines who adds a new block to the chain. They need massive computing power for that. That’s where miners come in. They use specialized hardware to do the job. Bitcoin is the most famous PoW blockchain. It’s super secure, yet super power consuming, too.
Proof of Stake (PoS) and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): Mechanism and Evolution
Proof of Stake is quite different. It chooses block creators by looking at the number of coins they hold. If you own more, you have a higher chance to be the one. It’s not about who has the most powerful machines now. It’s about who’s got more skin in the game.
PoS makes things cheaper and greener. It uses less energy than PoW. Way less. And it’s getting popular in the crypto world. Ethereum, a big name in crypto, is moving from PoW to PoS. That’s a big deal, showing the growing PoS benefits in cryptocurrency.
Let’s talk DPoS, shall we? Delegated Proof of Stake takes PoS further. How? By adding a voting system. In DPoS, coin holders vote for representatives. These reps validate transactions and maintain the blockchain. It’s democracy in action on the blockchain!
DPoS is fast. It scales well, meaning it can handle more without slowing down. But there’s a trade-off. Fewer validators could mean more centralization. That’s why it’s crucial to understand the PoS vs DPoS differences. Everyone needs a fair shot, without handing over too much power.
Both PoS and DPoS have improved the node validation process in blockchain. They’re more energy-efficient compared to PoW. Still, some worry about their security. Could attackers with lots of coins override the system? This is where Byzantine fault tolerance comes into play. It’s a security feature. It stops failures when some nodes are unreliable.
In PoS, if you stake your coins, you can be a validator. This builds a more secure system. Validator nodes and security go hand in hand. They help prevent bad actors from messing with the network. And let’s not forget about stake-based consensus advantages. They bring better speed and less energy consumption to blockchain. That’s what we like to see!
Remember, all these models aim for one goal: to decide who makes the next block. Whether it’s by mining in PoW, staking in PoS, or voting in DPoS, each plays a crucial part. They’re gatekeepers, ensuring only legit transactions make it. They keep blockchain trusty and running smooth. We’re in the middle of a consensus transformation, folks. Let’s see where it takes us.
Evaluating the Impact of Consensus Mechanisms on Blockchain Efficacy
Environmental Considerations of PoW and the Shift Towards Sustainability
You might know how blockchain works. But did you think about its impact on our planet? It’s huge! Let’s talk proof of work, or PoW for short. PoW is like a huge race where miners compete to solve puzzles and get new coins. Yet, this race uses more energy than entire countries! It’s amazing but also a bit scary, right?
Now, we’re seeing a shift. People want sustainability. They ask, “Can we keep our digital worlds and protect our real one too?” And that’s where proof of stake, or PoS, comes in. PoS doesn’t need the crazy race like PoW. Instead, it’s like a lottery where the more coins you have, the more chances you get to add a new block. It cuts down on energy use a lot. We still keep our network safe and get to be kinder to Earth!
Performance Metrics: Speed, Scalability, and Security in Different Consensus Algorithms
Digging deeper, performance is key in blockchain. We want it fast, able to grow, and super secure. So, how do these popular models measure up?
PoW is reliable but slow and tough to scale up. Your transaction could take minutes or even hours! PoS speeds things up and can handle growth better. And then there’s delegated proof of stake, DPoS. It’s like PoS but with a twist. A group of users gets picked to take turns adding blocks. This makes things even faster and allows more transactions.
What about keeping everything safe? In comes Byzantine fault tolerance, or BFT. It’s a way to make sure that even if some folks try to mess with the system, we’re still good. If you tie BFT with PoS, you get a strong mix of speed and security.
And let’s not forget about how many people a blockchain can serve! Scalability in consensus models is a big deal. We need our blockchains to keep up with more users and more transactions. PoS and DPoS have a leg up here. They’re built to scale without needing more power like PoW.
So, we’ve got different paths for blockchain to run well. From PoW mining to staking in PoS, each has its place. But it’s clear which way the wind is blowing. We all want a digital world that’s quick, wide-reaching, and safe. And let’s make sure it’s one where our planet doesn’t pay the price.
Exploring Advanced Consensus Mechanisms and Future Directions
Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) and Its Role in Enhancing Security
Did you know some blockchain systems are like fortresses? They use a trick called BFT. BFT stands for Byzantine Fault Tolerance. It’s a way to keep blockchains safe.
Imagine a group of guards. They must all agree to open the gates. Even if some guards turn bad or mess up, the city stays safe. This is what BFT does. It keeps your digital coins safe like the city. If some computers go rogue or fail, the blockchain won’t break.
Byzantine Fault Tolerance explained is simple. It’s a rule for computers to agree in tough conditions. Even with troublemakers, BFT makes sure all honest computers come to the same decision. This is key for security in blockchains.
Now, let’s dig deeper. Sometimes, in the blockchain, there are bad actors or broken nodes. BFT steps in to stop them from causing harm. Each node in the network must agree with the others before a transaction is final. If nodes don’t agree, no harm done. The network pauses that move. This is how BFT keeps your blockchain safe.
The strength of BFT is crucial for big systems. Big names in finance or health might use blockchain one day. They will need BFT to trust the system.
So, understanding BFT is like knowing the secret of the guards. It lets us trust the digital world a bit more.
Innovations in Energy-Efficient Algorithms and Crypto-Governance Models
Now let’s talk about saving energy. Some blockchain ways are big energy eaters, like PoW. PoW stands for Proof of Work. It uses a lot of power because it makes computers solve puzzles. That’s the PoW mining mechanism.
When we compare proof of work vs proof of stake, things change. Proof of Stake (PoS) is different. It’s like picking a guard based on their trust, not how fast they run. PoS puts someone in charge based on how much they have invested.
Pros and cons of PoW? It’s safe but burns lots of energy. PoS benefits in cryptocurrency mean less energy use and it’s faster.
There’s more! Enter Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS). Think of DPoS as a council making quick choices. It’s faster than PoW and PoS but still safe. With DPoS, people vote to pick a few in charge. The others trust them to make good choices. This can speed things up!
Blockchain validation methods must be quick, use less power, and keep things fair. Energy-efficient consensus algorithms are what we’re working on now. We want to keep your digital stuff safe without hurting our planet.
We’re finding new ways, like staking in blockchain. This lets people earn rewards for keeping the network going. The node validation process in blockchain is also key. We’re making sure each part of the system checks the others.
To sum it up, we’re making sure everything runs smooth in blockchains. We’re keeping it safe and using less energy. That’s the job of finding better ways to agree in the digital world. Changes like PoS and DPoS help a lot!
In the future, we’ll keep hunting for the best mixes. We’ll keep making these digital fortresses better for everyone. The mix will include speed, energy use, and rock-solid trust. We want it all working great for when you use it!
In this post, we dived deep into blockchain’s core – consensus mechanisms. We unpacked how they work and their role in keeping digital ledgers secure. From Proof of Work to Proof of Stake and even the advanced Byzantine Fault Tolerance, we’ve seen a lot.
We know now, consensus is vital for blockchain operations. It’s the engine under the hood of every blockchain, deciding how trust and security happen and how new blocks get approved. It’s clear, too, that different models affect blockchain speed, safety, and its eco-footprint.
Technology never stops, and as blockchain grows, so will these systems. We looked at new, green algorithms and ways blockchains can govern themselves. Who knows what exciting consensus methods we’ll see next?
Keep eyes on blockchain’s ride to the future—it’s shaping up to be an interesting journey. Remember, it’s not just about keeping pace with tech, but understanding what lies beneath can pave the way for smarter, more informed decisions in a digital world.
Q&A :
What are the main types of consensus mechanisms used in blockchain?
Consensus mechanisms are the protocols that allow nodes in a blockchain network to agree on the validity of transactions and thus achieve decentralization without the need of a central authority. The main types of consensus mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), and Proof of Authority (PoA). Each of these has different requirements for validating transactions and securing the network, and they come with their own set of advantages and drawbacks.
How do Proof of Work and Proof of Stake differ?
Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) are two distinct consensus mechanisms with different approaches to validating transactions. PoW requires miners to solve complex mathematical problems, which consumes substantial computational power and energy. The first miner to solve the problem gets to add a new block to the blockchain and is rewarded with cryptocurrency. PoS, on the other hand, involves validators who are chosen to create new blocks based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to ‘stake’ as collateral. PoS is generally considered to be more energy-efficient than PoW.
Why are consensus mechanisms important in blockchain technology?
Consensus mechanisms are the heart of blockchain technology as they ensure the integrity and security of data without the need for a central authority. They enable network participants to reach a common agreement on the state of the ledger. This is vital for maintaining the decentralized and tamper-resistant nature of blockchain, which in turn fosters trust among users and supports a wide range of applications from cryptocurrencies to smart contracts.
Which consensus mechanism is best for transaction speed and scalability?
Transaction speed and scalability are two critical issues that blockchain networks aim to improve. Among various consensus mechanisms, some are designed to optimize for faster transaction speeds and greater scalability. For example, Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) allows for quick processing of transactions by having a limited number of delegated nodes or validators. This makes DPoS-based blockchains like EOS and Tron very scalable compared to PoW networks like Bitcoin. However, the “best” mechanism depends on the specific requirements and trade-offs a particular blockchain network is willing to make.
Can consensus mechanisms impact the environmental sustainability of blockchain?
Yes, consensus mechanisms can greatly impact the environmental sustainability of blockchain networks. Proof of Work (PoW), the mechanism used by Bitcoin, Ethereum (currently transitioning away from PoW), and other cryptocurrencies, is well-known for its high energy consumption. This is due to the computation-intensive mining process. Conversely, Proof of Stake (PoS) and other less resource-intensive mechanisms, such as Proof of Authority (PoA) or Proof of Space (PoSpace), offer a more environmentally friendly alternative as they require significantly less power to operate. As a result, there is a growing trend towards adopting such mechanisms to create more sustainable blockchain ecosystems.


RELATED POSTS
Ongoing Research Projects in Blockchain: Decoding Tomorrow’s Tech Revolution
Explore ongoing research projects in...
Can you short on Coinbase Pro?
Can you short on Coinbase...
How Blockchain will be used in the future: Help to transform industries
How will blockchain revolutionize industries...
Disadvantages of Blockchain: Beyond the Hype, What Are the Real Costs?
Navigate the limitations of blockchain...
Kelp DAO Airdrop – How to Earn Money from Kelp Miles
The Kelp Miles program within...
What is blockchain security?Is Your Digital Fortress Unbreachable?
What is blockchain security? Explore...
How to Secure Private Keys: Your Essential Guide to Cryptographic Safety
Learn how to secure private...
What Makes the Connection Between Blockchain Technology and Cryptocurrencies Special?
Blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies form...
Steps Involved in Blockchain Technology: Unraveling the Digital Ledger’s Mysteries
Discover the steps involved in...
What Is A Distributed Ledger: A Beginner’s Guide
Unveiling the Fundamentals of Distributed...
Custodial vs Non-Custodial Wallets: Which Secures Your Crypto Best?
Custodial vs Non-Custodial Wallets: Understanding...
Exploring 2 Roles of Permissioned Blockchain
A permissioned blockchain restricts access...
What is blockchain technology and How does it work?
What is blockchain technology and...
Unlocking the Mystery: How Does Blockchain Work for Beginners?
How does blockchain work? Understanding...
Comedian Airdrop – Token BAN Leads the Memecoin Trend
In the world of memecoins,...
Regulations for Blockchain Technology: Navigating the New Legal Landscape
Understanding the legal framework for...