How to Secure Public Keys: Think it’s a walk in the park? Think again. This is about locking down your digital assets tight. With cyber threats on the rise, knowing how to secure public keys isn’t just smart; it’s crucial. I’ll break it down simply – no jargon, just plain talk on beefing up your security. You’ll learn the works: from basic PKI knowledge to the top-tier strategies for keeping your keys away from prying eyes. Stick with me, and you’ll become a pro at shoring up those digital defenses. Let’s dive in and turn your public key fortress into an uncrackable stronghold.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
What is PKI and Why It’s Essential for Secure Communications
Public Key Infrastructure, or PKI, is a way to secure stuff we send online. Think of it like sending a locked box through the mail. The person who gets it needs a special key to open it. That’s what PKI does. It locks data so only the right person can unlock it.
When you use PKI, your info is safe from prying eyes. It’s like whispering a secret into a friend’s ear. Nobody else can hear it. That’s why banks and shops use it when you buy stuff. They don’t want anyone stealing your card number.
The Role of Asymmetric Encryption in PKI
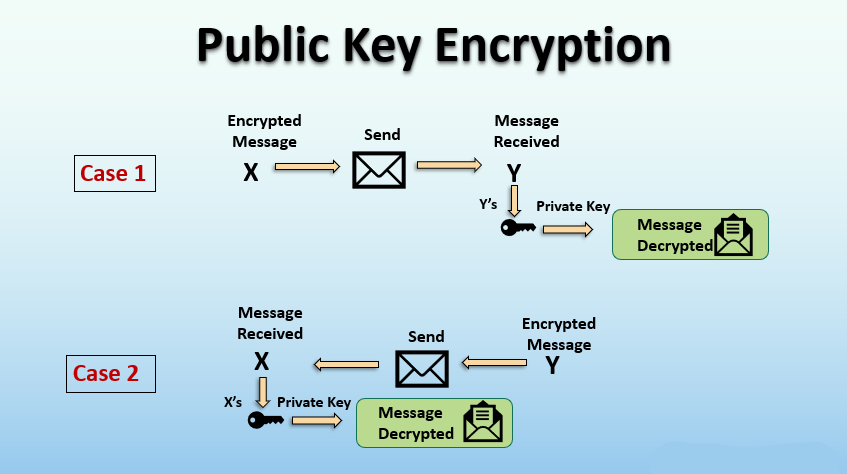
PKI uses two keys. One is public; you can give it to anyone. The other is private; you keep it safe. When someone sends you data, they lock it with your public key. But only your private key can open it. It’s like having a mailbox where anyone can drop mail, but only you have the key to open it.
Asymmetric encryption keeps things safe but not so tough to use. It makes sure no one can mess with your stuff without the right key. It’s a strong lock for your digital doorstep.
Best Practices for Public Key Encryption and Management
Secure Key Generation and Distribution Techniques
When you’re working with public key encryption, it’s a bit like guarding a castle. You want strong walls and trusted guards. For keys, this means making them in a way that’s hard to crack. Secure key generation starts with random numbers. Think of it like rolling dice but way more complex. You want your key to come out unique and tough.
Now, let’s talk about giving out keys safely. Imagine a key exchange like passing notes in class. You don’t want anyone else to peek. So, you use secure methods to share your public keys. This might be through trusted paths like secure websites or face-to-face meetings.
Public Key Cryptographic Standards Compliance
It’s also about following rules, known as standards. These rules are like a secret recipe that keeps everyone safe. They make sure your public keys work well and stay safe. When you stick to these standards, you help keep your data and everyone else’s data locked tight. Think about it as playing a sport. You need to know the rules to play fair and avoid problems.
Experts use these rules to avoid risks and keep keys from falling into the wrong hands. You need to make sure your public keys can stand up against hackers. That’s like making armor out of the strongest metal. This keeps secrets safe and sounds within the castle walls, where only the right people can reach them.
Implementing Key Security Protocols and Storage Solutions
Key Lifecycle Management: Archiving and Destruction Strategies
We need strong rules for keeping our keys safe. They must cover making, using, storing, and throwing away keys. When you make a key, it should be random and tough to guess. You should keep it in a safe place that only a few can access. Think of it like a treasure map. You wouldn’t leave that lying around!
Keys need to be backed up, too. This means making copies to keep in different secure spots. If a key gets lost or broken, you can pull out a backup without panic. Backups also need strict control to avoid leaks.
Key archiving is about putting old keys away safely. You may still need these keys to read old messages or files. So you pack them up and store them where hackers can’t reach them.
Then comes destruction. When a key has served its time, you must destroy it totally. This makes sure it won’t be used in the wrong way later. It’s like shredding your personal papers. No traces left for snoopers to find.
Safeguarding Cryptographic Keys with Advanced Storage Hardware
Now, let’s talk about advanced hardware for key storage. Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) are like vaults. They keep your keys locked tight. Only certain people can get in with the right checks in place. It’s a bit like having a special, super-secure locker for your keys.
You store a key in an HSM, it stays away from the online world. This makes it harder for thieves to swipe your keys. They can’t just hack in; they’d need to break into the physical HSM.
Such gear has built-in checks. These make sure the key has not been changed or messed with. It’s like a secret handshake. If the handshake doesn’t go just right, the HSM knows something’s up.
Each time a key gets used, the HSM logs it. These logs are proof of who touched the key and when. Like a sign-in sheet at a top-secret club, it keeps track of comings and goings.
But what if something goes wrong? What if the HSM stops working? This is where secure key escrow comes in. It means you have a backup plan. A trusted third party holds onto a copy of your keys, in case of emergency.
Remember, even with the best tools, we still need smart rules and careful actions by people. Together, they form a powerful shield around our precious keys. Our goal is to keep the bad guys out and let the good stuff flow safely.
Maintaining and Securing PKI Architecture
Managing SSL/TLS Certificates for Web Security
SSL/TLS certificates are web security rock stars. They make sure data sent over the internet is safe. When you see a lock icon next to a website’s address, know that SSL/TLS is at work. They are like sealed envelopes for online messages. Only the right receiver can open them. This stops sneaky folks from peeking at your info. To keep this shield strong, you must check your SSL/TLS certs often. Make sure they have not expired. Replace old ones before they cause trouble. It’s like checking the locks on your doors at home.
When picking SSL/TLS certificates, don’t just grab any. Choose trustworthy ones. Look for certs from respected issuers. These issuers check who owns the site. They make sure the site is real and safe. It’s like getting a good lock from a trusted locksmith. Always keep private keys secret. If someone else finds them, they can unlock your data. Protect them like you would a house key. Never share it with strangers.
Monitoring and Renewing Keys to Mitigate Vulnerability Risks
Stay sharp about key security. Hackers keep finding new tricks. If your keys get old, hackers might break them. Check them like you would batteries in a smoke alarm. Make sure they are fresh and work well. Renew keys before they wear out. This helps keep your secrets safe.
When you swap out a key, tell everyone who needs the new one. This is key exchange security. It’s like giving a new house key to your family. You don’t want to lock them out. Keep a list of who has the key. This is an access control list. It’s very important.
If you find a key is not safe, fix it fast. This is key revocation. It’s like knowing you lost a house key. You would change your locks in no time. After you cut a new key, throw the old one away properly. This is key destruction. Think of shredding old bank papers. It’s best to make sure no one can use them.
Backing up keys is also key. This is secure key backup. Do it the right way. It’s like having a spare house key, just in case. If you lose your key, you are not stuck. But keep the backup in a safe place. Only let certain people reach it. This will avoid public key exposure. You wouldn’t leave your spare house key just anywhere.
Keep track of every time you use a key. This is an audit trail. Think of it as a sign-in sheet for a club meeting. It helps figure out who came in and out. This way, if something goes wrong, you know where to look. It’s also good to store keys safely. This protects keys in transit. Think of moving houses. You wouldn’t throw your stuff in an open truck.
To sum up, keep your SSL/TLS certificates and keys sharp and safe. Do regular checks. Choose them well. Keep private keys secret. Switch old keys with new ones. Keep a close eye on who has access. If a key goes bad, swap it. Back up keys properly. Always know when and where keys are used. With these tips, your online house will stay safe and sound.
In summary, this blog post has given you a solid grasp of Public Key Infrastructure. We’ve learned what PKI is and why it protects our online chats. We saw how asymmetric encryption is essential to this system. We talked about making and sharing keys safely, and following public key standards. Then, we looked at safe ways to handle key life phases, and where to keep these keys securely. Finally, we delved into managing SSL/TLS certificates and updating keys to keep security tight.
I hope these insights equip you to strengthen your digital defense. PKI is no small topic, but it’s essential for a secure online presence. Remember, excellent key management and staying up-to-date makes all the difference! Stay safe and secure out there.
Q&A :
How can I ensure my public key remains secure?
Securing your public key is crucial for maintaining the integrity of encrypted communications. To keep your public key secure, it’s essential to implement best practices such as using strong cryptographic algorithms, storing the key in a secure environment, sharing it carefully and through trusted channels, and using key management systems for enterprise-level security. Regularly updating and replacing keys also adds a layer of security. Remember, while a public key is meant to be shared, it should only be distributed in ways that do not compromise the corresponding private key.
What are the risks associated with exposing public keys?
While public keys are designed to be shared openly, improper handling can still pose security risks. Exposure through insecure channels can lead to man-in-the-middle attacks, where a malicious actor intercepts the key to decrypt or alter communications. Moreover, if the public key is not authenticated, it can be replaced with a key controlled by an attacker, compromising security. To mitigate these risks, always verify the authenticity of public keys and use secure methods for distribution and storage.
Can strong encryption algorithms protect my public key?
Strong encryption algorithms form the foundation of public key security. These algorithms, such as RSA, ECC, and AES, are designed to create a secure channel for sharing information. However, the security also depends on key length and complexity. Longer and complex keys are harder for attackers to compromise. Regularly updating your encryption algorithms and monitoring for any vulnerabilities or updates in cryptographic standards are critical for maintaining public key security.
What is the best practice for sharing my public key?
The best practice for sharing your public key is to distribute it through secure and authenticated channels. This could include using a trusted Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), digital certificates from a recognized Certificate Authority (CA), or secure websites using SSL/TLS protocols. Additionally, you could employ digital signatures to verify the integrity and authenticity of the public key being shared. Ensure that your public key is accessible only to intended recipients and that there are methods in place to confirm its validity.
How often should I update or replace my public key?
The frequency of updating or replacing your public key depends on several factors, including the sensitivity of the data being protected, the strength of the key, and the prevalence of emerging threats. As a general rule of thumb, for high-security situations, you should consider key rotation on an annual basis or in accordance with industry or organizational security policies. Additionally, if a key is suspected to have been compromised, it should be replaced immediately. Staying informed about advancements in cryptography will help you determine an appropriate key lifecycle.

RELATED POSTS
Proof of Elapsed Time in Crypto: Unveiling the Mystery Behind Secure Consensus
Discover the advantages of PoET...
Peaq Crypto: A disruptive Blockchain platform
Peaq Crypto, a high-performance layer...
How will blockchain be used in the future: Beyond Bitcoin and Boundless Possibilities
How will blockchain be used...
Basic Explanation Of How Blockchain Works: Blockchain Revolutionizes Transactions
Discover the Basics of Blockchain:...
Real-world Applications Of Blockchain Technology: Beyond Bitcoin’s Buzz
Revolutionizing finance, trade, and security....
How to protect your crypto private key: Unbreakable Security Tips
Learn how to protect your...
Unveiling The Future: Benefits Of Using Blockchain In Different Industries
Benefits of using blockchain: transform...
Blockchain Breakthroughs: Blockchain Trends And Predictions In Financial Services
Discover the latest trends and...
Blockchain Architecture Demystified: Unlocking the Digital Backbone
What is Blockchain Architecture? Understand...
What is Data Tokenization? – The Key to Secure Data Management
What is Data Tokenization? This...
Vessel Finance: The DEX with near-zero gas fees
In the ever-evolving world of...
Smart Contracts: Unlocking Efficiency and Security in Transactions
Advantages of smart contracts -...
Blockchain Mysteries: What is a transaction in blockchain?
What is a transaction in...
Fishwar Airdrop – Play to Earn on the Sei Blockchain
Fishwar Airdrop, a prominent project...
Regulations for Blockchain Technology: Navigating the New Legal Landscape
Understanding the legal framework for...
Why Solana Layer 2 Sonic is the Key to High-Performance Gaming
Solana Layer 2 Sonic is...