What is blockchain consensus algorithm, you may wonder? Simply put, it’s the backbone that keeps the blockchain alive—securing digital trust in a decentralized world. From Bitcoin to your favorite altcoin, they all rely on this silent gatekeeper to reach agreement. Think of it as the unsung hero ensuring every transaction is legit without needing a middleman. Now, the crypto-world buzzes with terms like Proof of Work and Proof of Stake. But what do they mean, and why should you care? Let’s dive in, demystify these mechanisms, and see why they’re crucial for blockchain’s promise of a secure digital future.
Understanding Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms
The Role of Consensus in Blockchain Functionality
Blockchain works like a team game. Everyone needs to agree on the score. This agreement is called consensus. It makes sure all players play fair. Consensus is key for trust in the blockchain game.
Comparing Proof of Work and Proof of Stake
Let’s explore two main ways a blockchain agrees, or reaches consensus. Think of Proof of Work (PoW) like mining for gold. Miners solve hard math problems. They use lots of computer power. The first to solve it, wins a block of transactions and rewards, like new coins.
Proof of Stake (PoS) is different. It’s like a raffle. The more coins you hold, the more chances to validate and earn rewards. You don’t need big, power hungry computers.
PoW blockchain, like Bitcoin, uses lots of energy. It can be slow. But it’s been around a long time. Many trust it because it’s like the original game.
PoS blockchain has a newer idea. It uses less energy. It can be faster. But it’s like changing game rules. Players are still learning to trust it.
These two are a big part of how blockchain maintains consensus. They help stop cheating, like double spending. This is when one player tries to score the same point twice.
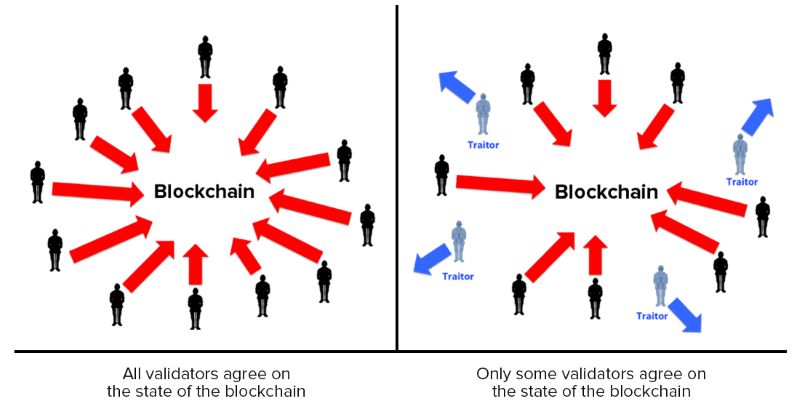
Byzantine Fault Tolerance, or BFT, is another way to keep the game fair. It helps even if some players are trying to mess up. Decentralized ledger technology uses BFT to keep everyone honest.
Nakamoto consensus is named after Bitcoin’s creator. It’s a mix of PoW and some other rules. It also helps keep the blockchain game fair and safe.
Now, consensus without mining is a fresh idea. It’s like playing a game without needing to dig for treasure first. This is meant to save energy.
The blockchain validation process is how the game score is checked. It’s important everyone agrees. This helps keep the game honest.
Ledger agreement mechanism is just a fancy way of saying how players decide what score to write down. It’s a big deal because it helps everyone feel okay about how the game is played.
Node validators are like referees. They check the game and the score. These are computers, making sure everything in the blockchain is right.
Smart contracts and consensus match game rules with the scorekeeping. They automatically make sure the right points are scored when players do certain things.
We’ve looked at a game, digging for treasure, raffles, and keeping the score fair. We made it fun to know about blockchain consensus. Now, blockchain isn’t a game, but if it was, it’d be the most secure game ever because of consensus mechanisms!
The Evolution of Consensus Protocols in Blockchain
From Nakamoto Consensus to Advanced BFT
Blockchain consensus mechanisms keep everyone honest. They’re the heart of blockchain tech. Here’s how it all started: Satoshi Nakamoto created Bitcoin and the underlying consensus called Nakamoto consensus. It used Proof of Work (PoW), where miners solve puzzles for rewards. It was groundbreaking. But it had a flaw: it used a lot of power.
Since then, we’ve seen more types come up. Proof of Stake (PoS) changed the game. Instead of solving puzzles, people lock up some of their coins. These folks are picked to add new info to the blockchain, based on the amount and how long they’ve staked their coins. It saves a lot more energy. We also have Byzantine Fault Tolerance, a name that sounds tough. It’s a system that works even if some of the parts fail or can’t be trusted. It keeps the network running smoothly.
Imagine a bunch of computers agreeing on what’s true without needing to know or trust each other. This is how blockchain maintains consensus. All across the world, node validators keep an eye on each other. This way, they make sure every transaction follows the rules. So, no funny business like spending the same coin twice.
But what’s next? How do we make it work even better? That brings us to Advanced BFT, a fancy way of making sure everyone plays by the rules. It’s fast, it’s safe, and more importantly, it doesn’t bog down as it grows.
The Shift Toward Eco-friendly Consensus Protocols
Now, let’s talk about going green with blockchain. People worry about how much juice all this computing chews up. That’s why we talk about consensus without mining. Think of a world where we keep our ledgers in check without burning coal. That’s where staking in blockchain consensus shines. It’s like planting a tree instead of running a power-sucking machine. It’s part of the big plan to keep things clean.
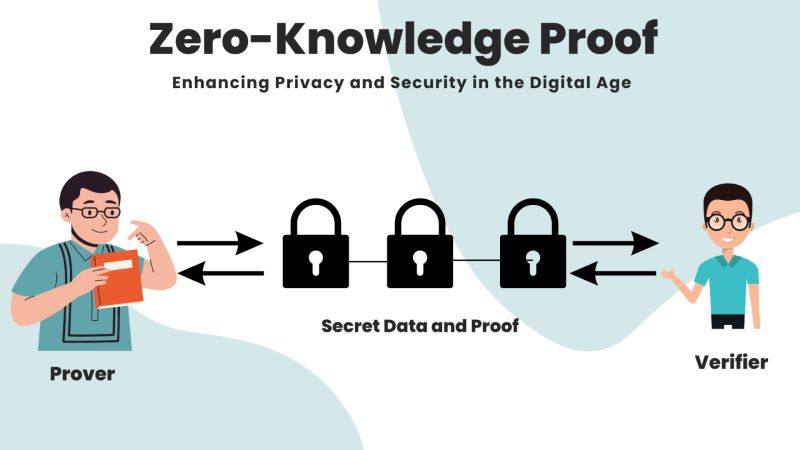
Here’s something cool: Zero Knowledge Proof consensus. It’s a bit like whispering a secret without actually spilling the beans. It keeps things private and still proves you’re telling the truth. This way, we don’t need as much computing, which means saving more energy.
The goal is clear: we want to secure a digital world with trust at its core. We do this by making sure every part of the system checks in with the rest. We’ve come from the days of Nakamoto and his PoW blockchain. We’ve moved to PoS blockchain, with its lighter energy footprint. And we keep pushing the limits of what these cryptographic algorithms can do.
The ledger is the backbone of it all. It’s a book that tells the story of every coin. We all agree on this story thanks to things like the PBFT protocol, Raft, and Paxos—nerdy words for different ways to agree.
As part of this green shift, we’re also thinking about how to pick the folks who add to the ledger, how hard it should be to mine new coins, or if we should mine at all. It’s a wild ride, but the direction is clear. We’re steering towards a blockchain world that’s safe, fast, and gentle to our planet.
Ensuring Trust and Participation in the Validation Process
The Significance of Node Validators in Achieving Consensus
In the world of blockchain, trust is king. Node validators are its knights. They work hard to keep our digital realm secure. Think of a blockchain like a group project. Node validators are the folks who check everyone’s work. They make sure no one cheats and that all the info checks out. This is how blockchain maintains consensus. It’s like a digital nod that says, “Yes, this transaction is legit!”
Validators use rules called consensus protocols in blockchain. This is like having the answer key. It helps them to agree on the current truth on the network. Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) are two ways they do this. PoW blockchain relies on solving complex puzzles. It’s like a race where the fastest computer wins the right to add new info. In PoS blockchain, validators are chosen based on how many coins they hold and are willing to “lock up” as a stake.
Both ways help achieve consensus on blockchain, but they work differently. PoW uses loads of computer power. PoS is like a game of chance with your coins. Blockchain consensus mechanisms use these to verify transactions without needing a middleman.
Byzantine Fault Tolerance is another way to achieve trust. It makes sure the blockchain keeps working even if some validators turn evil or mess up. It’s like having a backup plan when a few group members bail on you.
Addressing the Challenges of Blockchain Forks and Validator Coordination
But what happens when validators disagree? Sometimes, blockchain forks. This is when a blockchain splits into two. It’s like a road that forks into different paths. Some validators may go one way, some another. These forks can happen during upgrades or when some folks in the blockchain community want to change the rules.
Handling these forks is key. It ensures that the chain stays true to its original vision. It also keeps the system fair for everyone. Validators need to coordinate well, or things can get messy.
Then comes block producer selection. It’s a way to pick who gets to add the next block of data to the chain. It’s like picking a team captain in sports. Block producer selection is crucial. It makes sure the system is smooth and no bad actors get the chance to cause harm.
Trustless consensus systems are cool because you don’t need to trust anyone. Instead, you trust the system’s rules. This helps prevent problems like double spending. That’s when someone tries to spend their digital money twice.
The blockchain validation process sees to it that all is well. It’s the heart of what keeps the blockchain beating strong. Validators play a huge role in this. Without them, there’d be no trust. And in blockchain, trust is everything.
So, node validators, we salute you! Your work makes sure our digital world stays upright, fair, and secure. Hooray for trust in the land of ones and zeros!
Balancing Scalability and Security in Consensus Algorithms
The Trilemma of Speed, Security, and Decentralization
In the world of blockchain, there’s a tough puzzle to crack. It’s finding the perfect blend of speed, safety, and everyone getting a say – that’s the trilemma for you. To keep things secure and running without a hitch, blockchain consensus mechanisms are the brains of the operation. They make sure each new block in the blockchain is the real deal.
Now, each type of consensus method brings its strengths to the table. Take Proof of Work (PoW), for instance. It’s been around the block—pun intended! It’s reliable but likes to take its sweet time and munches on a lot of power. On the flip side, you’ve got Proof of Stake (PoS). It’s the new kid, quicker and greener, given it doesn’t crave that power rush like PoW. PoS lets holders of the virtual currency help call the shots. They’re like the guardians of the digital realm, staking their own coins to keep things in line.
But squaring this circle between speed, security, and fair play ain’t easy. If you try to bolt down one corner, another might pop up. Crack the speed, and you might loosen the bolts on security. It’s a delicate balancing act, making sure everyone plays fair without turning the blockchain into a sleepy snail or an energy monster.
Future Trends: Staking Mechanisms and Zero Knowledge Proofs
Looking ahead, the blockchain brainiacs aren’t resting on their laurels. Innovative ideas are cropping up. One shining star is the idea of staking mechanisms. Think of it like getting rewards for being a good digital citizen. You lock up some of your virtual coins and that helps keep the network strong. It’s got folks excited because it cuts down on the energy bill and still keeps things ticking like clockwork.
Zero Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs) are another wizardry in the mix, bringing a whole new game. ZKPs are like sharing a secret without giving it away—super secure and clever! It proves you know something without spilling the beans on what it is. This keeps your data under wraps while still playing by the rules of the blockchain.
Both these trends are like the superheroes of blockchain. They swoop in to save the day, fighting to keep everything speedy, secure, and fair. But the real kicker is that they do it without telling the whole world your business or burning through the planet’s energy. As we gear up for the future, these are the kind of breakthroughs that get folks like me pumped. They’re not just good for the tech—they’re good for all of us.
In blockchain’s big journey, we’ve come a long way, but there’s still some road to travel. We’ve gotta keep our eyes peeled for the clever, eco-friendly ways to lock in agreement across a world of computers. It’s like making a pinky promise in the digital playground; we want everyone to stick to it without a fuss. It’s all about that trust, woven into the very fabric of this digital tapestry, one block at a time.
In this post, we dived into the backbone of blockchain: consensus methods. We explored how consensus is key to blockchain’s work. Then, we compared two major types – Proof of Work and Proof of Stake. We saw how blockchain consensus evolved over time, moving from the basic Nakamoto method to more complex and eco-friendly systems. We also discussed the vital role node validators play and the issues they face, including forks and coordination hurdles.
Finally, we tackled the tricky balance between fast, safe, and wide-reaching consensus algorithms. Cutting-edge ideas like staking and zero-knowledge proofs hint at an exciting future for blockchain.
Think of consensus as the rule-keeper of blockchain. It’s what makes the whole system tick. Whether it’s Bitcoin or a new startup, these methods decide how we all agree in the digital world without trusting a middle person. As we see more progress and innovation, these protocols will become even better at juggling speed, safety, and open use. That’s something to look forward to in the blockchain space!
Q&A :
What Is a Blockchain Consensus Algorithm?
Blockchain consensus algorithms are essential mechanisms used to ensure all participants in a decentralized network agree on the truthfulness and validity of transactions. They are vital for maintaining the integrity and security of a blockchain.
How Does a Consensus Algorithm Ensure Trust in a Blockchain Network?
Consensus algorithms enable network nodes to agree on the ledger’s state without needing a central authority. By following a set of rules, these algorithms ensure trust is established through a majority decision or a particular proof mechanism, which confirms transactions are valid and should be added to the blockchain.
What Are Some Common Types of Blockchain Consensus Algorithms?
There are several types of consensus algorithms widely used in various blockchain networks. The most prominent include Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT). Each has its unique way of achieving consensus and comes with different advantages and trade-offs.
Why Is the Choice of Consensus Algorithm Important for a Blockchain?
The choice of consensus algorithm has significant implications for a blockchain’s performance, security, and governance. It influences the speed of transaction verification, the network’s resistance to attacks, the degree of decentralization, and energy consumption. Choosing the right algorithm is crucial for tailoring the blockchain to its intended use case.
How Do Consensus Algorithms Affect Scalability and Transaction Speed in Blockchain?
Consensus algorithms play a critical role in determining a blockchain’s scalability and transaction processing speed. Some algorithms, like PoW, can be slower and less scalable due to high energy and computational requirements. In contrast, algorithms like PoS or DPoS are designed to offer faster transaction throughput and better scalability, which are essential for widespread blockchain adoption.