Blockchain buzz fills our feeds, but grasping its core can be tricky. Take blocks, for example. What is a block in blockchain? It’s not just tech jargon—it’s the backbone of how blockchains tick. Each block is a data chunk, recording batches of transactions. Think of it as a digital ledger page that’s tamper-proof. Our dive into blockchain’s building blocks will shed light on their makeup and vital role in this tech marvel. We’ll explore their creation, security, and lifecycle, making the complex world of blockchain crystal clear. Ready to peel back the layers? Let’s get started on this block by block adventure.
Demystifying the Building Blocks: A Look into Blockchain Anatomy
The Composition and Functionality of Block Structure in Blockchain
Let’s dive into blockchain. It’s like a digital ledger but cooler. Think of it as a chain where every link is a block. Each block is vital for keeping the blockchain running smooth and safe.
Blockchain blocks are like boxes. They store and protect transaction data. This is key for understanding blockchain technology. Blocks keep info like, who sent what and to whom. Once a block is full, it locks down. Then, it links to the next block in the chain. It’s like a game of trust, and each block keeps the score.
Elements of a Block: From Transactions to Timestamp
Now, every block has certain elements that make it special. First up, we got the block header. The block header is like a block’s ID card. It holds the block’s fingerprint, called a cryptographic hash. No two are alike. This keeps each block unique and safe.
Next, let’s talk about transactions. A block can carry a bunch of them. Transactions are like sending a text that says, “Hey, I gave you some digital money.” They tell the story of who’s trading what in the blockchain world.
Here’s a cool part. Each block also has a timestamp. It’s like a time stamp on a letter. It tells us when the info was added. This helps keep everything in order.
Understanding blockchain is not just about knowing these parts. It’s about seeing how they all work together. It’s a team effort. The block header, transaction data, and timestamp join forces to secure the ledger on the blockchain.
Each block also adds to the blockchain’s total size. We keep an eye on block size limitations to make sure things run fast and smooth. When a block is done, it gets a unique number, called the ‘height.’ It’s like saying, “Congrats, you’re block number 1000!”
In blockchain mining, people work hard to find new blocks. It’s like a treasure hunt. When they win, they get a prize called the block reward. This prize is some of that blockchain’s digital money.
One last thing in a block is the nonce. It’s a tricky number miners have to find to seal a block. It’s like the last piece of a puzzle. Once they find it, they can add the block to the chain.
So there you have it. Blocks are super smart. They are secure and keep everything running just right. They make sure everyone on the blockchain can trust the system. Best of all, they work 24/7 to keep our digital ledger up to date.
Blocks are the stars in the blockchain show. They work together, making sure every trade counts and is safe. Each block is part of a bigger story, working with the whole blockchain team. Now you know what a block is and why it’s such a big deal in blockchain!
Securing the Chain: Cryptography and Consensus in Blockchain
How Cryptographic Hash Functions Seal Blocks
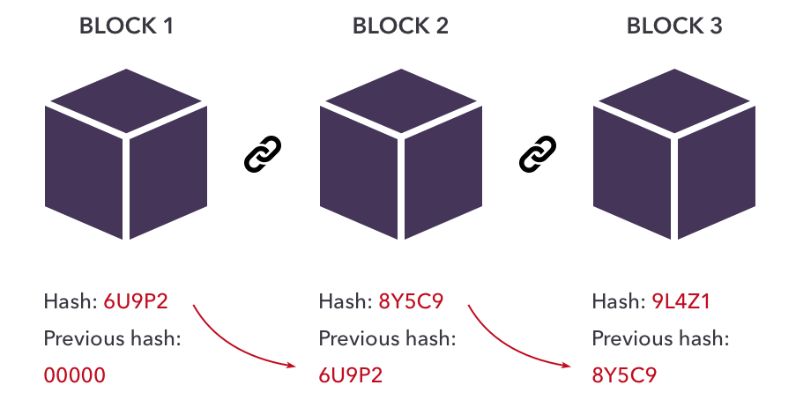
Every block in a blockchain has a unique code called a hash. Think of it like a seal on a letter. It locks in the block’s data. If data changes, the hash changes. Big deal! It tells everyone something’s different. This is how blockchain keeps data safe. No one can change a block without changing the hash.
The Role of Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain Coherence
Blockchain uses consensus to agree on data. It’s like having a class vote on a game to play. If most agree, that’s the game. This process makes sure all agree on the blocks. It’s key for trust. It’s how blocks are checked and added to the chain. It keeps the blockchain running right without one boss. All users have the power.
Expanding the Ledger: How New Blocks Are Formed and Verified
The Mining Process and the Quest for Block Rewards
Think of blockchain as a book. Each page is a block. These pages fill up with folks sending money, making deals, or using smart contracts. When a page is full, it needs a special code to lock it. This code is a mix of math and guessing. It’s called mining. Mining is tough work. It needs lots of power and smart computers to get right. But guess what? This hard work pays off. Solving the problem first means you win new coins. We call this the block reward. It’s like a prize for adding a new page to our book.
Understanding the Block Validation and Confirmation Process
Now, how do we know a new page is good? Others in the network check it. They make sure it follows rules and every deal is true. This is block validation. Once the block is okay, it’s glued to the last page of our book. This is block confirmation. A timestamp plants a time on it. Now no one can change this page. It is part of a chain of blocks. Super safe and stuck in time. It’s a smart system. They all work together to keep our book, the blockchain ledger, growing and secure.
Mining blocks and keeping a blockchain safe is pretty cool. It’s how we trust who owns what, without needing a middleman. Every time we add a page to our book, we’re writing history that can’t be erased. That’s blockchain for you—trust in bits and bytes!
From Genesis to Continuity: The Lifecycle of a Blockchain Block
The Significance of the Genesis Block in Blockchain Creation
Let’s dive into the birth of a blockchain. At its start, we have the genesis block. This is block number one, the very first page in the blockchain’s history book. It’s special because it kicks off the whole chain of blocks. Without this first block, there’s nothing to build on. When a blockchain is born, the genesis block is there from the very start. It’s like the anchor that holds the chain in place.
Now, why does this matter? Imagine you’re starting a tower of blocks. If your first block is solid, your tower can grow tall and strong. The genesis block in blockchain works the same way. It sets the rules, like how many coins there are to start with. Once we make this block, it stays put forever. It’s a one-of-a-kind, and we keep it safe because it’s the root of all that follows.
Ensuring Integrity: Blockchain Immutability and Node Functions
Keeping a blockchain true and unchanging is a big deal. That’s where “blockchain immutability” comes in. It means once we add data, it’s there to stay. No take-backs, no erasing. It’s like writing in pen, not pencil.
How do we make sure of this? Enter blockchain nodes. These are like the guardians of blockchain. Nodes are computers linked to the blockchain network. They have two key jobs. First, when new data comes in, nodes check it out. They make sure it follows the rules and that it’s legit.
Next is their second job. Once they say the data’s good to go, nodes lock it in with a super-complex math puzzle, known as a cryptographic hash. Think of it like a secret code that’s really hard to crack. If someone tries to mess with the data, the code won’t match up, and the other nodes are like, “No way, not on our watch!”
Because of this, the blockchain stays honest and safe. Every block has a number, called a height, like steps on a ladder. And just like that, each block is linked to the one before it, making a chain. If a block is block number 50, it will check in with block number 49 first, just to be sure it’s in the right line.
If the data checks out, boom – we add a new block to the blockchain. It’s like a team, where every player has a job to ensure the game runs smoothly. Only here, the game is keeping our blockchain secure and running like clockwork.
That’s the magic of how a blockchain block lives, from the first to the last. It’s all about starting strong with the genesis block, then growing with care and lots of checking. This way, our blockchain can stay reliable and trustworthy, like a best friend who never lets you down.
In this post, we peeled back the layers of blockchain’s complex structure. We explored how each block is built and how transactions get stamped with a timestamp. Our journey uncovered the power of cryptography in locking down data, and we saw how consensus keeps the whole chain in check.
Then, we dug into how miners add new blocks, seeking rewards. We also learned how blocks get checked and okayed. We celebrated the genesis block, the seed from where every blockchain starts, and looked at how immutability and nodes keep the chain true.
My final thought – blockchain is not just smart tech, it’s a fortress for our digital dealings. Each part, from the first to the last block, works to make sure our data stays safe and sound. Understanding blockchain helps us trust where our information goes and grows. It’s simple, really: blockchain’s like a puzzle that, when put together right, opens up a world of secure and seamless exchanges. Let’s keep unlocking its potential, one block at a time.
Q&A :
What Exactly Constitutes a Block Within a Blockchain?
A block in blockchain technology is a digital package of data that carries transactions for the ledger. Each block contains a unique code called a hash, transaction details, a timestamp, and a reference to the hash of the previous block, which links them in a chronological chain.
How Does a Block Function in the Context of Blockchain?
Blocks function as the individual pages of a blockchain ledger. When a block’s data capacity is reached, a new block is created and linked to the previous one. This forms an immutable and transparent sequence of transaction records that are verified by network participants, known as nodes.
Can You Modify the Information Contained in a Blockchain Block?
Once a block is added to the blockchain, it is extremely difficult to alter its contents due to the cryptographic hash function. Any modifications to the block data would change the hash identifier and break the chain of blocks unless a majority of the network agrees to the change, which is highly unlikely in a secure blockchain.
Why is the Structure of a Block Significant in Blockchain Technology?
The structure of a block is significant because it ensures the integrity and security of the blockchain. With the hash linkages between blocks, the blockchain creates an unbreakable chain of custody for the data, preventing fraud and unauthorized alterations.
What Happens When a Block is ‘Full’ in a Blockchain?
When a block reaches its data capacity, it is closed and added to the chain, and a new block is created to continue the recording of transaction information. The full block remains on the blockchain as a permanent record, and each subsequent block strengthens the validation of all previous blocks.