Have you ever wondered what is a distributed ledger? We’re about to dive into the tech that’s changing how we handle data and trust in the digital age. Picture a world where every transaction, no matter how small, gets stored not in one place but across many. That’s the magic of distributed ledgers—think of it as a team sport where each player keeps a copy of the game plan. Gone are the days of sole gatekeepers. Now, imagine a network where everyone has a say, and every move is on record for all to see. Ready to understand how this spells security and freedom like never before? Keep reading to unlock the secrets that make distributed ledgers a game-changer.
Unveiling the Fundamentals of Distributed Ledger Technology
Understanding Distributed Ledgers and Their Function
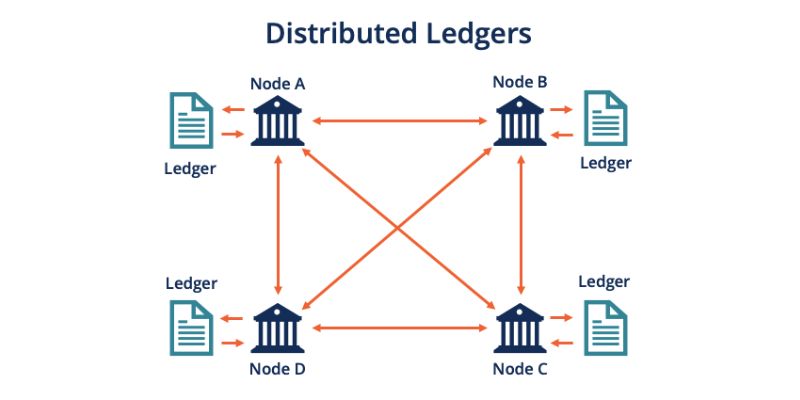
Picture a book that stores every money move you make. Now, imagine not just one book but many books shared across a wide network of computers. This network is what we call a distributed ledger. It is a shared, fixed record of data that no single person owns.
Each page of our book is like a block in a blockchain. A blockchain is an example of a distributed ledger. When you make a money move, like sending cash to a friend, this gets added to a page. Every move is put in a line of code and mixed up to keep it safe. This is what we call encryption.
Now, you might wonder, how do we trust what’s in the book? That’s where something special called a consensus mechanism comes into play. It is a rule that everyone in the network uses to agree on what gets added to the ledger. No lies can get by because every computer must agree before anything new is put into the ledger.
Exploring the Sharpest Differences: Distributed Ledger vs Centralized Ledger
Let’s now think about the big showdown: distributed ledger vs centralized ledger. A centralized ledger is like a diary that only one person writes in and has. It’s like a bank that keeps all the information about your money in one place. What’s risky here is that if the book is lost or someone sneaks a peek, we could have big problems.
On the other hand, with a distributed ledger, there is no need for just one person or group to take care of the book. It’s out there on lots of computers, split up into bits, which makes it super tough to mess with. Even if someone tries to change a line, the other computers won’t agree to it, and the change won’t stick.
One of the biggest highlights of distributed ledgers is security. Since the ledgers are spread across many places, a bad guy can’t simply go to one spot and change the information. They’d have to change it on every computer at once, which is pretty much impossible. This makes the technology very helpful for keeping things like money and property records safe.
In short, while a centralized ledger is all about one spot holding all the power and risk, a distributed ledger shares everything and makes it strong like a team. This helps stop fraud and creates trust through teamwork.
Speaking of trust, we call distributed ledgers immutable. That means once something is in there, it can’t be changed or taken out. Think of writing with a magic ink that never fades or rubs away. It’s there for good, which is excellent for making sure our records stay pure and true.
So, to sum it up, distributed ledgers are like sturdy, shared books that keep track of our deals and doings using secret codes, rules all agree on, and teamwork. It’s a big step forward in how we trust each other with our money and important info on the web. This tech is strong and getting smarter every day, opening doors to all sorts of cool uses we’re just starting to explore.
The Architectural Make-up of Distributed Ledgers
An Insight into Various Types of Distributed Ledgers
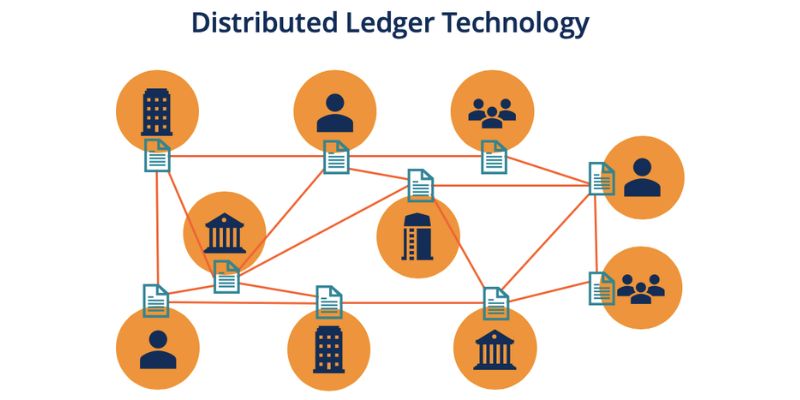
Picture a big book where you can write down who owns what. But, instead of one book, many copies exist and everyone has one. That’s the core idea behind distributed ledgers. In the world of tech, we call this ‘distributed ledger technology’, or DLT for short.
DLT is a fancy way of saying that we have a special database. This database doesn’t sit in one place, like at your bank. It’s spread out across many computers, called ‘nodes’. Each of these computers has the same records, making it hard to mess with the data. This makes DLT super safe and fair for everyone using it.
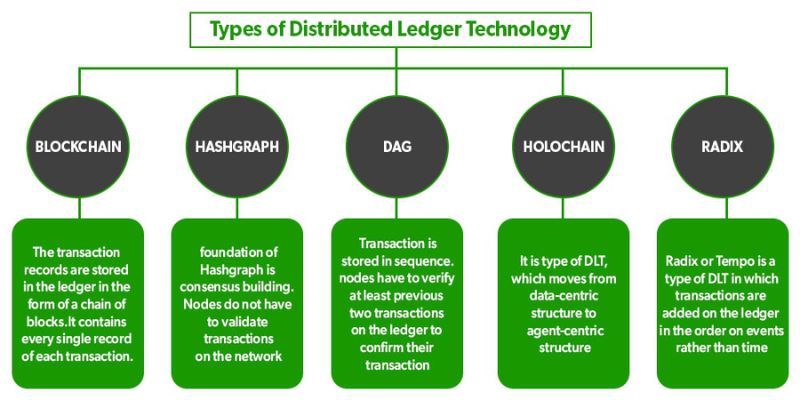
Now, there’s lots of different types of these ledgers. You might have heard of ‘blockchain’, which is one kind. It stacks info in ‘blocks’. When a block fills up, you link it to the next one, making a chain. That’s why it’s called ‘blockchain’. It’s like building with Lego – each piece snaps to the last one to make something bigger.
We also have other DLT types, like ‘DAGs’, which stands for Directed Acyclic Graphs. They spread out like branches, no loops. With DAGs, things can move faster but it can get pretty complex, too.
Sometimes, we use smart contracts on these ledgers. They’re like usual contracts but they run themselves when conditions are met. Let’s say you’re selling lemonade. You can set up a smart contract that says, “When I get a dollar, give one cup of lemonade.” No need for anyone to check; the smart contract does it.
Smart contracts run on blockchain platforms. These are like the stages on which our digital deals happen. They help make sure everyone plays by the rules.
These tech wonders aren’t just cool; they help businesses. They make things clearer and safer when shipping goods around the world. They can also make sure artists get paid when their music plays. DLT is also super handy in finance. It helps people send money without worry, and it keeps track of who owns what.
Deciphering the Role of Consensus Mechanisms
In a distributed ledger, there’s no boss to say what’s right or wrong. Instead, we use ‘consensus mechanisms’. These are rules that help all the computers agree on what the records should say.
Think of it like a game where everyone must agree on the next move. If someone tries to cheat, the others won’t let them. That’s how these ledgers stay honest. Without these rules, anyone could try to change records for their gain.
There are different ways to make this agreement. One common way is called ‘Proof of Work’. It’s like a puzzle contest. The first computer to solve the puzzle gets to update the ledger. But, these contests use a lot of power, and that’s not great for our planet.
That’s why we also have ‘Proof of Stake’. Here, you can help update the ledger if you have a lot of the digital money, or ‘stake’ in the game. It’s like being a trusted player because you’ve got more coins in the pot. This uses less power, so it’s better for Earth.
Now that you know about DLT and how it works, you can see why it’s a big deal. It’s more than just tech jargon; it’s a whole new way to keep track of info and make sure everyone plays fair.
The Real-World Utility of Distributed Ledgers
Investigating Distributed Ledger Applications Across Industries
Let’s dive right into the world of distributed ledgers and see how they shine in real business. From tracking a tomato’s journey from farm to store to securing health records, these ledgers do it all! They’re like magic books where once you write something, it’s there forever. No eraser can rub it away. And guess what? Everyone can check what’s written to make sure it’s true.
Banks use them to send money fast and safe. Meanwhile, stores can keep an eye on goods, making sure they are fresh and real. By sharing data across many places, it’s super hard for bad guys to mess with it. This makes things extra secure and we can all trust it more.
Bridging the Gap: Public vs Private Ledgers
Ah, the tale of two cities: public versus private ledgers. Think of the public ones as a big, open park. Anyone can stroll in, have a picnic, and play frisbee. That’s like Bitcoin or Ethereum – anyone can join the party. But with private ledgers, it’s different. It’s like a private party at a cool club. You need to be on the list to get in. Banks and companies love these because they pick who can peek and poke around.
So, why does this all matter? Well, if you’ve got secret sauce recipes or clever ideas, you might want a private ledger. But if you’re all about sharing and being open, a public ledger is your jam.
By using these ledgers, we can make everything better – faster, cheaper, and even greener. And the more we use them, the smarter we get about making them work for us. It’s like leveling up in a game where everyone wins.
Knock, knock – who’s there? More trust and less funny business in how we trade, how we agree, and even how we play games online. It’s exciting stuff, really. And we’re just getting started. There’s a whole universe of ways to use these clever ledgers, and we’re just scratching the surface. Keep your eyes peeled, because the distributed ledger is here to stay and it’s changing the world, one block at a time!
Navigating the Challenges and Evolution of Distributed Ledgers
Recognizing and Overcoming Distributed Ledger Challenges
Distributed ledgers are like big books shared by many. They record every trade, sale, or deal. Unlike a regular book, this one has pages all over the world. In this way, no one person can claim the book or change its stories alone. We call this blockchains, a type of distributed ledger technology (DLT).
When using distributed ledgers, we face some bumps in the road. These bumps include how to agree on what’s true or fair (consensus mechanisms). Imagine a game where players must all agree on the next move. This is what happens with distributed ledgers. It’s tough but key for trust in the system.
Next, keeping the ledgers safe is a big deal. We use complex locks (cryptographic algorithms) to protect them. These are like secret codes that only the right key can open. Just as a lock stops a chest of treasures from being stolen, these codes keep data safe.
Yet, distributed ledgers face a tricky question on speed. How fast can the ledger add a new page without mistakes? This is ledger transaction speed. It’s like how fast you can write a note without messing it up.
Another challenge is how these ledgers talk to each other (ledger interoperability). Think of each ledger as a person who speaks a different language. If they want to share stories, they must learn a common language.
Envisioning the Future: Ledger Scalability and Interoperability
Let’s dream up the future of DLT. First, we want to grow bigger without losing pace (ledger scalability). That means adding more pages to the book without the writing getting slower. It’s not easy, but it’s what we need for more people to join in.
The goal is to weave ledgers together (interoperability of ledgers). Like bridges between islands, we want ledgers to connect and share easily. Real simple – the more they chat, the more powerful they become.
We’re also looking at how to let only some people turn the pages (permissioned distributed ledger). It’s a bit like having a club with a secret handshake. This can help make things safer and more organized.
In the world of DLT, we keep pushing forward. We believe these systems can make things better for all – from selling apples to buying houses. Distributed ledgers give everyone a fair shot. They make sure no story in the big book gets lost or changed by someone up to no good.
Ledgers from the past were lonely and easy to mess with. Now, we have a net that spreads wide, catching more details and holding them tight. From farms tracking seeds to banks sending cash, these ledgers can handle it all. They can grow big, stay safe, and make sure that at the end of the day, what’s fair is what happens.
So, we dive deep into these challenges, find fixes, and ride the wave of endless possibilities. Welcome to the world of DLT – sturdy, swift, and smart.
In this post, we’ve explored the nuts and bolts of distributed ledger technology. We began by defining distributed ledgers and how they differ from centralized ones. Then, we delved into their inner workings, like the various types and vital consensus methods.
We also looked at how different fields use these systems, weighing up the pros and cons of public versus private ledgers. Finally, we discussed the hurdles these ledgers face and the exciting directions they’re heading towards, including scalability and working together.
To wrap it up, distributed ledgers are changing how we track and share info across the globe. They’re complex but hold huge promise for a more open and connected world. As we move forward, watching this tech evolve will be both a challenge and a thrill. Let’s keep our eyes peeled for what’s next!
Q&A :
What Exactly is a Distributed Ledger?
A distributed ledger is a database that is consensually shared and synchronized across multiple sites, institutions, or geographies, accessible by multiple people. It allows transactions to have public “witnesses,” thereby making a cyberattack more difficult as it would have to attack all the copies simultaneously.
How Does a Distributed Ledger Differ from a Traditional Database?
Traditional databases, such as SQL or Oracle databases, are centralized, with an authoritative figure who administers and maintains the database. A distributed ledger, on the other hand, lacks central administration and is inherently resistant to data modification because all participants own an identical copy of the ledger.
Why are Distributed Ledgers Considered More Secure?
Distributed ledgers are generally considered to be more secure because they are decentralized. Each transaction is recorded and must be confirmed and verified by consensus of the majority of the participants in the network. Furthermore, because every transaction is cryptographically linked to the previous transaction and distributed across multiple nodes (computers), it is extremely difficult to alter any single transaction without detection.
What are Some Real-World Applications of Distributed Ledger Technology?
Real-world applications of distributed ledger technology include cryptocurrency systems like Bitcoin, supply chain monitoring, identity verification, voting systems, and many more. These applications benefit from the increased security, transparency, and immutability that distributed ledgers provide.
Can Distributed Ledgers Operate Without Cryptocurrency?
Yes, distributed ledgers can operate without the need for a cryptocurrency. While many distributed ledgers (like Bitcoin’s blockchain) involve a cryptocurrency as a reward for participating in the network, the technology itself is not limited to financial applications and can be used to record a wide variety of transaction types.