Elastic Chain ushers in a new era for decentralized applications (dApps) with unparalleled scalability and interoperability. Discover the ZKsync 3.0 ecosystem and its potential applications!
What is Elastic Chain?
Elastic Chain, also known as ZKsync 3.0, is an ecosystem of multiple Layer-2 blockchains built using ZKsync’s ZK Stack technology. ZK Stack is an open-source toolkit that allows developers to easily deploy Ethereum-compatible ZK Rollups. Its key feature is the seamless interoperability between ZK Chains, enabling users and assets to move freely without barriers.
Elastic Chain is designed to address the issue of liquidity fragmentation and fragmented user experience – a common problem in the current blockchain ecosystem. ZKsync 3.0 envisions a future where users can easily and securely access and utilize assets on any blockchain.
Structure and operation of Elastic Chain
ZKsync 3.0 is designed with a unique architecture consisting of three main components that work together to create a powerful and efficient Layer-2 system:
ZK Router
Role: The ZK Router is the foundation of the entire Elastic Chain network. It acts as a “central brain,” managing the state of all ZK Chains within the ecosystem.
Functions:
- Registration management: Processes registration requests from projects wishing to deploy new ZK Chains on Elastic Chain.
- Interaction coordination: Facilitates secure and efficient interaction between ZK Chains.
- Liquidity maintenance: Ensures overall liquidity for the entire ecosystem, allowing for seamless asset flow between chains.
Characteristics: The ZK Router is implemented as a set of smart contracts on the Ethereum mainnet, inheriting the security and decentralization of L1.
ZK Gateway
Role: The ZK Gateway is a crucial bridge between the Ethereum network (L1) and the ZK Chains (L2). It handles all cross-chain transactions and interactions between the two network layers.
Functions:
- L1 & L2 connection: Enables users to securely and efficiently transfer assets and data between Ethereum and ZK Chains.
- Transaction verification: Employs Zero-Knowledge proof technology to verify transactions from ZK Chains before submitting them to Ethereum.
- Performance optimization: Applies advanced techniques such as Proof Composition and State Diff Compression to minimize costs and accelerate transaction processing speed.
Mechanism of operation:
- Proof composition: Combines transaction proofs from multiple ZK Chains into a single batch for verification on Ethereum, saving costs and time.
- State diff compression: Compresses the state data of ZK Chains before sending it to Ethereum, optimizing bandwidth and costs.
- Faster finality: Ensures fast transaction confirmation times by requiring ZK Gateway validators to verify transactions.
- Liveness: Allows each ZK Chain to manage its own validator system, ensuring independence and flexibility.
- Censorship resistance: Provides censorship resistance at a lower cost compared to L1 solutions.
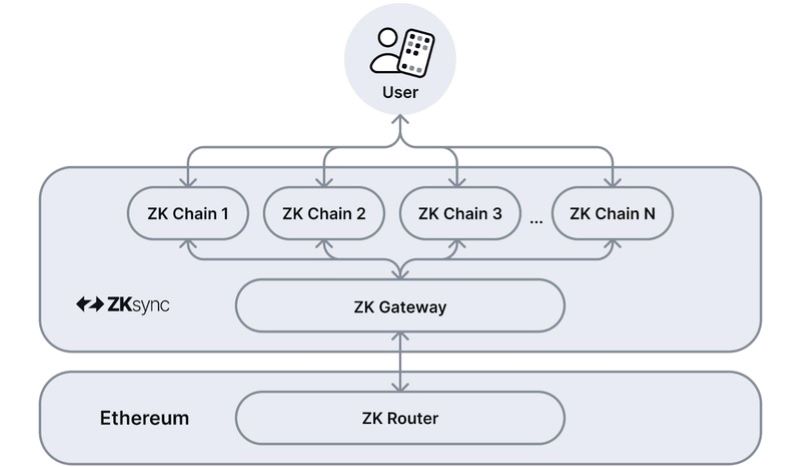
ZK Chains
Role: ZK Chains are independent Layer-2 blockchains built on the Elastic Chain platform. Each ZK Chain can be designed with its own structure and functionality to serve different purposes.
Characteristics:
- Interoperability: ZK Chains can interact with each other through the ZK Gateway, allowing users and assets to move freely between chains.
- Inheriting L2 Benefits: ZK Chains benefit from the advantages of ZK Rollups such as fast transaction speeds, low gas fees, and scalability.
- Flexible Customization: Developers can customize ZK Chains to meet the specific needs of their projects.
Advantages of Elastic Chain
Superior scalability
- Meeting growing demand: ZKsync 3.0 is designed with a “federation” structure of ZK Chains, allowing the system to scale flexibly to meet increasing transaction demand without impacting performance.
- Unlimited scalability: ZKsync uses the term “Elastic” to emphasize the system’s infinite scalability, enabling it to adapt to the rapid growth of the blockchain ecosystem.
Seamless interoperability
- Eliminating barriers between chains: Users can easily and securely move assets and interact between ZK Chains without needing to use bridges.
- Unified user experience: ZKsync 3.0 provides a seamless experience as if using a single blockchain, eliminating the complexity and risks of switching between networks.
High security
- Inheriting Ethereum’s security: ZKsync 3.0 is built on the Ethereum platform, inheriting the top-notch security of this blockchain.
- Secure ZK Rollups: ZK Rollups technology is considered one of the most secure Layer-2 solutions available, minimizing attack risks.
Optimal performance
- Fast transaction speeds: ZK Rollups enable significantly faster transaction processing compared to Layer-1.
- Low gas fees: By optimizing the transaction verification process, ZKsync 3.0 minimizes gas fees for users.

Flexible customization
- Modular Smart accounts: ZKsync 3.0 supports modular smart accounts, allowing users to customize their accounts and transaction experience according to their needs.
- ZK stack: The ZK Stack toolkit provides developers with high customizability, enabling them to build ZK Chains with unique features and functionalities.
Superior interoperability
- Impressive AMM test results: Compared to other chain-of-chains solutions like Superchain (Optimism) and AggLayer (Polygon), ZKsync 3.0 demonstrates superior performance in terms of interoperability and throughput.
Comparing Elastic Chain with other solutions
Currently, Elastic Chain is not the only solution aiming for the chain-of-chains model. Other Layer-2 projects are also developing similar ecosystems, most notably Optimism’s Superchain and Polygon’s AggLayer.
Superchain (Optimism)
Superchain is a network of Optimistic Rollups built on the OP Stack platform. Similar to Elastic Chain, Superchain aims to create an ecosystem of chains with seamless interoperability, providing a unified user experience.
Differences
- Technology: Superchain uses Optimistic Rollups, while Elastic Chain is based on ZK Rollups. ZK Rollups are considered superior in terms of scalability and security due to the use of Zero-knowledge proofs.
- Interoperability: Currently, native interoperability between OP Chains within Superchain is still under development. Meanwhile, Elastic Chain has implemented seamless interoperability from the outset.
- Ecosystem: Superchain has a thriving ecosystem with many prominent projects such as Base, opBNB, and Manta Network. However, Elastic Chain is also attracting the attention of major projects and has the potential for rapid growth.
AggLayer (Polygon)
AggLayer is Polygon’s scaling solution that enables different blockchains to interact with each other efficiently. AggLayer acts as a standardization framework, providing a common interface for chains to connect and exchange data.
Differences
- Mechanism of operation: AggLayer focuses on connecting existing blockchains, while Elastic Chain focuses on building an ecosystem of new ZK Chains.
- Interoperability: AggLayer allows interoperability between chains through a common interface, while Elastic Chain allows native interoperability between ZK Chains.
- Performance: Elastic Chain demonstrates superior performance in terms of interoperability and throughput in practical tests.
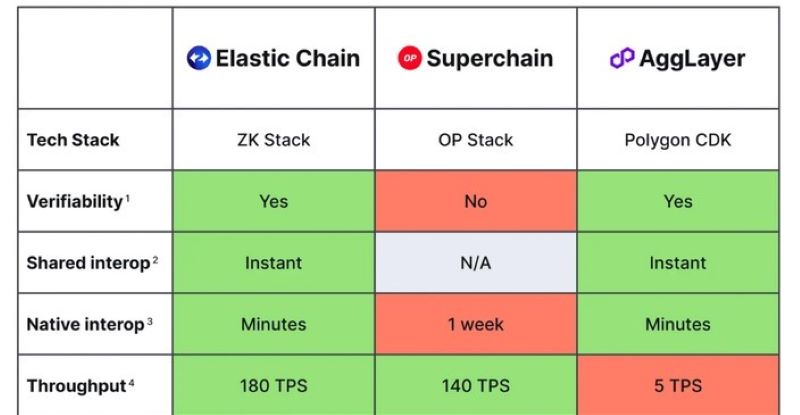
ZKsync 3.0 stands out with its advanced ZK Rollups technology, seamless interoperability, and superior performance. Compared to Superchain and AggLayer, Elastic Chain has certain advantages in building a scalable, secure, and efficient Layer-2 ecosystem.
However, the chain-of-chains race is still ongoing, and each solution has its strengths. The success of Elastic Chain will depend on many factors, including ecosystem development, user acquisition, and community support.
Elastic Chain ecosystem
With its innovative architecture and superior scalability, Elastic Chain is rapidly becoming an attractive destination for blockchain projects. This ecosystem is constantly expanding with the participation of various decentralized applications (dApps) spanning various fields such as DeFi, NFTs, GameFi, and Web3.
Key projects in the Elastic Chain ecosystem
- Lens protocol: A decentralized social network that allows users complete control over their data and content. Lens Protocol is building on Elastic Chain to leverage its scalability and seamless interoperability, creating a foundation for a true Web3 social network.
- Cronos zkEVM: Crypto.com’s Layer-2 chain, providing a scaling solution for DeFi and NFT applications on the Cronos ecosystem. Cronos zkEVM integrates with Elastic Chain to enhance interoperability and liquidity access.
- Nodle: A decentralized IoT device connectivity network that uses Elastic Chain to ensure scalability and security for millions of connected devices.
- Space and Time: A decentralized data platform that combines on-chain and off-chain data querying capabilities. Space and Time leverages Elastic Chain to provide an efficient, secure, and verifiable data storage and querying solution.
- Zero: A security and privacy protocol for Web3 applications. Zero integrates with Elastic Chain to provide decentralized authentication and authorization solutions.
- Sophon: A Layer-2 payment system focused on speed and scalability. Sophon utilizes Elastic Chain to provide efficient payment solutions for e-commerce and mobile payment applications.

Development potential
The Elastic Chain ecosystem is in its early stages of development but has already shown great potential. With the support of ZKsync and the developer community, Elastic Chain is expected to attract more innovative projects in the future.
Benefits for projects
- Scalability: Building on Elastic Chain, projects can easily scale without encountering bottlenecks.
- Interoperability: Leveraging Elastic Chain’s interoperability, projects can connect with other blockchains and access shared liquidity.
- Security: Inheriting the security of Ethereum and ZK Rollups.
- Performance: Fast transaction speeds and low gas fees.
- Community: Participating in a dynamic and growing ecosystem.
Elastic Chain (ZKsync 3.0) is a promising Layer-2 solution that promises to address blockchain scalability and interoperability challenges. With its innovative structure, superior performance, and rapidly growing ecosystem, Elastic Chain can play a crucial role in shaping the future of the blockchain industry.
Join Blockchain Global Network to follow the development of Elastic Chain and take the lead in new opportunities in the blockchain world!

RELATED POSTS
Keith Grossman: The journey from media to finTech
Discover the life and career...
Ethereum ETFs have been approved by the SEC
The recent announcement that ethereum...
Easily Join the TENEO Airdrop with This Step-by-Step Guide
The TENEO Airdrop is a...
Comedian Airdrop – Token BAN Leads the Memecoin Trend
In the world of memecoins,...
Sonic Labs Airdrop – Discover the Super HOT Token Burn Mechanism
One of the highlights of...
Why Solana Layer 2 Sonic is the Key to High-Performance Gaming
Solana Layer 2 Sonic is...
Crypto Currency on Futureverse – Breakthrough for the Future of Digital Finance
Crypto currency on Futureverse represents...
Bitcoin Charlotte and 3 Expected Growth Signals
Bitcoin Charlotte is not just...
Memefi Coin Airdrop: Airdrop Timeline and Launch of Memefi Token
The Memefi Coin Airdrop presents...
The Tokenomics of U2U Network – Sustainable Value for Users and Investors
The Tokenomics of U2U Network...
When was Blockchain Technology invented? A journey through its origins
Ever wondered, “When was blockchain...
What is dYdX? A deep dive into Decentralized trading
What is dYdX? It is...
Blum Airdrop – A Ready Guide to Earning Tokens
Blum Airdrop is a fantastic...
Can my Phantom Wallet be hacked?
Wondering, “Can my Phantom Wallet...
What is Airdrop in the Crypto World? Exploring Its Benefits and Risks
Curious about What is airdrop...
Near coin Revolution: Is this the Crypto you’ve been waiting for?
Near Coin is making waves...