Let’s talk about the heart of blockchain: how it agrees on data. Sure, it sounds dull. It’s not. It’s the tech world’s clash of the titans. In this deep dive, we’re pitting giants against each other in a comparison of different consensus mechanisms. You’ll see how these digital rulebooks shape everything from your transaction speed to the planet’s health. We’ll explore the muscle behind Proof of Work and see if Proof of Stake is the new champ in town. Get ready to understand the tech that could change how we all do business.
Understanding Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain Technology
The Role of Proof of Work (PoW) and Its Mechanics
Let’s start our adventure with Proof of Work (PoW), the original heart-thumper of blockchain security. It’s like a giant, complex puzzle. Computers race to solve it. The first one to finish gets to add a new block of transactions to the chain. This work keeps our crypto coins safe.
PoW makes sure everyone’s playing fair without needing a referee. It’s not about luck; it’s savvy and raw computer power. Miners crunch numbers day and night, which takes tons of energy. They’re like the powerhouse players of the blockchain.
But with the spotlight on going green, some folks are kind of worried. They see the energy bill for all this number crunching and it gives them the jitters. We’re talking about the same energy a small country might use. Yikes!
Proof of Stake (PoS): A New Era of Block Validation
On the flip side, we have Proof of Stake (PoS), a newer player in the game. This one’s all about what you own, not how much muscle your computer has. If you hold coins, you can join in. It’s like having a golden ticket to help run the show.
PoS is like a raffle. The more you hold, the better your chances to be picked to add a new block. But don’t get it twisted – it’s not all random. You’ve got to put skin in the game and lock up some coins as a promise to play nice.
This method is a real energy sipper compared to PoW’s drinking-from-a-firehose style. We’re looking at maybe using the power of a neighborhood, not a nation. That’s a relief to folks wanting a cleaner, greener crypto world.
Both PoW and PoS help to keep our digital dollars smooth and reliable. They lock up the ledger, so no joker can sneak in and mess with it. These guardians of blockchain keep us trusting that everything’s tickety-boo when we send or get coins.
As we march into the future, PoS is stealing the spotlight. Yet, PoW still has its die-hard fans. It’s been around since the birth of Bitcoin, after all. But can it keep up with our green dreams and the need for speed? That’s the burning question.
The blockchain gang is always cooking up something new. We’ve got whispers of hybrids and even stuff that sounds like it’s out of a sci-fi book. But for now, PoW and PoS are our go-to heroes, each with their own flavor of safekeeping the blockchain world.
While we treasure every shiny coin in our digital wallets, it’s good to know PoW and PoS have got our backs. They make sure that everything’s on the up and up, from every coin’s trip around the world to the newbies joining the party.
So whether you’re a miner with a rig that could make a gamer weep or you just like to keep your coins snug in your wallet, knowing about PoW and PoS can make you feel like a smart cookie in this wild, wild west of cryptocurrency.
Assessing Environmental and Operational Impacts
The Energy Consumption of PoW versus PoS Systems
We see Proof of Work (PoW) in big names like Bitcoin. It uses computer power to keep the network safe and create new coins. But this power use is huge—it’s like a small country’s worth of electricity. Now enter Proof of Stake (PoS). It’s a newer way that cuts down the power bill. With PoS, owning a slice of the coin is enough to help run things. People lock up their coins as a kind of promise, saying they’ll follow the rules.
Environmental Considerations of Consensus Algorithms
When we dig into how these systems impact our planet, PoW’s energy use stands out. It’s a heavyweight, pulling a lot of power for mining. This has folks worried about the climate effects. But with PoS and other systems like Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) and Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT), the energy use drops. These don’t need big farms of computers running day and night.
By using these less power-thirsty ways, like PoS or DPoS, we can still get the security and trust we need without the big carbon footprint. That’s a win for our wallets and our world. Systems like proof of authority or proof of contribution throw in new angles to the mix. They can make things even leaner and greener.
Validator nodes are the backstage heroes here. They’re the ones checking transactions and keeping things in order. With PoS or DPoS, we’re talking fewer nodes that need less juice to stay on. They’re like the energy-saving bulbs of the blockchain world. Smarter, sleeker, and kinder to Mother Earth.
And hey, with all this talk of going green, it’s not just about feeling good. We’re seeing the rise of eco-friendly crypto staking too. Instead of just mining for new coins, people can now stake their existing coins. This means they get to join in, earning rewards without firing up a power plant.
Even more, consensus mechanism evolution is happening right in front of us. Ethereum, for example, is moving from PoW to PoS. This change is part of a big shift we’re seeing across the space. It’s all about finding that sweet spot. We want a system that’s strong and fast, but not at the cost of our skies and seas.
Each consensus method, from the old-school PoW to the lean PoS, to the fast DPoS, or the sturdy BFT, shapes how we validate cryptocurrency transactions. It guides how we build trust within a decentralized world. It’s clear that the less power we gobble up, the better it is for everyone—block by block, coin by coin.
The Evolution and Future Trends of Consensus Models
From Ethereum’s Shift to The Rise of Hybrid Models
Blockchain started with Bitcoin and its Proof of Work. Now, we are seeing so much more. Ethereum, a giant in the blockchain world, made a massive move. It shifted from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake. This change was big news. It cut energy use a lot. This switch tells us where things are going.
We are now looking ahead to hybrid models. These models mix old and new ways to get the best results. They often join Proof of Stake with other systems. For example, Delegated Proof of Stake or Byzantine Fault Tolerance. The goal is to make blockchains run smooth while staying safe.
Examining the Increased Importance of Decentralization in Consensus
People love blockchain for its trustless nature. It means no need for a middle man. This is thanks to how we do consensus – how we agree on what’s true on the blockchain. Decentralization helps with security too. More spread out control means harder to attack.
Over time, decentralization got more attention. Why? Because people want fairness and power with users, not just a few. Also, too much central power poses risks. So, Proof of Work versus Proof of Stake isn’t just about energy. It’s about who has a say and how.
Long ago, blockchain meant Bitcoin and its Proof of Work. Those days are in the past. We see Proof of Stake, Delegated Proof of Stake, Byzantine Fault Tolerance, and more. They all have their place. They all fit different needs.
But, blockchain security protocols are key. They keep things safe. Block validation mechanisms are the gears that make sure every block is right. But how do we use them? That’s where things like hybrid models come in. These models share power more, and they work well in many cases.
So, Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake bit showdown is about energy, yes. But it’s also about how we shape our digital futures. We want a blockchain world that’s safe, green, and gives everyone a chance to take part. The future will likely blend many methods. Old ones and new ones. Ones we man now and ones we’ll dream up tomorrow.
Cryptocurrency validation methods have come far. But we’re not done yet. The ride has just begun. Decentralization and consensus go hand in hand. As we move forward, this pair will drive the blockchain bus. We’ll see energy needs drop and fairness rise. That’s the goal.
Validator nodes, proof of burn, crypto staking – they’re all part of the mix. They each play a role in this growing ecosystem. It’s not just about counting coins. It’s about building a world where trust is built into the system. And where every one of us has a voice in the grand crypto conversation.
As we explore new paths, like proof of contribution or proof of authority, we keep learning. We blend ideas to find better ways. This is how consensus evolves. It’s shaped not only by tech but by our dreams for a world where tech works for all. This is the mission of blockchain’s heart – to connect us in ways fair and true, without the need for a trusty handshake, because the code itself is the trust we rely on. The evolution of consensus is the evolution of blockchain itself. It’s a journey. It’s our journey, together.
Security and Scalability in Blockchain Consensus
How Validator Nodes Influence Blockchain Security and Integrity
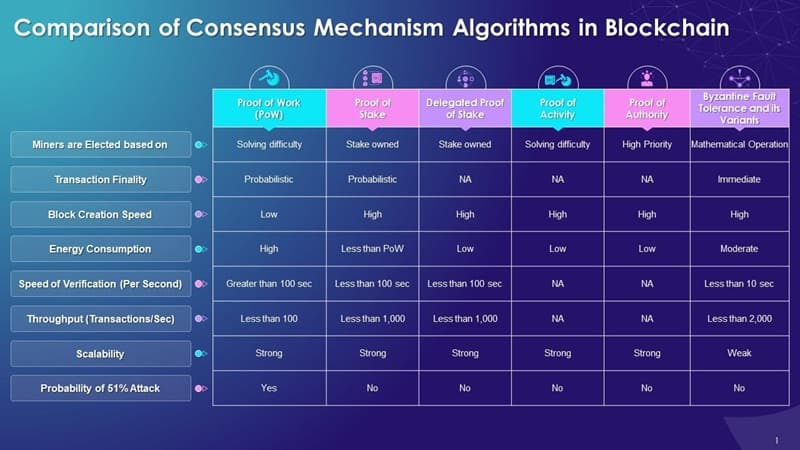
Validator nodes are key to keeping a blockchain safe and correct. They check and agree on all the transactions. This trustless system lets users know that their transactions are secure without needing to trust other users. Each consensus method, from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS), depends on certain types of validator nodes. In PoW, miners are validators who solve complex math to add a new block. In PoS and its variations like Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), validators are chosen based on how many coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as a form of security deposit.
PoW gives security through hard-to-solve puzzles, which makes it costly and time-consuming for attackers to alter the chain. PoS, on the other hand, boosts security by asking validators to have skin in the game. They could lose their stake if they act badly. Delegated Proof of Stake ups the ante by letting coin holders vote on who should validate, creating a more democratic version of PoS.
Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) is another method to keep blockchains secure. It tackles the issue of trust among nodes, ensuring the network stays up even if some nodes fail or act maliciously. In short, validator nodes are the guardians of blockchain accuracy and reliability, and each consensus algorithm gives these nodes different powers and responsibilities.
The Ongoing Balance Between Scalability and Network Security
One of the biggest puzzles in blockchain is finding the sweet spot between safety and speed. More validators mean more security but can lead to a slower network. This trade-off is where Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake starts to really matter. PoW, known for its use in Bitcoin, is secure but also a heavyweight in energy consumption and it doesn’t scale that well. As tasks get distributed to miners all over the world, it can take a lot of time to reach a consensus.
Proof of Stake promises better scalability. It cuts the need for complex math problems, which means blocks can be created faster and with less energy. This shift matters a lot, especially for block validation mechanisms that aim to process transactions quickly, as with Ethereum’s consensus change to PoS. It’s all about doing more with less—fewer resources to validate but still keeping the integrity intact.
The balancing act doesn’t end there. Enter distributed ledger technologies like DPoS and BFT. They refine the balance, often streamlining the validator process by reducing the number of nodes needed for consensus or shortening the time to reach an agreement while still combating attacks on the network. In the end, whether it’s reducing energy consumption, defying hackers, or just making sure Alice can send Bob that crypto without a hitch, the dance between scalability and security is a delicate one. It’s about building a system robust against threats, but also nimble enough to handle our ever-growing digital world’s demands.
We dove into blockchain consensus, exploring Proof of Work and Proof of Stake. We learned how these models work and their roles in the blockchain. Then, we tackled their energy use and how they affect our planet. Next, we looked at where consensus tech is headed, from Ethereum changing its game to new, mixed models popping up. Finally, we talked about keeping networks safe and working well as they grow.
Here’s my take: blockchain tech is evolving super fast, especially with how it agrees on stuff without a boss. Proof of Work did the job but used too much power. Proof of Stake seems like a cool new boss, cutting down bills and helping Earth. Still, keeping things safe and speedy is a tricky dance with no easy steps.
I’m excited to see how smarter tech will make blockchain better for everyone. Stay sharp and watch this space – blockchain’s future is just warming up!
Q&A :
What are the main types of blockchain consensus mechanisms?
Different consensus mechanisms ensure agreement on the state of the blockchain among distributed parties. The most prominent types are Proof of Work (PoW), which involves solving complex mathematical puzzles; Proof of Stake (PoS), which relies on validators’ economic stake in the network; and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), where stakeholders vote on a limited number of delegates to validate blocks. Other notable mechanisms include Proof of Authority (PoA), Proof of Burn (PoB), and practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (pBFT), each with its unique process for achieving consensus among nodes in a blockchain network.
How do consensus mechanisms affect the security and efficiency of a blockchain?
Consensus mechanisms play a pivotal role in the functionality of a blockchain by ensuring that all participants agree on a single source of truth, which is necessary for maintaining security and integrity. Security is influenced by how difficult the mechanism makes it for malicious actors to compromise or attack the system. Efficiency impacts how quickly and with what computational or financial resources a new block can be added to the chain. For instance, PoW is considered secure but energy-intensive, whereas PoS offers quicker transactions and less energy consumption.
Which consensus mechanism is best suited for scalability?
For scalability, consensus mechanisms that can process a high volume of transactions quickly and with minimum fees are preferred. DPoS and PoS are generally seen as more scalable than PoW, mainly because they do not require extensive computational power. The specific mechanism best suited for scalability can depend on the network’s size, the number of transactions, and the desired balance between decentralization, security, and speed.
How do Proof of Work and Proof of Stake differ in terms of energy consumption?
Proof of Work (PoW) is well-known for its high energy consumption because it requires significant computational power to solve cryptographic puzzles. In contrast, Proof of Stake (PoS) does not require computational power for mining; rather, it involves validators being chosen to create new blocks based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral. Consequently, PoS is generally viewed as a more energy-efficient alternative to PoW.
Can a blockchain use multiple consensus mechanisms simultaneously?
While most blockchains typically employ a single consensus mechanism, there are scenarios where a hybrid approach is utilized, combining elements of different mechanisms to leverage their strengths and mitigate their weaknesses. Implementing multiple consensus mechanisms can be complex but may offer enhanced security, reduced energy consumption, or improved transaction speeds. Advanced blockchain architectures may support such combinations for specific use cases to balance decentralization, security, and efficiency.


RELATED POSTS
Popular Blockchain Security Audit Companies: Unveiling Industry Watchdogs
Discover the leading blockchain security...
Guide to voting in Project Catalyst
Ready to help build Cardano?...
Blockchain Smart Contracts: Unveiling 7 Game-Changing Applications
Unlock Efficiency: Explore Smart Contracts'...
Exploring the Use of blockchain technology in different sectors
The use of blockchain technology...
Infrared Finance: Leading PoL Staking on Berachain
Infrared Finance has emerged as...
Blockchain Revolution: Examples Of Blockchain In Healthcare
"Examples of blockchain in healthcare:...
Easily Join the TENEO Airdrop with This Step-by-Step Guide
The TENEO Airdrop is a...
Role of Blockchain Security Audits: Your Crypto Safe Haven?
Enhance Blockchain Security with Audits....
Emerging Trends in Blockchain Security: Next-Gen Safeguards Unveiled
Emerging trends in blockchain security:...
Interoperable Blockchains: Unpacking Hidden Security Risks
Understanding the security risks in...
Kuroro Beasts: An engaging NFT Game on Ronin
Kuroro Beasts – An NFT...
Challenges Of Implementing Blockchain For Businesses: Is Your Business Ready?
Navigate Blockchain Integration Barriers |...
Challenges of Blockchain: Can It Truly Prevent Voter Fraud?
Challenges of using blockchain for...
Blockchain Technology News: Unveiling the Future of Tech Transformation
"Stay updated on blockchain technology...
Emerging Consensus Mechanisms: Beyond PoW and PoS, What’s Next?
Emerging consensus mechanisms (alternatives to...
Future Trends in Blockchain Security: Staying Ahead of Threats
Future trends in blockchain security:...