As your go-to blockchain guide, I get a ton of questions. At the top? What are the different types of blockchain? Well, imagine a universe brimming with diverse planets; that’s the blockchain world for you, ranging from fully open spaces to highly secured private zones. Ready to learn? Grab your cyberspace gear, and let’s dive into the realms of public blockchains with their open-door policy, contrasted by the controlled access of private and permissioned blockchains. Each one has its design, its crowd, and its unique strengths. Whether you’re a techie or just blockchain-curious, stick with me, and let’s decode this digital enigma together!
The Fundamentals of Blockchain Technology and Its Core Characteristics
Understanding Blockchain Technology Basics
Let’s dive into the world of blockchain. Think of it as a book where you write stuff down. Everyone has a copy of this book, so it’s tough to lie about what’s written. We call this book a “ledger”, and since it’s digital and spread across the globe, we say it’s “distributed”. Every change or “transaction” in this ledger is checked by lots of computers. These computers agree on what’s true and what’s not. This process is called “consensus”, and it is crucial.
Now, this might get a bit techy, but stick with me. These transactions, they’re wrapped in a digital block. Secure math stuff, called “cryptography”, keeps them safe. Once a block is full, it’s added to a chain of other blocks. That’s the “blockchain”. Simple, right?
It’s super tough to change things once they’re written. So, people can’t cheat. This means the ledger is “immutable”. Fancy word, but it just means unchangeable.
Exploring Distributed Ledger Types
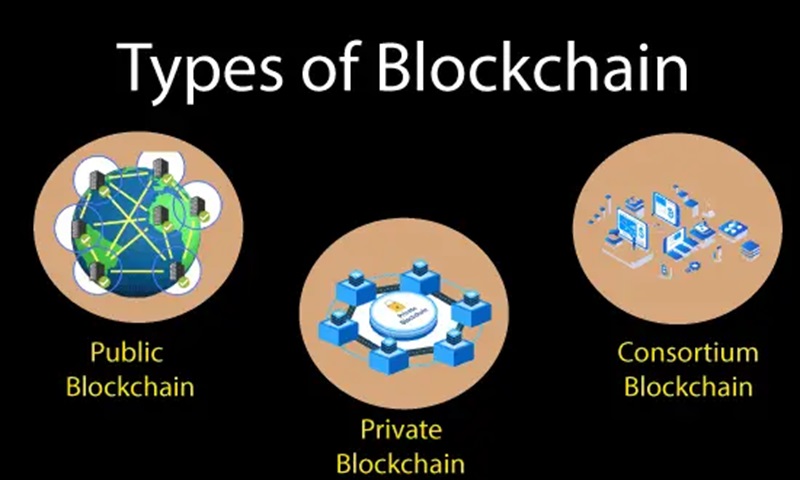
Imagine a playground with no rules; that’s a bit like a “public blockchain”. Anyone can come and play; anyone can see what’s happening. “Public” means just that – open for everyone. And “decentralized” adds the magic sauce. It means no boss is in charge. “Bitcoin” and the “Ethereum platform” run this way. They use “cryptocurrency” to reward people who help run the system.
“Private blockchain” is like a private club. You need an invite to join in and see what’s going on. This is for biz folks who want to keep things hush-hush but still enjoy blockchain perks. Some companies run this for things like “supply chain” or keeping records.
Then you got the “permissioned blockchain”. It’s like the bouncer at a party. You can’t just waltz in. They check if you’re on the list first. These chains are more about who can do what.
The experts toss around terms like “Proof of Work” or “Proof of Stake”. These are ways computers agree on the truth. They’re like different flavors of ice cream; they all cool you down, just taste different.
“Sidechains” and “cross-chain technology” let different blockchains talk to each other. You know, like friends sharing secrets. This helps them work together better.
The “hybrid blockchain”? It’s the best of both worlds. A bit public, a bit private, trying to get the perks from both sides.
Blockchain isn’t just about “money” or “cryptocurrency”. It can help keep anything secure—from your medical records (“blockchain in healthcare”) to who you are (“identity verification”).
Blockchains can grow fast or slow—that’s “scalability”. It’s a big deal because too slow and no one will use it.
In short, blockchain is a smart, reliable buddy. It’ll keep a secret, won’t lie to you, and works for everyone from big biz to everyday folks. Keep an eye on this tech—it’s still cooking up surprises.
Distinguishing Between the Types of Blockchains
Public Blockchains Explained: Features and Functions
Let’s talk about public blockchains, shall we? They are like a party where everyone is welcome. They let anyone join and take part. In these systems, all the records are open for everyone to see. That’s what we mean by “decentralization.” No one person or group is in charge. Everyone follows the same rules, made by the whole group. The best-known examples are Bitcoin and Ethereum. These blockchains use a system where lots of computers agree on the records. It’s called consensus. This way, the records stay accurate and secure.
These public chains rely on a process called mining or staking. This is where people use computers to verify the records. One popular method is Proof of Work (PoW). Another is Proof of Stake (PoS). PoW has computers solve tough puzzles. PoS lets users who own more currency have a say in the process. These systems help keep everything fair and running smoothly.
Private and Permissioned Blockchains: Characteristics and Use Cases
Now let’s peek into the world of private blockchains. Think of these as a VIP room in the party. Not everyone gets in. Only certain people get keys. This means they’re not as open as public ones. Companies like to use these for their business. They can control who gets to use the blockchain. This makes sure their data stays safe. They often use these systems to keep track of things like supply chains.
Permissioned blockchains are a bit different. They’re like a mix of the VIP room and the main party. They let some parts be open to many but keep key parts locked down. Groups like banks might use these. They offer a mix of secrecy and openness. This helps with things like managing your own data.
Both private and permissioned blockchains use consensus, just like public ones. But they have their own special rules about who can take part in this process. These can be quicker and more efficient for certain tasks because fewer people are involved.
To sum it up, blockchains come in different shapes and sizes. Each kind has its own special features. Some are wide open, and some are more closed off. It all depends on what you need. The key is how they handle who gets to join and how they check the records. They all aim to provide safe and reliable ways to keep and share data. That’s the heart of blockchain technology!
This ride through the blockchain universe shows us the wonders of how we can trust and use data in new ways. Whether it’s a big open party or a small private gathering, blockchains have a spot for everyone. They spark change in how we handle data, manage businesses, and even how we trust each other. The next time you hear about blockchains, you’ll know that they’re not all the same. They are a tapestry of unique and smart systems that keep our digital lives running.
Dive into Decentralization: Consensus Mechanisms and Cryptocurrency Networks
Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain: PoW vs PoS
Let’s talk about how blockchains make sure everyone agrees, or reaches a consensus. It’s like when kids vote for their favorite game to play. Instead of games, blocks of info must get a thumbs up from the network. Blockchain uses special “voting” rules to be fair and safe. The two main ways are called Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
PoW is like a math race. Computers solve tough puzzles to prove they work hard. The first to finish gets to add a new block and earn some coins. This way, no one tricks the system because cheating means doing a lot of hard work for nothing.
PoS works a bit differently. Here, the system picks validators based on how many coins they hold and are willing to “freeze” as security. If they try to cheat, they lose their coins. This way, those with a stake in the network help keep it running smoothly.
Both ways have pros and cons. PoW uses more power but is well-tested. PoS is newer, and uses less energy.
Ethereum Platform and Bitcoin Blockchain: Pioneers in Cryptocurrency
Now, let’s chat about the trailblazers of the crypto world. Ethereum and Bitcoin set the stage for cryptocurrencies. Think about them as the first kids on the playground.
Ethereum is like a playground where kids can build their own games. It’s not just about voting on which game to play. It lets people write “smart contracts.” These are like set rules for games that run by themselves once they start. So, if you’ve got Ethereum, you’re not stuck with plain old currency; you can make all sorts of other digital assets.
Bitcoin, on the other hand, is like playing tag where the only rule is to not be “it.” It’s a straightforward digital cash system. It was the first to use blockchain, and it’s all about sending and getting bitcoins. It’s simple, but it works and has been around the longest.
Both these systems are open for everyone to join. That’s because they’re public. Public blockchains are like games where every kid on the playground can play. Private ones, though, are like having a secret club. Only members can see what’s going on.
In all this, blockchain keeps things safe. It’s a chain of blocks with info that everyone checks. No one can change a block once it’s in the chain without everyone noticing. That’s like trying to cheat at tag and not getting caught. Tough, right?
So there you go. Blockchains can make sure people play fair, whether the kids play a simple game of tag or build whole new fun stuff on Ethereum. And they keep finding new ways to do just that.
Blockchain Applications: Enterprise Solutions and Beyond
Smart Contract Infrastructures and Their Implementation
Smart contracts change how we do deals. They are kind of like vending machines. You pick a snack, pay, and the machine gives it to you. In smart contracts, rules are made. When rules are met, things happen automatically. Picture a self-operating contract that kicks in when conditions are right. No need for a middleman!
Blockchains hold these smart contracts. This makes them safe and trustworthy. They help businesses trade, agree on deals, and share stuff without worry. For, say, a writer, a smart contract makes sure they get paid when they hand in their work. It’s quick, easy, and clear. Everyone knows what’s what.
The Ethereum platform is king for smart contracts. It uses blockchain to make a place for these contracts to live and work. People like it because you can make many different kinds of smart contracts with it. This helps a lot of industries. Like, it helps musicians track who listens to their songs and lets them get paid right.
But there’s more! Smart contracts can also help track things we buy — from food to phones. They can show every step a product takes. From making it to selling it. This makes sure things are what they say they are. It also stops fake products from getting into the market.
The Role of Blockchain in Supply Chain and Data Security
Now, let’s talk about supply chains. They are all the steps a product goes through. From being made to being in your hands. Blockchains are super good here. They make every step clear to see. People can’t change them. So, we can trust that our stuff is good and came the right way.
Imagine buying a toy. With blockchain, you can know where the parts came from. You can see how they were put together. And you can check that people worked in good conditions to make it. This builds trust for us as buyers.
Then, there’s keeping data safe. This is big, especially for private info. Blockchains protect data well. They use tough math to lock it up tight. This is called encryption. These blocks of data connect in a special way. It’s like a chain that no one can break.
If we use blockchains in healthcare, for example, your health records can be very secure. Only the right people can see them. And they can’t be changed. So, you and your doctor would know your info is safe and right.
In short, smart contracts and blockchain keep things smooth, safe, and clear. They help businesses run better. They make sure we get quality products. And they keep our private info safe. It’s like building a future where we can trust the digital world as much as the real one.
We’ve journeyed through the layers of blockchain technology, from its basics to its varied types. We’ve seen how public blockchains like Bitcoin are open for all, while private ones keep things under wraps for select groups. We’ve learned that consensus is key in keeping the networks in harmony, with PoW and PoS keeping the blockchain fair and square. We dived into Ethereum and Bitcoin, the big names leading the crypto pack. Lastly, we checked out how smart contracts work and how blockchain helps keep supply chains tight and data secure.
To wrap it up, blockchain is more than tech talk—it’s a game-changer for businesses and beyond. Remember, whether it’s keeping your transactions safe or shaking up entire industries, blockchain’s power is vast and full of possibilities. Keep your eyes peeled; this tech is making waves, and you don’t want to miss the boat.
Q&A :
What are the Main Varieties of Blockchain Technology?
Blockchains can be broadly categorized into four types: public blockchains, private blockchains, consortium blockchains, and hybrid blockchains. Public blockchains, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, are open and decentralized. Private blockchains are permissioned and centralized within an organization. Consortium blockchains are semi-decentralized and governed by a group of organizations. Lastly, hybrid blockchains blend elements from both public and private blockchains, offering a balance between control and decentralization.
How Do Different Types of Blockchains Compare in Terms of Accessibility?
The accessibility of a blockchain depends on its type. Public blockchains are fully accessible to anyone who wants to participate in the network, without needing permission. In contrast, private blockchains restrict access to certain users with permissions, making it a closed network. Consortium blockchains offer limited accessibility, usually to a select group of participants, such as multiple organizations working together. Hybrid blockchains regulate access depending on the data or application, providing both public and controlled access points.
Can You Explain the Security Features across Different Blockchain Types?
The level of security in a blockchain system often correlates with its type. Public blockchains offer strong security through wide distribution and consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake, making them resistant to attacks. Private blockchains have heightened security controls due to their permissioned nature, but as they have fewer validators, they could be more susceptible to internal security breaches. Consortium blockchains strike a balance, as multiple organizations maintain security collectively. Hybrid blockchains can adjust their security measures based on the sensitivity and nature of the data being handled.
What Are the Use Cases for Each Type of Blockchain?
Different types of blockchains serve various use cases. Public blockchains are ideal for cryptocurrencies and decentralized applications (DApps) that benefit from open participation and transparency. Private blockchains are suitable for enterprise use, including supply chain management and confidential data handling within a company. Consortium blockchains are often employed in cross-organizational tasks, such as banking transactions between financial institutions, where trust is required but must be spread across various entities. Hybrid blockchains can be applied in scenarios that need both public validation and private transactions.
How Does Governance Work within Different Blockchain Structures?
Governance in blockchain varies by the type of network. Public blockchains typically utilize a decentralized governance model, where decisions are made through community consensus or via foundational protocols. Private blockchains are governed by a single organization, which makes all the rules and decisions. Consortium blockchains share governance among the established group of organizations participating in the network, often through a pre-defined agreement or voting system. Hybrid blockchains combine governance elements from both public and private models, with the flexibility to tailor the approach to specific use cases and needs.


RELATED POSTS
Future of On-Chain Code Audits: Revolutionizing Collaborative Cybersecurity
Enhance blockchain security with on-chain...
How to Secure Private Keys: Your Essential Guide to Cryptographic Safety
Learn how to secure private...
Fuel Airdrop – Grab the opportunity to receive free Fuel tokens
The Fuel airdrop is an...
The Governance Token in TON: An In-Depth Analysis
The governance token in TON,...
Tomarket Airdrop – Explosion of the Super Countdown Event
The Tomarket Airdrop event is...
Understanding the Stock to Flow Model – How to Optimize Investment
The Stock to Flow Model...
2024 US Election Results – Political Shock and the Future of Cryptocurrency
The 2024 US election results...
What Is A Sybil Attack? Sybil Attacks Uncovered
What is a Sybil attack?...
Guide to voting in Project Catalyst
Ready to help build Cardano?...
Examples of Secure Blockchain Implementations: Unveiling Industry Innovations
Examples of secure blockchain implementations...
New Threats to Blockchain Security: Are Your Investments at Risk?
Protect Your Blockchain: New Threats...
Kraken Launched Layer 2 Ink with $25 Million Support from Optimism
In a landmark move within...
Unlocking the Blockchain: Comparison of different consensus mechanisms
Understanding different consensus mechanisms in...
Blockchain For KYC/AML: Streamlining Compliance For The Future
Blockchain for KYC/AML: Revolutionizing compliance...
Detailed steps to participate in the BSX Airdrop quickly
Are you ready to dive...
Blockchain Smart Contracts: Unveiling 7 Game-Changing Applications
Unlock Efficiency: Explore Smart Contracts'...