Have you ever heard of physical Bitcoin? While Bitcoin is commonly known as a purely digital cryptocurrency, physical Bitcoin is a relatively new and intriguing concept. So, what exactly is physical Bitcoin and how does it differ from digital Bitcoin? Let’s dive in!
What is physical Bitcoin?
Physical Bitcoin is a fascinating concept in the cryptocurrency world. Essentially, it’s a physical object (often a coin or token) that represents a specific amount of Bitcoin.

How it works
- Private key: Embedded within each physical Bitcoin item is a private key – a unique string of characters that grants access to a particular Bitcoin wallet.
- Encryption: This private key is securely encrypted and protected within the item.
- Owning Bitcoin: By owning one of these coins, you essentially own the corresponding amount of Bitcoin associated with that private key.
Creating Physical Bitcoins
Physical Bitcoin is not as simple as printing a piece of paper with a QR code linked to a Bitcoin wallet. The process of creating a it involves a delicate blend of art, technology, and security.
Here’s a breakdown of the process:
Design and production
- Design: Designers create unique designs for the physical Bitcoin, often incorporating iconic elements related to Bitcoin or blockchain technology.
- Material selection: Precious metals like gold and silver, copper, or specialized materials are commonly used. Each material offers distinct aesthetic and durability properties.
- Manufacturing: Production processes may include casting, engraving, plating, and polishing. 3D printing is also employed for intricate designs.
Information encoding
- Wallet creation: A new Bitcoin wallet is generated, containing a public and private key.
- Private key encryption: The private key is encrypted and converted into a QR code or barcode.
- Physical encoding: The QR or barcode is imprinted onto the physical Bitcoin.
Security
- Layered encryption: For enhanced security, Bitcoin wallet information is often encrypted using multiple layers.
- Anti-Counterfeiting measures: Specialized materials and anti-counterfeiting techniques are implemented to prevent replication.
Verification and certification
- Quality control: The final product undergoes rigorous quality checks for finish, accuracy, and overall quality.
- Certification: Some manufacturers provide certificates of authenticity for each physical Bitcoin, guaranteeing its legitimacy.

Why is the Physical Bitcoin worth more than its digital counterpart?
- Uniqueness: Each Coin has a unique serial number, making it a rare and collectible item.
- Collectibility: It are often viewed as collectibles, similar to antique coins or rare stamps.
- Tangible value: The materials used to create it contribute to its overall value.
- Psychological factors: People are often willing to pay a premium for items that hold symbolic or personal value.
Note
- Volatile value: Like digital Bitcoin, the value of physical Bitcoin can fluctuate significantly over time.
- Risk of loss: Loss or theft means losing both the physical asset and the encrypted Bitcoin associated with it.
Outstanding advantages of Physical Bitcoin
- Tangibility: Perhaps the most important advantage of this form of coin is its tangible nature. Unlike its digital counterpart, which exists solely in the digital realm, physical Bitcoin is a tangible object that you can hold and own. This provides a sense of security and control for many individuals.
- Unique gift: It makes for a truly unique and meaningful gift. It’s not just a physical item but also a symbol of modern technology and finance.
- Educational tool: It simplifies the understanding of Bitcoin, especially for newcomers. Owning a physical Bitcoin coin helps individuals visualize the concept of cryptocurrency more clearly.
- Security: In certain circumstances, this form of coin can be considered more secure than digital wallets. Storing it in a safe place reduces the risk of hacking.

Disadvantages of physical bitcoins
While physical Bitcoin offers an intriguing and tangible experience of cryptocurrency ownership, it comes with a number of notable drawbacks. Here are some of the primary disadvantages of it:
Risk of loss
- Theft: As a physical object, it is susceptible to theft. If not carefully secured, you could permanently lose the Bitcoin it represents.
- Damage: It can be damaged by physical forces such as collisions, fires, or environmental factors.
Production and storage costs
- High costs: Producing this type of coin requires specialized technology and materials, resulting in high production costs.
- Storage costs: Securing a safe place to store it can be expensive.
Difficulty in transactions
- Inability to directly transact: Unlike digital Bitcoin, physical Bitcoin cannot be used directly to pay for goods or services. To utilize the Bitcoin, you must first convert it to its digital form.
- Slow confirmation times: The process of converting physical to digital can be time-consuming and costly.
Volatile value
- Dependent on Bitcoin price: The value of it is directly tied to the market price of Bitcoin. If the price of Bitcoin decreases, the value of physical Bitcoin will also decline.
Difficulty in verifying authenticity
- Counterfeits: There are numerous counterfeit physical Bitcoin products on the market, making it challenging for buyers to distinguish genuine products.
Lack of widespread legal recognition
- Unclear legal status: In many jurisdictions, physical Bitcoin lacks clear legal recognition, which can lead to legal complications when using it.

Are Physical Bitcoins a good investment?
As the name suggests, physical Bitcoins are tangible objects that represent a specific amount of Bitcoin. Often designed for aesthetic and collectible value, they have become popular among cryptocurrency enthusiasts. However, considering it as an investment warrants careful consideration of the following factors:
- Intrinsic value: The true value of this form of coin lies in the underlying digital currency it represents. As such, its value fluctuates along with the broader Bitcoin market. As the price of Bitcoin rises or falls, so does the value of physical Bitcoins.
- Liquidity: Compared to digital Bitcoins, it is significantly less liquid. Buying and selling physical Bitcoins is often more complicated and time-consuming.
- Risk of loss: As a physical asset, it is vulnerable to theft, damage, or loss. Without proper storage and security measures, investors risk losing all of their Bitcoin holdings.
- Costs: n addition to the intrinsic value of the Bitcoin it represents, this form of Bitcoin incurs additional costs such as production, shipping, and insurance. These costs can increase the total cost of investment.
- Collectible value: Some physical Bitcoin pieces, designed by renowned artists or limited in quantity, command a premium due to their collectible nature. However, collectible value is subject to market dynamics and can be volatile.
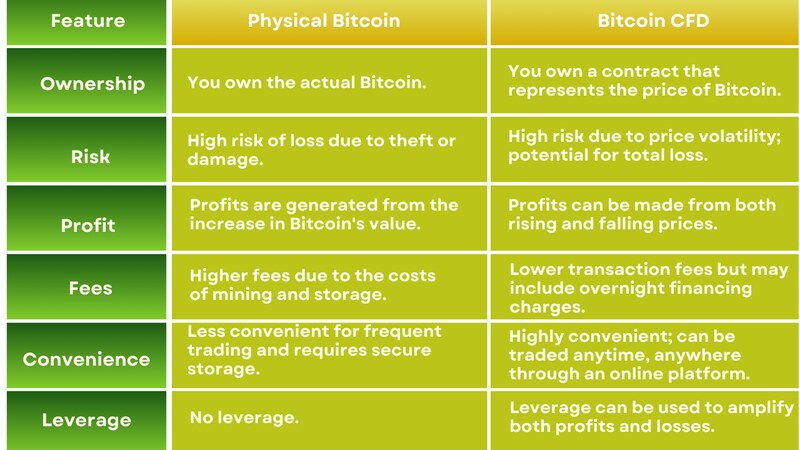
Compare physical bitcoin with bitcoin CFD
A Bitcoin Contract for Difference (CFD) is a financial derivative that allows traders to speculate on the price movements of Bitcoin without actually owning the underlying asset. Instead of buying Bitcoin directly, traders enter into an agreement with a broker to exchange the difference in the price of Bitcoin between the time the contract is opened and closed.
Key differences
See details in the table below.
Physical Bitcoin is an intriguing and novel concept within the cryptocurrency realm. However, before investing in it, it’s crucial to carefully weigh its pros and cons. If you have any further questions about this Blockchain Global Network article, feel free to leave a comment below, and we’ll be happy to assist you promptly!

RELATED POSTS
Who has Andrew Tate’s Crypto Wallet?
Who has Andrew Tate’s Crypto...
Pencils Protocol: Optimizing DeFi yields on Scroll
In the vast landscape of...
LazyOtter Airdrop – Increase Your Chances of Owning Tokens with DeFi Vaults
LazyOtter Airdrop brings a safe...
Rho Markets Airdrop – A Promising Opportunity
The Rho Markets Airdrop is...
What is Bitcoin Lightning Network? Revolutionizing Crypto Transactions
What is Bitcoin Lightning Network?...
Peaq Crypto: A disruptive Blockchain platform
Peaq Crypto, a high-performance layer...
ID Token and Access Token Demystified: How They Power Secure Web Applications
ID Token and Access Token...
SEC to Host Second Crypto Meeting on April 25
The U.S. Securities and Exchange...
Blockchain Technology Images – Visualizing the Future of Digital Innovation
Ever wondered how Blockchain Technology...
Toby Airdrop: A complete guide to participation from A to Z
Participate in the Toby Airdrop...
NebulaStride Airdrop – Tips to Maximize Income
To maximize your income from...
The Future of Decentralized Finance: Key Trends for 2025
The decentralized finance (DeFi) landscape...
Fuel Airdrop – Grab the opportunity to receive free Fuel tokens
The Fuel airdrop is an...
Blockchain Technology News Update – HOT Trends for 2025
Blockchain technology news is abuzz...
Zircuit Airdrop – Breakthrough Potential for Early Investors!
Zircuit Airdrop is not just...
What is Crew3? Detailed guide to join and participate
Crew3 is a community platform...