Modern supply chains are often complex and lack the transparency needed to ensure authenticity and efficiency. This creates risks of fraud, delays, and waste. By providing a shared, unchangeable record of every transaction, blockchain for supply chain tracking offers a powerful solution to build trust and streamline operations from producer to consumer, making the entire process verifiable at every step.
What is blockchain in supply chain management

At its core, blockchain in a supply chain context is a decentralized, immutable digital ledger. Think of it as a shared record book that is duplicated and distributed across a network of computer systems. Each transaction, or block, is cryptographically linked to the one before it, forming a chain. Once a record is added, it cannot be altered or deleted without the consensus of the network, ensuring a permanent and transparent history of a product’s journey.
This technology moves beyond traditional centralized databases, which can be vulnerable to manipulation or single points of failure. In a supply chain, this means every participant, from the raw material supplier to the retailer, can access the same source of truth. They can view a product’s origin, location, and status in real time. This shared visibility establishes an immutable record of transactions, which is the foundation for enhanced supply chain traceability and integrity.
Key benefits of using blockchain for supply chains
Integrating blockchain technology into supply chain management unlocks transformative advantages over traditional systems. These benefits address persistent challenges in trust, efficiency, and security. Implementing blockchain for supply chain tracking provides a single, verifiable source of truth, fostering unprecedented collaboration among all participants from producer to consumer.
- Enhanced Transparency: Every transaction is recorded on a shared, immutable ledger. This gives all stakeholders a real time, end to end view of the supply chain, eliminating information silos and building trust.
- Unmatched Security: Data recorded on a blockchain is cryptographically linked and cannot be altered retroactively. This inherent security drastically reduces the risk of fraud, theft, and counterfeiting across the network.
- Pinpoint Traceability: Companies can instantly trace products back to their origin with precision. This capability is crucial for managing recalls, verifying authenticity, and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
- Automated Efficiency: The advantages of smart contracts automate key processes like payments and compliance checks, reducing paperwork, delays, and human error.
How does blockchain supply chain tracking actually work
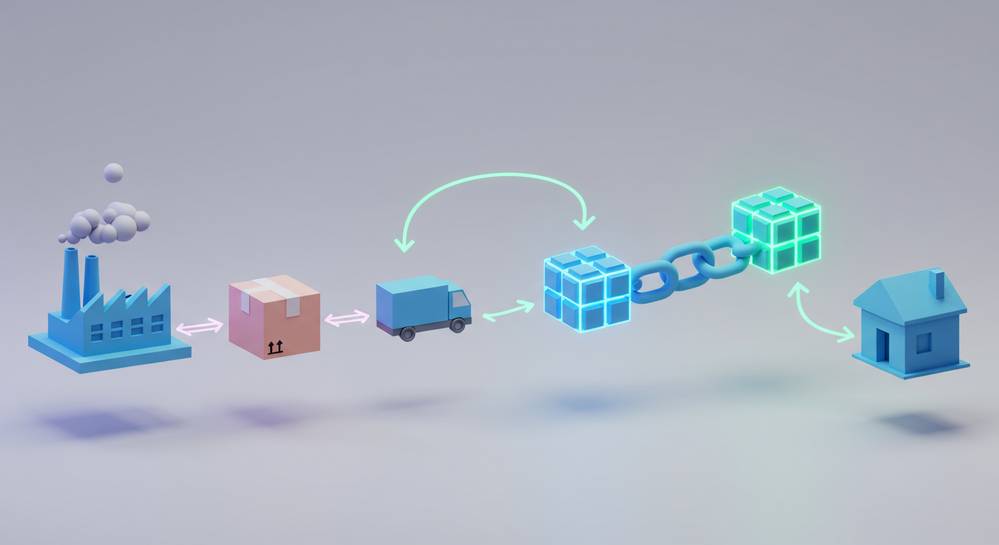
The practical application of blockchain in a supply chain creates a verifiable digital trail for physical goods. This process effectively turns products into unique digital assets that can be tracked on an immutable ledger. First, a product is assigned a distinct digital identity using technologies like QR codes or RFID tags. This identity is then recorded as the initial transaction, or genesis block, on the blockchain, marking its entry into the system.
As the product moves, each step like processing or shipping is recorded as a new, time-stamped block. Each block contains key details and is cryptographically linked to the previous one, forming a secure chain. All authorized participants can view this growing history but cannot alter it. This mechanism, core to undefined, ensures a single, trusted record of the product’s entire lifecycle from origin to consumer.
Real world examples and current challenges
While the potential of blockchain is immense, its adoption is still progressing. Understanding both successful implementations and existing hurdles provides a realistic view of its current state. The journey towards widespread use of blockchain for supply chain tracking involves navigating these practical realities.
Successful implementations
Several major corporations are already leveraging blockchain. Retail giants like Walmart use the IBM Food Trust platform to track food products from farm to store, enhancing food safety and reducing waste in minutes instead of days. Similarly, the diamond industry leader De Beers utilizes its Tracr platform to verify the authenticity and conflict-free origin of diamonds. These examples demonstrate the technology’s power to create trust and transparency in complex global supply chains.
Adoption challenges
Despite these benefits, widespread adoption faces significant obstacles. The initial cost and technical complexity of implementation can be prohibitive for smaller companies. Success also hinges on industry-wide collaboration, as all partners must agree to use a standardized system. Furthermore, technical issues like scalability and interoperability between different blockchain platforms remain key challenges that the industry is actively working to solve.
The integration of blockchain in supply chains is not a futuristic concept; it is a practical technology actively solving today’s most pressing issues of transparency, security, and efficiency. By creating an unchangeable and shared source of truth, it empowers businesses and consumers alike. To explore how these solutions can be tailored for your specific needs, visit Blockchain Global Network and discover the future of logistics.

RELATED POSTS
Nillion Airdrop – Leading the Trend from Testnet to Mainnet
By participating in the Nillion...
Kishu Inu Coin: A guide to investing in this Meme Token
Discover Kishu Inu Coin, a...
SEC to Host Second Crypto Meeting on April 25
The U.S. Securities and Exchange...
Understanding the Stock to Flow Model – How to Optimize Investment
The Stock to Flow Model...
What Is a Crypto Exchange? Exploring Different Types and Their Functions
Looking to invest in the...
What is Make Frens Airdrop? How to participate
Make Frens Airdrop is an...
How to add binance smart chain to metamask?
If you’ve been asking “How...
Not Pixel Airdrop – Optimize Profits from Pixel
To optimize profits from Not...
Unlocking the Future: Understanding Blockchain Interoperability Protocols
The decentralized promise of blockchain...
Exploring the Growth of the Blockchain Technology Market in 2024
The blockchain technology market is...
Bitlayer Airdrop and the opportunity to earn token exchange points
The Bitlayer Airdrop is not...
Future of On-Chain Code Audits: Revolutionizing Collaborative Cybersecurity
Enhance blockchain security with on-chain...
Polymarket airdrop – Smart investment for the Web3 generation
With the Polymarket airdrop, users...
What is polygon crypto – The Layer 2 Solution for Ethereum
What is polygon crypto? It...
Remis Launches: A New Era in GameFi Innovation
On February 1, 2025, Remis...
Dunes Airdrop – Optimizing liquidity from resting assets
Dunes Airdrop brings a solution...