Impact of consensus algorithms on security: some say it’s a tech boon, others fear it’s a crack in our digital armor. Join me as I dig deep into this hot topic. We’ll look at how these algorithms either beef up or bust your data’s safety. Can they stand up to the smartest hacks and attacks? Are they doing more harm than good? Gear up to unpack the nitty-gritty of blockchain security, tackle the tough talk on 51% attacks, and size up whether Proof of Work trounces Proof of Stake in the security showdown. With today’s threats ever-evolving, knowing the role of cryptography and how node validation keeps us a step ahead is crucial. Get ready to sort fact from fear, knowledge from noise. Let’s dive in!
Unpacking the Security Implications of Consensus Algorithms
Assessing Blockchain Security Across Different Consensus Models
In blockchain, security keeps our coins safe. It’s like a complex lock for digital money. The consensus algorithm is a key part of this lock. Just like there are many types of locks, there are many algorithms out there. Two main types are Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). They work to achieve the same goal – agreement in a network – but do so in different ways.
Let’s dive into PoW, first used by Bitcoin. Here, miners solve puzzles to create blocks. The goal? Find a special number called a nonce. This takes a lot of computer power, which costs money. Miners don’t want to spend money for nothing. So, they usually keep the network safe to keep their rewards safe.
Now, the Proof of Stake is different. In PoS, validators, not miners, create new blocks. They do this by putting their own coins at stake. Think of it as a raffle where coins are the tickets. The more coins you have, the better chances you have to create a block. Validators are careful. They know messing up means losing their own coins.
Both methods have their own defense strategies for the network. In PoW, the more puzzle-solvers (miners), the safer the network gets. In PoS, the idea is wealth-based. People with more coins don’t want to break the system that makes them rich.
The Particular Risks of 51% Attacks and Approaches for Mitigation
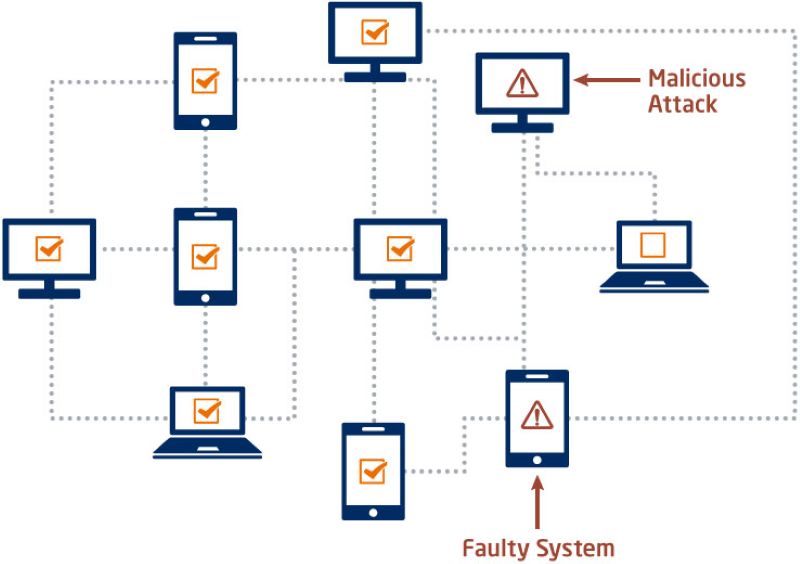
A big risk in blockchains is the 51% attack. Imagine someone has over half the power in a network. They could change rules, refuse new blocks, or get away with the same money twice.
How can we stop this? For PoW, we make sure no one has too much computing power. More miners mean power is spread out. For PoS, the risk is high for attackers. They would need over half the coins staked. That’s a lot of money, and not easy to do.
Also, there’s something called Byzantine fault tolerance. It’s a way for systems to reach a consensus, even if some parts fail or turn evil. It’s like having backup plans for your backup plan. The goal is to keep the network running smoothly and securely, no matter what.
Lastly, we have node validation security. Nodes are the many computers that make up a network. They check transactions and blocks. Imagine you’re playing a game, and everyone’s watching you. If you cheat, they’ll see. With blockchain, nodes are like the watchers. They help prevent tampering and keep the system honest.
In conclusion, consensus algorithms are complex but crucial. They ensure security in our digital world. PoW and PoS are different, but both vital to blockchain security. With threats like the 51% attack, we must be ever-vigilant. We need to protect our netizens’ digital belongings with the utmost care.
Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake: A Comparative Security Analysis
Energy Consumption and Its Relationship with Security in PoW
Proof of Work is like a big, lock-down safe. It keeps our blockchain details safe by making folks solve hard math puzzles. These puzzles stop bad players because they take a lot of work and power. But using loads of energy can be a security risk too. Imagine if the electricity goes out. With no juice, the safe won’t work right, and security drops.
But why does it eat so much power? Proof of Work needs a high hash rate. That’s a big number showing how fast puzzles get solved. A high hash rate means better security, but it’s hungry for electricity. More energy means more chances to guess right and lock down the safe from thieves like Sybil attackers and the dreaded 51% attacker. But if the energy bill gets too high, or the power goes dark, we could be in hot water. That’s why some folks are looking ways to keep the blockchain safe without the giant power tab.
The Stakeholder Dilemma: Incentives and Security in PoS Systems
Now, Proof of Stake is a whole other ball game. Instead of solving puzzles, folks who own a part of the blockchain, the stakeholders, get to help run the show. They check new entries and keep the ledger straight. But they need to put their own coins on the line as a promise to play fair.
You might ask, “Does this keep the ledger safe?” Yes, because losing their stake scares ’em straight. If they mess up, their coins say bye-bye. But hey, not everyone’s rich, and that’s the rub. Proof of Stake can end up with the same rich folks in charge ‘cause they have more coins to stake. This can lead to a different kind of trouble like “nothing at stake” problems, where it doesn’t cost much to cause havoc.
Is Proof of Stake safer than Proof of Work? It’s tough to say. No grinding away at puzzles means we’re kinder to the planet, but it also means trust lies with the rich. It’s like picking the schoolyard monitor. You hope they’re good kids who won’t take your lunch money just because they can. The question of incentives is big here. Stakeholders gotta stay honest, or the trust goes poof. It’s not just about the system, but about keeping a fair playground for all.
Each system has its pros and cons. Both lock down our blockchain in their own ways. Proof of Work makes you spend bucks on energy for a super high hash rate and solid security. Proof of Stake makes the rule keepers risk their own cash to stay honest. Whether one is better than the other, that’s up to how much we value the energy we use, and how much we trust the folks holding the biggest slice of the pie. It’s not just tech; it’s about people, power, and staying on the level. We’ve got to stay sharp and find the balance that keeps our digital world secure.
The Role of Cryptography and Validation in Enhancing Ledger Security
Understanding Byzantine Fault Tolerance in Decentralized Systems
Byzantine fault tolerance is key for safe blockchains. It stops failures in some nodes from harming the whole network. Imagine a group of generals, trying to attack a city from all sides. They must agree on a plan. But some might not get the message or could try to trick the others. Byzantine fault tolerance is like having a secure way for generals to talk and agree, even if some generals are not honest or messages get lost.
This means even if bad actors are present or nodes fail, the network stays up. Cryptography is the secret sauce here. It scrambles data to keep our blockchain talks safe and checks if information is true. Each node in the network holds a piece of the puzzle. They work together to see the big picture and make sure everything matches up.
Node validation is this process in action. Imagine every block in the blockchain as a locked box. Nodes are like inspectors with a special key – the cryptographic validation. They use this key to open the box, check inside with the rules of the blockchain, and if all’s good, they seal it with a new lock. Only if most inspectors agree, the box gets a spot in the chain. If one tries to cheat, the others will see it right away, as the locks won’t match.
Node Validation Practices and Their Contribution to Distributed Network Safety
Node validation is essential for keeping the network safe. It’s how new blocks get the OK. Validators check transactions against the blockchain’s history. This stops spending the same coin twice. Think of it as having referees in a game, ensuring everyone plays fair. Without them, players might break the rules.
With Proof of Work, validating involves solving complex puzzles. It takes a lot of computer power but secures the network by making attacks expensive. But this uses lots of energy, which is not great for our planet. Proof of Stake, on the other hand, has validators put up their own coins as a promise they’re honest. If they’re caught cheating, they lose their stake.
This is why node validation is the backbone of ledger security. Without it, blockchains would be wild lands where double spends and tampering could run free. But with it, every user, every transaction, every smart contract gains the trust that’s vital in the crypto space.
Each time I break down the idea of consensus algorithms and validation, it hits home just how much these behind-the-scenes heroes – the nodes and the cryptography they wield – shape our blockchain experience. From ensuring every transaction is airtight to keeping our digital assets safe from the sneaky clutches of hackers, these complex processes are much like the skilled crafters molding the gears of a fine watch. It’s a marvel of digital engineering that turns personal trust in code and community into an immutable, unstoppable force.
Emerging Threats and the Evolution of Decentralized Security Mechanisms
Tackling New Vulnerabilities: From Sybil to Stake Grinding Attacks
Blockchain security is a tricky thing. We must fend off sneaky hackers every day. Why does this matter? Well, new kinds of attacks keep popping up like summer weeds. Take Sybil attacks, for example. Folks create fake identities to harm the network. But we’re not helpless. To fight this, we use nifty tech called Sybil attack prevention. This tech checks users to make sure they’re real. Clever, isn’t it?
Then there’s something called a stake grinding attack. This is where folks game the system. They do this by making many blocks in a blockchain to earn more than their fair share. It’s like cutting in line, only worse. You get ahead, but at others’ expense. We’re on it, though! We tweak rules to make these attacks useless.
Validators and Their Growing Influence in Blockchain Security Dynamics
Now, let’s chit-chat about validators. Validators are like the hall monitors of blockchain. They’re key players who make sure everything’s on the up and up. Each block added has to get a nod from these folks. What this means is, they protect the ledger from being tampered with. How cool is that?
So, with Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake, things get interesting. Proof of Work is like a mad dash, where computers race to solve puzzles. But this eats up heaps of energy. Proof of Stake, though? It’s like a lottery. Your ‘ticket’ is how many coins you have. Some say it’s a greener way to go.
Now, you’ve heard of minting coins, right? It’s like making fresh cash. In the blockchain world, it’s not about the coins; it’s about the block. Get the block right, and you mint new coins. But get it wrong, and the whole system could crash. And nobody wants that.
In Proof of Work, folks mine coins by solving hard math. Computers work hard and gobble up lots of power. It’s a heavy lift, alright. Some don’t like this because it’s like leaving the lights on all day and night. Wasteful, they say.
In Proof of Stake, it’s different. You put up coins — your stake — to get a shot at adding a block. The more you stake, the better your chances. Some folks think this is a lot fairer. But there are catches. What if big coin holders always win, or what if someone tries to cheat? We keep an eye out for these tricks.
Validators also step in when things get messy. Think of a network like a big puzzle. All pieces must fit. Validators are there to give the thumbs up if the piece fits just right. They can even boot out bad blocks that don’t belong. That keeps the puzzle clean and everyone playing fair.
All this talk about attacks might make you wary. Don’t fret. These decentralized security mechanisms are strong. They’ve got cryptographic consensus methods that are top-notch. This means a super-smart way to agree on what’s true and what’s false, all across the network. It’s like having a superpower against ledger tampering risks.
And let’s not forget, with great power comes great responsibility. Validators have got to be on their toes all the time. One slip, and things could go sideways. But, take heart. These folks are picked because they’re trusted. They keep things square, and that’s what keeps blockchain so solid. So, while the attackers never sleep, neither do our guardians of the ledger. It’s a round-the-clock job, but someone’s got to do it, right?
In this post, we’ve dived into how different consensus methods shape blockchain safety. We looked at how blockchains guard against attacks and compared proof of work with proof of stake systems. We also saw the part cryptography and node checks play in keeping ledgers safe.
Keeping our data secure is vital. As we saw, each system has its risks and defenses. Some use lots of energy, others rely on owners’ honesty. Tech keeps changing, and so do threats. We must keep up, from Sybil to stake grinding attacks, ensuring validators stay fair.
Remember, with every new tech, security evolves too. We’ve got to stay sharp and informed. Let’s keep pushing for secure, fair systems we can trust. It’s the only way to keep the digital world safe for all.
Q&A :
How do consensus algorithms enhance security in blockchain technology?
Consensus algorithms are fundamental to the security and functionality of blockchain technology. They establish a reliable, consistent, and stable environment by ensuring all participants in the network agree on the validity of transactions. This unanimity prevents double-spending and fraudulent activities, as altering recorded transactions would require the consensus of all participants, which is practically impossible to achieve in a widespread, decentralized network.
What are the security risks associated with faulty consensus algorithms?
Faulty consensus algorithms can jeopardize the entire blockchain network, leading to a range of security issues such as the 51% attack, where an entity gains control of the majority of the network’s computational power and can influence the consensus process. This manipulation can result in double-spending, censorship of transactions, and a loss of trust in the system’s integrity.
Why is consensus important for the security of distributed networks?
In distributed networks, consensus is critical because it ensures that all nodes, or participants, are synchronized and abide by the same protocol rules. Without consensus, there would be no agreed-upon method for validating transactions or blocks, leading to potential security breaches, network forks, and the inability to reliably verify information.
How do different consensus algorithms impact the overall security of a cryptocurrency?
Different consensus algorithms, such as Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), have unique mechanisms that directly impact the security of a cryptocurrency. For instance, PoW requires significant computational work to validate transactions, making it difficult to compromise the network. Meanwhile, PoS and DPoS rely on staking and delegation, which can offer faster transaction times and reduce the risk of centralization. However, each has its vulnerabilities and trade-offs that must be carefully managed to maintain security.
Can consensus algorithms prevent Sybil attacks, and if so, how?
Consensus algorithms can help prevent Sybil attacks, where a single adversary creates multiple fake identities to gain disproportionate influence in a network. By requiring nodes to demonstrate a commitment, such as performing computational work (PoW) or holding a stake in the network (PoS), the algorithms increase the cost and complexity of successfully carrying out a Sybil attack, thereby enhancing the network’s resilience against such threats.


RELATED POSTS
Exploring the Bitcoin Halving Cycle – Future and Price Predictions
Exploring the Bitcoin Halving Cycle...
Forgotten Runiverse: A promising NFT Game on Ronin Network
Forgotten Runiverse is emerging as...
Blockchain Security Essentials: Navigating the Regulatory Terrain
Understanding the Regulatory Landscape for...
Blockchain For Securities Trading: Revolutionizing Securities Trading for Investors
Advancing securities trading with #Blockchain...
2024 US Election Results – Political Shock and the Future of Cryptocurrency
The 2024 US election results...
Primary versus secondary market – Understanding Clearly for Effective Investment
Primary versus secondary market are...
Blockchain and Bureaucracy: How will governments use blockchain in the future?
How will governments use blockchain...
Preparing Blockchains: Quantum Computing’s Inevitable Impact
Protecting blockchain from quantum attacks:...
Blockchain Trends and Predictions: The Future of Tech Unveiled
"Blockchain trends and predictions: Embracing...
What is Distributed Ledger Technology in Blockchain?
Discover the fundamentals of distributed...
Comparative DAG vs Blockchain: Decoding the Future of Tech Networks
Compare the Structural Differences: DAG...
How does a 51% attack work? How Can Undermine Blockchain Security
Understand the mechanics of a...
Cost of Blockchain Security Audits: Are You Investing Wisely?
Understanding the Costs of Blockchain...
Negative Impact of Blockchain on Education: Are We Overlooking Risks?
Protecting Education: Examining the Negative...
What is rate limit exceeded on twitter?
What is rate limit exceeded...
Economic Bubble in Crypto – 3 Experiences to deal with it
In the volatile cryptocurrency landscape,...