You’ve heard the buzz about blockchain, but what’s behind it all? In “Unlocking the Mystery: How Blockchain Technology Revolutionizes Transactions,” I strip down the hype and give you the basic explanation of how blockchain works. No jargon, just simple terms that paint a vivid picture of this game-changing tech. It’s like the internet of money – a ledger that no single person owns but everyone can trust. Imagine a world where every transaction is safe, and secure, without middlemen – that’s blockchain. So, grab a coffee and let’s dive into a world where every block, every chain, and every transaction opens doors to endless possibilities.
Demystifying Blockchain: The Foundations of a New Era in Transactions
Distributed Ledger Basics and Their Role in Blockchain
Imagine a magic notebook that many folks can write in at the same time. They can all see what each other writes in real time. This is like a distributed ledger. In a blockchain, this magic notebook is digital. And once you’ve written in it, nobody can erase it. This is key to understanding blockchain.
Now imagine each page of the notebook has a lock only the writer has a key for. That’s one way blockchain keeps our stuff safe. Nobody can change what you wrote if they don’t have your key. This is part of why people really trust blockchain.
Here’s how it breaks down. Every person in the blockchain has their own page. When we do deals with each other, we shout it out to everyone. People called nodes check the deal to be sure it’s good. They check using rules called consensus mechanisms. Think of it like you and your friends deciding what game to play – you all have to agree before you start.
Once everyone agrees, the deal gets locked onto a page with a special math trick called cryptography. Each page also has a secret code that’s tied to the one before it. This makes a chain of pages, or a blockchain. It’s like a treasure map; if you mess with one part, the map stops making sense.
Cryptography: The Shield of Blockchain Security
Okay, so what’s this cryptography thing? It’s like a secret code for our deals on the blockchain. You’ve got two keys. One only you keep, called a private key, and one you can share with others, known as the public key. Together, they keep your deals safe.
When you want to make a deal, you lock your message with your private key. It’s like you’re using your secret code. Then the person getting your message uses your public key to open it. If it works, they know it’s really from you. This is how blockchain spots fakes and keeps our deals safe.
And the best part? Once the deal is locked in, it can’t change. It’s set in stone, or in this case, set in the blockchain. This means everyone can trust each deal is real and hasn’t been fiddled with.
In the end, blockchain is like a game of building blocks with your friends, but the blocks are really special. Everyone can see them, but only you can open your own. Once they’re put down, they’re stuck for good. This helps keep things honest and everyone’s stuff safe.
So, this is the big secret to blockchain – it’s a smart way to write deals down that everyone can trust. It’s no wonder so many people are excited. It’s like a super notebook that can change the way we do so many things, like buying stuff, voting, and even playing games. Thanks to this nifty tech, we can look forward to a future with less tricks and more trust.
The Inner Workings of Blockchain Technology
Understanding How Blocks and Chains Interact
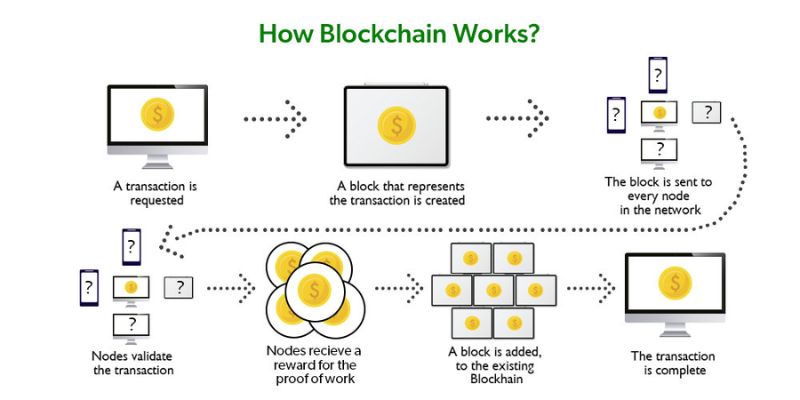
Imagine blockchain as a digital chain of blocks. Each block holds a bunch of user transactions. When a new transaction happens, it’s broadcast to a peer-to-peer network. This network is made up of folks with computers called nodes.
Nodes check the transaction using known algorithms. They look at the transaction’s details and the user’s status. After nodes agree the transaction is legit, it’s combined with other transactions. This creates a new block for the blockchain.
Each block has its unique code called a hash. The hash is like a fingerprint. It’s super important because it ties the new block to the one before it. This is how we get the term “blockchain.” Blocks are placed one after another, making a long chain.
Now, transactions are set in stone, so to speak. Once part of a blockchain, the block can’t be changed without altering all future blocks. That’s because of the hash. If one block’s hash is altered, it’s a dead giveaway that something’s fishy. The blockchain is safe because everyone can see if a block was tampered with. By checking the unbroken chain of hashes, we trust the blockchain.
Unraveling the Significance of Hash Functions and Immutable Records
Hash functions are the math that turn transactions into a hash. Think of them as a blender. You put in fruits, or transaction details, and get a smoothie, or hash. Even if you use the same fruits, a tiny change makes a different smoothie. Same with hashes – a tiny change in transactions gives a whole new hash.
Hashes are key for security. Each block’s hash must match up with the previous block. This creates an unchangeable record of transactions, called an immutable ledger. It’s like building with Legos. Once you connect them, they stick.
And this matters a lot. With an immutable ledger, everyone knows every transaction is true. No one can cheat and change a record. This builds trust among users. So you can see why blockchain’s a big deal in the digital world – it’s a record keeper that never lies.
Blocks and chains, hashes and ledgers, all work together in blockchain tech. This lets us share info and trust each other, without needing a middleman. Bitcoin and other digital currencies use blockchain to stay secure and transparent. But there’s more to it than money. Health records, votes, and contracts can all use blockchain. It’s changing how we keep and share important information. It’s quite the game changer, isn’t it?
Ensuring Consensus and Security in Blockchain
The Mechanisms of Achieving Network Agreement
In blockchain, how do all users agree on the data? They use a process called consensus. Consensus keeps everyone honest and ensures that each copy of the ledger is the same. This makes our information safe and trusted.
The Role of Nodes and Miners in Maintaining Blockchain Integrity
What are nodes, and what do they do? Nodes are like guards who watch over blockchain. Each node has a full list of the blockchain’s history. They check new blocks to make sure they’re right. If a node finds a block is wrong, it rejects the block. This means that to change the blockchain, you would have to fool all the nodes at once, which is very hard.
Now, think about miners—what is their role? Miners are special nodes. They work hard to add new blocks to the chain. They solve tough puzzles to do this. When they solve one, they show their work to all the other nodes. If the nodes agree the block looks good, it’s added to the chain. Miners get a prize for their hard work. This work is a big part of keeping the blockchain safe.
Let’s talk about the blockchain network. What does it do? The network lets all the nodes talk to each other. It is like a web where everyone shares what they know. This web is called a peer-to-peer network. No one is in charge of it, and everyone is equally important.
What is the block creation process? When transactions are to be added, they are put into a block. Each transaction is checked by nodes. Then miners start working on creating the block. They use a thing called a hash function. This turns the block’s info into a string of numbers and letters.
Why is a hash function important? It’s important because it makes data safe. If you change just one part of the transaction, the hash changes a lot.
What makes a blockchain an immutable ledger? Immutability means that once something is added to the blockchain, it can’t be changed. This is because of the hash. If you try to change a transaction, everyone would know because the hash wouldn’t match.
What about a decentralized system? To be decentralized means there’s no central control. Everyone has a copy of the transactions. This creates trust, because no single person holds all the power.
In conclusion, nodes and miners work together to keep blockchain truthful and safe. They do this by reaching network agreement and adding new, confirmed blocks through a very transparent and democratic process. This balance of consensus and security is what makes blockchain so powerful and reliable.
Blockchain in Action: From Theory to Real-World Applications
The Lifecycle of a Blockchain Transaction
Let’s dive into how a blockchain moves money from one place to another. In simple terms, it’s like a game of passing a message where everyone has to agree on what’s written.
First, someone sends a message, which is really just a transaction. This message is locked tight with special math called cryptography. This means only the right person can unlock and get it. It’s super private and secure.
Next, this message is mixed with other ones and added to a new block. Think of it as a box of messages that gets packed up. This new block then gets a unique code called a hash. It’s like a secret stamp that no one else can copy.
Now, the real magic happens—the block is added to the chain. But, only after everyone in the chain checks it’s all good. This is called consensus, and it’s like everyone nodding in agreement.
Once that’s done, the block is chained to the others and locked with the secret codes. It’s like a train of boxes, where each one depends on the one before it. And boom, the message is delivered!
Smart Contracts and Their Impact on Automation and Efficiency
Imagine you have a robot that makes deals for you. Smart contracts are kind of like that. They are special rules written in code on the blockchain. They kick into action when certain things happen.
For example, let’s say you want to buy a game from a friend. You can set up a smart contract that says, “When I put in the money, give me the game.” The blockchain makes sure this happens automatically, no need to check if everyone did what they promised.
These smart contracts can handle all kinds of deals, big or small. They make trading faster and less of a headache because everything is set up to run on its own. It’s like having a trusty robot helper in the digital world.
By using smart contracts, businesses save time and money. They don’t need as many people to check the deals are fair. The blockchain is always awake, never makes mistakes, and follows the code to the letter.
So, there you have it: a whirlwind tour of blockchain transactions and smart contracts. This is how blockchain makes trading safe and slick. It’s a game-changer for how we do deals and could change the whole world one day.
In this post, we unlocked blockchain’s secrets. We started by exploring the basics of distributed ledgers and why cryptography acts as blockchain’s shield. Then, we dived into the magic of how blocks and chains work together and why hash functions and unchangeable records matter.
We also examined how networks agree on data and how nodes and miners keep blockchains safe and sound. Lastly, we looked at blockchain in real life, from the steps of a transaction to how smart contracts make deals faster and smarter.
Blockchain isn’t just a buzzword; it’s a tech revolution transforming how we think about and handle transactions. Its promise for a secure, efficient future excites me, and I hope you feel the same. Trust in blockchain is growing, and now, you’re better equipped to understand its powerful impact.
Q&A :
What is the blockchain and how does it function?
Blockchain technology is a distributed ledger system where transactions are recorded with an immutable cryptographic signature called a hash. This means that if one block in one chain was changed, it would be immediately apparent it had been tampered with. When a new transaction or an addition to a digital ledger is made, it is encrypted and added to a “block” of data. That block is then linked to the chain, which provides a full and transparent history of transactions.
Can you explain what makes blockchain secure?
Blockchain is considered secure due to its decentralized nature and cryptographic algorithm. It is a chain of blocks, each containing data, that is controlled by no single authority. A blockchain is secure because each new block of transactions is linked back to previous blocks in a way that makes tampering mathematically challenging if not virtually impossible. This is enhanced by the network consensus needed to validate transactions and add new blocks.
How does blockchain verify transactions?
In a blockchain, transactions are verified through a process called mining, which involves validating data blocks and adding transaction records to a public record known as a ledger. Miners use powerful computers to solve complex cryptographic challenges that verify the authenticity of transactions. Once a transaction is deemed legitimate, it is clustered into a block with other transactions, and once a consensus is achieved among other nodes on the network, the new block is added to the blockchain.
What are the basic principles behind blockchain technology?
The basic principles behind blockchain technology include decentralization, transparency, and immutability. Decentralization removes the control that institutions or individuals typically have over systems, dispersing it across the network; transparency ensures that each transaction is visible to all participants; and immutability guarantees that once a transaction has been added to the blockchain ledger, it cannot be altered or deleted, which is enforced by cryptographic hashes.
How does a blockchain differ from traditional databases?
A blockchain differs from traditional databases in its structure and management. Unlike traditional databases, which organize data into tables, blockchain, as its name implies, structures data into chunks (blocks) that are strung together. This data structure inherently makes revisions very difficult: once a block is filled with data and added to the chain, it is very difficult to go back and alter the contents without consensus from the network. This leads to the unparalleled security benefits of blockchain.

RELATED POSTS
Role of AI: Reinventing Blockchain Security for a Safer Future
Role of AI in securing...
Market Maker Magic: How Crypto Liquidity is Shaped
"Discover the Vital Role of...
Identity Management and Compliance Solutions: Navigating the Maze of Modern Security
Identity management and compliance solutions...
Barriers to Blockchain Adoption: What’s Holding Back the Revolution?
Navigating Blockchain's Economic, Legal, and...
Security Testing Providers for Blockchains: Who’s Guarding Your Digital Gold?
The Critical Role of Blockchain...
Blockchain Revolution: Securing Your Future with Verified Educational Credentials
Explore how blockchain revolutionizes educational...
Blockchain Breakthrough: Sources of funding for blockchain research
Sources of funding for blockchain...
Challenges Facing Current Consensus Mechanisms: Are We Stuck?
Challenges facing current consensus mechanisms:...
How Blockchain Boosts Educational Equity: A Tech Revolution in Learning
How can blockchain promote educational...
Blockchain Security Breakdown: Why Trust is the Ultimate Currency
Discover the importance of trust...
Blockchain Breakthrough: Revolutionizing Education for a Brighter Future
Unlocking Educational Potential: Explore the...
Blockchain use cases: Unveiling 10 Innovative Real-World Applications
Transforming finance with blockchain technology:...
Primary versus secondary market – Understanding Clearly for Effective Investment
Primary versus secondary market are...
Blockchain Meets Education: Revolutionizing Learning Management Systems
Enhance e-learning with blockchain-enabled solutions....
What is rate limit exceeded on twitter?
What is rate limit exceeded...
Preparing Blockchains: Quantum Computing’s Inevitable Impact
Protecting blockchain from quantum attacks:...