Ever wonder how does blockchain technology work? It’s like a digital ledger, but super secure and shared across many computers. Instead of one person keeping all the records, everyone gets a copy. This means no single person can mess with the info. With special codes, called cryptography, it becomes a fortress for data. Let’s crack this code together, learn how these blocks link up, and see why it’s such a big deal beyond just coins and cash.
Demystifying Blockchain: The Core Principles
Understanding Distributed Ledger Technology
Imagine you have a special notebook. This notebook is shared with friends around the world. You all have a copy. Anything written in this notebook copies itself to all the others. It’s magic!
That’s how distributed ledger technology (DLT) works. It shares data across many computers. Everyone sees the same transactions. This makes it tough for anyone to cheat. It’s like a game where, to change a rule, you must ask all players. Most of them must agree. If they say no, the rule stays the same.
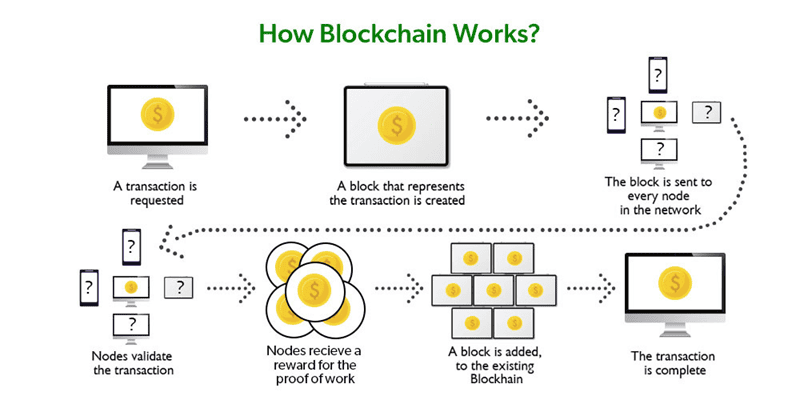
With blockchain, data forms blocks. Each block has a list of transactions. When one block fills up, another starts. It links to the previous block. This forms a chain, hence “blockchain.”
The Role of Cryptography in Securing Data
Think of a secret club’s handshake. It’s a special sign that proves you’re in the club. Cryptography is like this secret sign. It’s a way to hide data with complex math, so only certain people can read it.
In blockchain, cryptography keeps your info safe. When you send data, like money, you lock it with a secret key. You might hear this called “encryption.” Only the right person with their own secret key can unlock it. It’s like mailing a treasure chest. Only the person with the right key can open it.
Each transaction also gets a unique fingerprint. This is called a “hash.” It’s created using the secret keys I just mentioned. If the data changes, the hash changes too. Since every block has the hash of the last block, changing one block messes up the whole chain. That’s why data in blockchain is safe and stays as it is – we call this “immutable.”
Blockchains use these core principles to keep everything open yet secure. It’s like a transparent safe. You can see inside but can’t reach the treasure unless it’s yours.
Blockchain tech is changing our world, from how we use money to how we keep things fair. And the best part? It’s just the beginning. There’s more to learn and lots to explore. But for now, remember the notebook and secret club handshake – they’re the heart of blockchain.
The Mechanics of a Blockchain Transaction
Delving into the Blockchain Transaction Process
Picture a world where every move you make online stays safe. That’s what blockchain does! When you hear “blockchain transaction process,” think of it like a digital handshake that seals a deal. The magic begins when someone sends money or data.
First, the deal, or transaction, gets checked by a bunch of computers, called nodes. These nodes make sure everything is correct. Next comes the blockchain part. The transaction, with some others, gets bundled into a “block.” Now, it must join the chain. But how?
It needs a seal of approval, called a hash. Imagine a lock that only the right code can open. Each block gets its own unique hash — like a fingerprint. If someone tries to change the fingerprint, it won’t match anymore. So everyone quickly sees if someone messes with the block.
Once the block has its hash, the nodes get to work again. They use a consensus, like a group nod, to agree the block is valid. Then they add the block to the chain. Now it’s part of the ledger that everyone can see. It can’t be changed or removed. That’s the trust part.
Now, you get why blockchain is a big deal for safe online moves!
Unpacking Hash Functions and Their Importance
A hash function is at the heart of a blockchain’s magic — think of it as the wizard making sure every transaction is legit and safe. Hashing scrambles data into a string of numbers and letters. Each block’s data gets a unique hash. This hash is key because it protects the data.
Without hashing, blockchains wouldn’t be secure. It’s like a protective shield. If someone tries to change a block, the hash changes too. Because each new block’s hash uses the previous one, changing data in one block would mess up the whole chain.
Hashes tie blocks together and make sure they’re in the right order. Trying to alter a block isn’t worth it because it’s super obvious and sticks out. Plus, it would need a ton of computer power to change all following blocks before anyone notices.
And the whole network would see this. They’d need to fix or dump the bad block. This is what keeps everyone honest and makes the whole system trusted. Everyone can see everything, and that’s pretty cool when it comes to keeping our digital world safe.
So, yeah, hash functions might sound like a big word, but it’s just a tech way of sealing the deal on safety. With each new block, trust gets built, and your digital stuff stays secure, just like in the online handshake I talked about. And that, my friends, is the real wizardry of blockchain.
Constructing Trust: Consensus and Security in Blockchain
The Battle of Algorithms: Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake
In a blockchain, trust is key. No one controls it. It’s like a team game where everyone plays fair. To make sure no one cheats, we use special rules called consensus mechanisms. They help all computers agree on what’s true on the blockchain.
One popular rule is Proof of Work. Here, miners solve puzzles using lots of computers and energy. If they solve it first, they add a block of info to the chain and earn a reward, like Bitcoin. But it uses a lot of power, which worries some people.
Then there’s Proof of Stake. This one’s like a raffle. You hold coins, which gives you a chance to add a block and win more coins. The more you hold, the better your odds. But you don’t need big machines or tons of energy. This makes it kinder to our planet.
The Role of Nodes and Security Features
Nodes are the watchful eyes of blockchain. Think of them as many little guards checking on things. They keep copies of the blockchain and make sure every transaction follows the rules.
Every move on a blockchain is like a locked box full of secrets. Cryptography is the lock. Only the right key can open it. This keeps our stuff safe from hackers.
Blockchain also uses something called immutability. This means once info is in the blockchain, it can’t be changed or deleted. So, you can’t cheat by taking out your own mistakes or others’ good moves.
Smart contracts are rules written in code. They run by themselves when certain conditions are met. So, if I promise to send you a digital game when you pay, a smart contract will handle it. Once you pay, the game is yours, no questions asked.
Security on a blockchain is tough. It uses heavy-duty encryption, which means turning info into a secret code. This code is so hard to crack, it’s like trying to guess a code that is as long as a book filled with random letters and numbers.
To sum it up, blockchain makes sure everyone on the network plays by the rules and keeps their info safe. It’s a smart way to work together without needing to trust each other too much. We use crypto to lock our data and smart contracts to deal without hassle. It’s all part of making a safer digital world.
Beyond Bitcoin: The Expanding Universe of Blockchain Applications
From Finance to Healthcare: Exploring Diverse Blockchain Use Cases
Let’s dive deep into how blockchain can change the world, not just in money, but in many areas. Think of blockchain as a book where you can only add words, not erase. Once you write something, it’s there for good, for everyone to see. We use this “book” in finance, where it started with Bitcoin. Now, we’re discovering new ways to use it almost every day.
Healthcare is getting a blockchain boost, too. It makes sure patient records are safe and private. Only the people who need to see these records can. It’s like a lockbox that talks, giving info only to the right listeners. And in the world of buying and selling – the supply chain – blockchain helps track items from when they’re made till they reach your home. It’s like a magic trail that shows where your new sneakers have been.
The Evolution of Smart Contracts and Decentralized Applications (DApps)
Now, let me tell you about smart contracts. They are like pinky promises in the digital world. Smart contracts use blockchain to make sure everyone does what they said they would. No need for a middle man! And then, we have DApps, or decentralized apps. These are programs that run on a peer-to-peer network of computers. This means no one owns them, and everyone can help make them better.
What else could blockchain do? Imagine voting from your couch, knowing that your vote is completely counted and safe. Or, think about playing games where you truly own the items you find or earn. The possibilities are endless!
While blockchain can do lots of things, it’s important to know that it needs nodes, like tiny workers, that help keep it running. Everyone who participates can help decide how it works. This is what we call blockchain governance. It’s fair because everyone gets a say, not just one boss.
In the coming years, we can expect more creative uses for blockchain. From proving who we are to securing our homes and even our energy use, blockchain can make our lives better and safer. It’s like a superhero – always getting stronger and finding new ways to save the day. And you know what? We’re just getting started.
We just explored the nuts and bolts of blockchain, from ledgers to securing data. We kicked off by breaking down the distributed ledger and how cryptography keeps our info safe. Then, we dived into what goes on in a blockchain transaction and why hash functions matter a lot.
Next, consensus and security stood in the spotlight, showing us how networks agree through Proof of Work or Proof of Stake and how nodes beef up safety. Lastly, we looked beyond Bitcoin to see blockchain’s power in finance, healthcare, and more, thanks to smart contracts and DApps.
In all, blockchain is a game-changer. It’s reshaping how we trust, share, and secure data across many fields. As we keep unlocking its potential, who knows what we’ll achieve? Stay curious, keep learning, and let’s ride the wave of blockchain’s limitless possibilities together.

RELATED POSTS
Pencils Protocol: Optimizing DeFi yields on Scroll
In the vast landscape of...
Blockchain for Beginners: Unlocking the Mysteries of Decentralized Tech
Unlock the Basics of Blockchain...
Airdrop Coin 101: Seize Your Free Crypto Bounty Now!
Understanding the airdrop phenomenon in...
Unveiling the Achilles’ Heel: Top Common Vulnerabilities in Blockchains
Protecting Blockchains from Vulnerabilities: Uncovering...
Challenges of Blockchain Technology: Navigating the Digital Minefield
Struggling with blockchain scalability and...
Public Key vs Private Key Cryptography: Unlocking the Secrets of Digital Security
Understanding the Basics of Public...
Stable Coins Demystified: Your Essential Guide to Crypto Stability
What is a stablecoin? Explore...
Examples Of Blockchain Use Cases Beyond Cryptocurrency: Surprising Uses
Discover 10+ examples of blockchain...
Blockchain Security Audits: Essential Shields Against Cyber Threats
Understanding the Importance of Blockchain...
Timeline of Blockchain Development: A Revolutionary Tech Journey
Timeline of blockchain development: From...
Recent Advances in Blockchain Research in Financial Services: Revolutionizing Financial Futures
Recent advances in blockchain research...
Blockchain For Trade Finance: Streamlining Trade Finance for the Digital Age
Unlock the potential of blockchain...
Challenges Facing the Future of Blockchain: What Lies Ahead?
Challenges facing the future of...
Fundamental vs technical analysis in cryptocurrency investment
Fundamental vs technical analysis plays...
What Makes the Connection Between Blockchain Technology and Cryptocurrencies Special?
Blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies form...
Guide to voting in Project Catalyst
Ready to help build Cardano?...