Ever wonder, “How does blockchain work?” You’re not alone! Picture a digital ledger, super safe and shared across a network. It’s like a puzzle, made of data blocks. Each block has unique info, and when filled, joins a chain. That’s blockchain! It’s behind Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. Dive into the basics with me, and let’s unlock this mystery together, no tech jargon, just clear, simple talk. Get ready to learn how this cool, complex system keeps your digital coins safe.
Understanding the Building Blocks of Blockchain Technology
The Basics of Blockchain Technology Explained
Think of blockchain as a notebook filled with notes. Each note is a block. These blocks link together to tell a full story, like pages in the notebook. Now imagine, instead of one notebook, copies exist in many places at once. If someone tries to change a note, everyone must agree to it.
Blockchain technology explained simply is this: It’s a system for keeping records that everyone can trust because no one is in charge. Everyone keeps an eye on everyone else. What makes blockchain special is it’s digital, public, and, once something is written, no one can change it. This is called ‘immutability.’
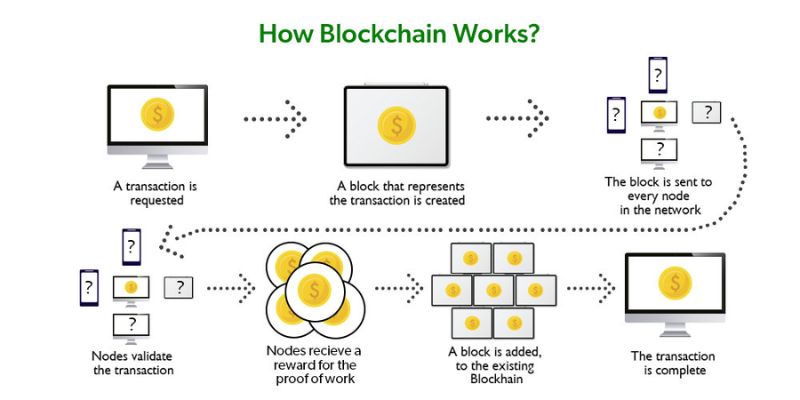
Let’s say you want to send a friend ten coins digitally. This action is a ‘blockchain transaction process.’ Here’s how it works. You say, “I want to send ten coins.” This message goes out to a network of computers, called ‘nodes.’
Each node has a complete record of all transactions made. The node checks if you have ten coins to send. If you do, the transaction goes to ‘miners.’
Miners use strong computers to solve a tricky puzzle, proving the transaction is good. This “proof” gets added to your transaction record. Then it goes into the notebook as a fresh note. That’s how blockchain transaction works.
Deciphering Cryptographic Hashing and Its Role
So, how do we keep these notes safe? By locking them with a ‘cryptographic hash.’ It’s like a seal that no one can break. Every time someone adds a new note, it gets its own seal. But this seal also locks to the last note’s seal. Like links in a chain.
It’s important because it means no one can swap a note without breaking the seals. If that happens, it stands out like a sore thumb. And since everyone has a copy of the notebook, a fake note can’t hide.
This seal is special. It’s unique to every note and comes from the info inside it. Change a tiny bit of the note, and the seal changes a lot. That’s how everyone stays honest.
Now, let’s make sure we’re clear: ‘blockchain and security features’ go hand in hand. The seals keep the notes safe. The many copies stop people from lying about what’s in them.
This safety helps with all kinds of things. People use blockchain for art, music, even buying houses. When you hear ‘distributed ledger technology,’ think of our notebook. It’s just a shared list of transactions that’s hard to mess with.
Remember, blockchain is a teamwork game. Every player, called a ‘node,’ has power. This setup is called a ‘decentralized network.’ No one has all the power, but everyone helps keep the network safe and sound.
Because of this, blockchain has a bright future. It can change the way we do many things, like track where our food comes from or make voting more honest. People are just starting to unlock what blockchain can do. It can even save energy by cutting out middlemen. That’s smart and green!
So, now you know the basics: blockchain is a shared notebook that everyone checks, with strong seals on each note. It’s making waves, and the world is just starting to catch on. Let’s keep our eyes open for what’s to come!
Delving into Transaction Processing on the Blockchain
Dissecting the Blockchain Transaction Process
Picture this: blockchain is like a game where each player keeps notes of all moves. When someone makes a move, such as sending digital money, that’s a transaction. Every player must agree it’s fair and follows the rules. If most agree, the move goes on the list that everyone shares.
The list I’m talking about is a digital ledger. Each move or transaction is put into a box called a ‘block’. Blocks are like pages of a ledger. To prevent cheating, blocks are locked with a complex math problem. Solving this is called ‘mining’. Miners compete to find the solution with computers. The first to solve gets to add the block to the chain of boxes – the blockchain.
The Function and Importance of Nodes in Verifying Transactions
In blockchain, nodes are like the judges of the game. A node is a computer that holds the blockchain. It checks all new moves to ensure they’re okay. Nodes talk to each other, making sure they all have the same notes.
For example, if Joe sends money to Sue, the nodes check Joe’s balance. They also make sure he hasn’t sent that same money to someone else. This is crucial because, unlike a referee, no one node is in charge. It’s a team effort. If most nodes agree, the transaction clears and joins the blockchain. This process is what makes blockchain secure and fair. It’s like having the ultimate check-and-balance system where everyone holds a copy of the rulebook.
Remember, blockchain technology isn’t just for geeks or tech whizzes; it’s for everyone. Understanding how it processes transactions brings us closer to a world where playing fair is part of the game.
Mechanisms of Consensus: Keeping Blockchain Honest
Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake: Debating Consensus Mechanisms
Let’s break down how blockchain keeps everyone playing fair. It’s all about rules known as consensus mechanisms. Proof of Work and Proof of Stake are two big players here, and they are quite different.
Proof of Work makes computers solve tough math puzzles to add new blocks of info. It’s like a race where the fastest computer wins the right to add a block and gets a reward. But it takes lots of power, which makes some people frown due to its heavy energy use.
On the other side, Proof of Stake picks a participant to add the new block based on how much digital currency they hold. It’s more like a lottery that favors the rich, but you don’t need as much energy. This makes people debate which one is better. Some say Proof of Work is fairer; others vote for Proof of Stake since it’s easier on the planet.
How Miners Validate Transactions and Forge Trust
Now, how do we know a transaction is good to go? Miners come into play. They check every transaction to make sure it’s legit. Picture a miner in a digital helmet, looking at transaction details closely. They’re the hall monitors of the blockchain. If they give a thumbs up, it means all is well, and the transfer can happen.
Miners help us trust the system because they keep a close eye on everything going on. They take data from transactions and turn it into crazy hard math problems. When they solve them, it’s proof they’ve done the work to check the transactions. That’s how trust is made with a cool high-five from technology.
Knowing just this much, you’re already getting the hang of blockchain. Think of it as a digital neighbor watching out for everyone. With miners and consensus rules, blockchain gives us a way to trust strangers in this digital playground. Isn’t that something?
The Dual Sides of Blockchain: Public and Private Networks
Exploring the Differences Between Public vs. Private Blockchain Systems
This will feel like learning to ride a bike. At first glance, public and private blockchains may seem similar, both being types of digital ledger systems. Yet, they are as different as bicycles and motorbikes.
Public blockchains are like parks. Anyone can enter and enjoy the space. These decentralized networks are open to everyone. Here, every person has a copy of all transactions. This ensures transparency but also means more energy use due to many verifying each transaction. Bitcoin is a famous example.
Private blockchains, on the other hand, are like private gardens. Entry is limited to those allowed. They are controlled by one group or company, making them less transparent but more efficient. Fewer people to verify transactions mean less energy use. They’re often used by businesses wanting to keep their data private.
Both kinds offer strong security features. But they serve different needs based on who can join and control them.
How Smart Contracts Function Within Various Blockchain Ecosystems
Now, let’s talk about what a smart contract is. Think of a smart contract as a computer program that works like a vending machine. You put in something, like cryptocurrency, and if the conditions are right, out comes a product, like ownership of a digital art piece.
In public and private blockchains, smart contracts automate agreements. No need for a middleman. When certain conditions are met, the contract automatically does what it’s supposed to.
For example, in a supply chain, smart contracts can release payments only when goods are delivered. They save time and reduce the chance of fraud or errors, as they’re bound by code instead of trust.
Understanding nodes in blockchain is crucial here. Nodes are like checkpoints in both public and private networks. They store, spread and preserve the blockchain’s information. They are key in making sure everything runs smoothly.
With this handy guide, you’ve just unlocked the first steps to understanding how public and private blockchains work and the smart contracts that shine within them. From providing greater security to optimizing performance, blockchain technology is adapting to the unique demands of various industries, promising a future where transactions are faster, cheaper, and more reliable than ever before.
In this post, we’ve unpacked the core elements of blockchain technology. We explored how this tech works, from the basics right up to its complex consensus mechanisms. We learned that cryptographic hashing keeps data secure, while transaction processing relies on a network of nodes. Nodes and miners work hard to forge trust in every transaction.
We also compared proof of work and proof of stake. They both keep the blockchain honest but work quite differently. Lastly, we looked at public versus private networks. Both have their uses and it’s smart contracts that add real power to these systems.
To sum up, blockchain isn’t just a buzzword. It’s a solid system that shapes how we exchange value securely. Understanding this technology’s working parts, you now know it’s not magic—it’s clever design and teamwork. Keep exploring and you’ll see just how blockchain is changing our digital world.
Q&A :
What is the basic principle behind blockchain technology?
Blockchain operates on the principle of a distributed and decentralized ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers. This ensures that no single entity has control over the entire blockchain, and that each transaction is transparent and immutable, meaning it cannot be altered once recorded.
How does a blockchain transaction get verified?
A blockchain transaction is verified through a process called mining, in which network participants, known as miners, use computational power to solve complex mathematical puzzles. When a puzzle is solved, the transaction is confirmed and added to a block. Each block is then linked to the previous block, forming a chain, hence the term blockchain.
Can information on a blockchain be altered or deleted?
Once a transaction is added to a blockchain, it is almost impossible to alter or delete. The information is encrypted and distributed across a network of computers, making tampering with any single record exceedingly difficult without being noticed by others in the network. This makes blockchain an exceptionally secure form of record-keeping.
Are blockchains only used for cryptocurrencies?
While blockchains are most widely known for their use in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, their potential applications extend far beyond. They can be used for smart contracts, supply chain management, voting systems, identity verification, and much more. As blockchain technology evolves, its uses are likely to expand into various sectors.
What makes blockchain technology secure?
Blockchain’s security comes from its use of cryptographic hashing, a decentralized structure, and consensus mechanisms that ensure all participating nodes in the network agree on the validity of transactions. Additionally, each block contains a unique cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a secure link between them, which makes altering any single block’s data nearly impossible without altering subsequent blocks as well.


RELATED POSTS
Lost Private Key in Blockchain: Unlocking Digital Dilemmas
Lost your private key in...
Stuart Alderoty: His role at Ripple
Discover Stuart Alderoty, Chief Legal...
Security of Proof of Work: Is Your Cryptocurrency Safe?
Security of Proof of Work...
Blockchain Secrecy: The Future of Fraud-Free Elections?
How does blockchain prevent voter...
Blockchain Revolution: Securing Student Records for the Future
Discover the impact of blockchain...
Exploring 2 Roles of Permissioned Blockchain
A permissioned blockchain restricts access...
Impact of Regulations on Blockchain Adoption: Navigating the Compliance Maze
Understanding the Impact of Regulations...
Exploring DLT in Blockchain: Navigating the Tech of Tomorrow
Understanding the Fundamentals of DLT...
Block Chain News: Unpacking Today’s Groundbreaking Developments
Explore the Latest Cryptocurrency Market...
What is Animoca Brands? Learn about the Blockchain empire
In the dynamic world of...
Decentralized Approaches to Blockchain Security: A New Era of Trust
Decentralized approaches to blockchain security:...
Unraveling the Mystery: What is a Block in Blockchain?
What is a block in...
How Blockchain Security Audits Safeguard Your Digital Assets
How Blockchain Security Audits Work:...
Don’t miss out on the DogX, Airdrop to X users
“DogX, Airdrop to X users”...
Blockchain Brilliance: How Students Can Master Their Data Management
Role of students in managing...
Cryptocurrency Analysis Essentials: Unlocking Profitable Market Insights
Explore the Crypto Market Landscape:...