What is blockchain architecture? It’s the skeleton of a new digital world. Peel back the curtain and you’ll see a complex array of parts working in harmony. Imagine a puzzle – one that spans the globe, involving countless computers. These pieces join forces, forming a tamper-proof system. It’s a vault for our digital assets, a new way to record everything without fear of corruption or loss. This architecture isn’t just a tech buzzword; it’s a blueprint for trust in the digital age. Get ready to dive deep as we break down every element, showing you how it all clicks into place.
Understanding the Core Components of Blockchain Architecture
The Role of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
Distributed Ledger Technology, or DLT, is key to how blockchains work. DLT is like a shared record book. Each person keeps a copy. This means everyone can see all the entries, and no single person can change them without others knowing. It makes the system fair and safe.
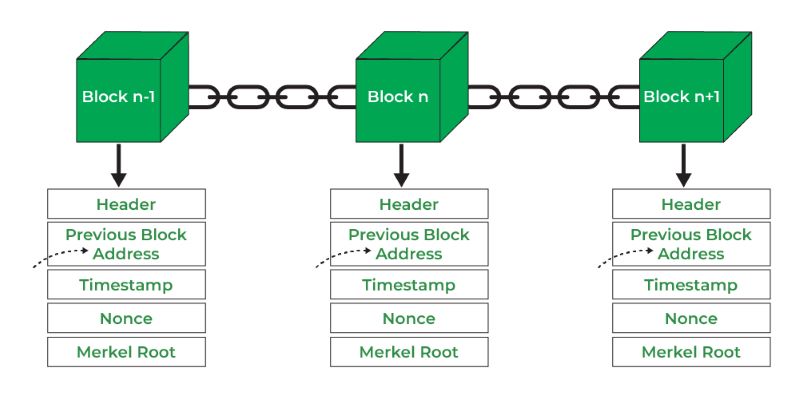
Now, let’s dive deeper. Inside DLT, you’ll find different components. Each record in this book, or ledger, is called a block. When we link blocks with security codes, we create a chain — thus, a blockchain. These codes are super tough to break, thanks to something called cryptography. That’s why it’s safe.
Because of DLT, blockchain lets us share details across the world quickly and accurately. This tech can track anything of value — like money or property. It’s a big shift from old systems, where one group held all the records.
Consensus Mechanisms Defined: Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake
How does blockchain make sure all its records are true? Through rules called consensus mechanisms. These are like games that all the computers play to agree on what’s true. The two big games are Proof of Work and Proof of Stake.
Proof of Work is like a tough math puzzle. Computers compete to solve it. The first one that does gets to add a new block to the chain. This takes a lot of time and power.
Proof of Stake is different. Here, if you have more of the blockchain’s coin, you have a bigger chance to add a new block. It doesn’t need tough puzzles like Proof of Work, so it uses less power.
Each system has its own perks. Proof of Work, for example, has been around longer, so it’s been tested more. But it uses tons of energy. On the other hand, Proof of Stake is newer and might not be as tested, but it’s greener since it uses less energy.
So, when we talk about DLT in blockchains, remember it’s all about spreading out the record-keeping to make things safer and fairer. And consensus mechanisms are the rules that keep everyone honest. Each has its own way to make sure that each entry in our digital record book is one we can trust.
The Structural Elements: Nodes, Networks, and Storage
Balancing Decentralization in Blockchain: Nodes and Networks
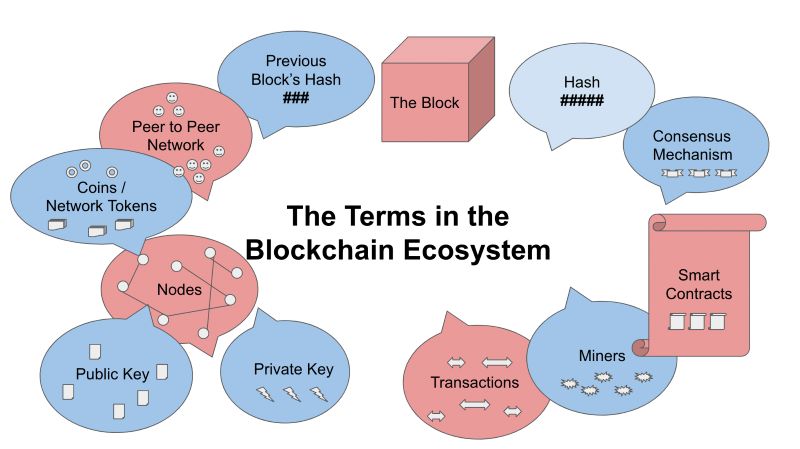
In blockchain, nodes are like the eyes and ears of the system. They are computers connected to the blockchain network keeping a copy of the data. Each node has the full history of all transactions. This makes sure no one can cheat. Decentralization is when no single place or person controls the system. It’s like a game where everyone follows the same rules, and no one is the boss. This setup is powerful but tricky. It needs many nodes working together well. They check on each other using rules called consensus mechanisms.
Public and private blockchains are two types of networks. A public blockchain is like a big open park where everyone can come and go. Bitcoin and Ethereum are in this group. On the other hand, private blockchains are like members-only clubs. Only some people can join. These are often used by companies that want more control and privacy.
Designing Data Storage Solutions with Blockchain’s Immutability
You might wonder, “Why is blockchain safe for keeping data?” The secret is immutability. Once data goes in, it can’t be changed or deleted. It’s like carving info into a stone tablet. Blockchain uses something called cryptographic hash functions to do this. These are like super complex puzzles. When you have data, these puzzles lock it up tight. Even a tiny change in the data rewrites the whole puzzle!
Smart contracts make this even smarter. They are like automatic rules on the blockchain. Let’s say you’re buying a song online. The smart contract holds your payment until it checks you got the song. Then, it pays the seller. It does what’s promised without anyone stepping in. Because of blockchain’s setup, you need many nodes to agree on changes. This is the transaction validation process. Every node checks the rules are followed. If they are, the new data gets added for everyone. This keeps the system honest and tough to fool.
Blockchain’s layers are like different floors in a building. Each has its own job. One layer might take care of transactions. Another might handle contracts or keep track of who owns what. It’s all put together to work like a well-oiled machine.
So, that’s a peek into blockchain’s nuts and bolts. By combining nodes, networks, and smart data storage, blockchain forms a sturdy and straight-shooting digital backbone. It’s changing how we think about trust and sharing info online. It’s not just for tech whizzes, but for all of us to use and understand.
Constructing the Blockchain Ecosystem: Interoperability and Security
Enabling Secure Transactions: From Validation to Byzantine Fault Tolerance
Think of blockchain as a team sport. Each player is a computer, or node. They work together to keep score. That score is our data. They agree before changing the score. This is called consensus. What if one player tries to cheat? The rest won’t let that happen. This is how blockchain stops fraud.
Secure deals, called transactions, happen on the blockchain. They are like trades in a game. Everyone checks the trade. They make sure it follows the rules. If the rules work, the trade counts. We use things called cryptographic hash functions to do this. They are like secret handshakes. Only those in the game know it.
But what if some nodes are bad? There’s a special rule for that. It’s named Byzantine Fault Tolerance. It allows the game to go on. It keeps the score right. Even if some players are trying to mess it up. It’s part of what makes blockchain safe.
Addressing Scalability and Interoperability in Blockchain Networks
Now, as more people join this game, it needs to handle more trades. We don’t want the game to slow down or stop. That’s what scalability means. Figuring this out is tough. But it’s key if we want everyone to play.
Interoperability is like making our game rules work with other games. Sometimes, we want to move scores between different games. This helps us connect and share. This way, no matter the game, we can still play together.
Blockchain is growing. It has to stay quick and open. We use things like sidechains. They are like extra courts. Some plays can happen there. This can free up space in our main game. New tech, like cross-chain, helps different blockchains talk to each other. It’s like making friends in new games.
As experts, we’re always working on these puzzles. To make blockchain better for all. It’s exciting to see where it will go. To see how it will help us play a fairer, more connected game.
Implementing Blockchain in Business: Use Cases and Adoption
Smart Contracts and Their Role in Enterprise Applications
Picture this: you’re signing a deal that can’t go wrong. That’s a smart contract for you—a set of rules on a blockchain that no one can tamper with. It’s like a vending machine for business deals. You put in your task, and out comes an action, all by itself.
These digital contracts cut out the middleman. No more waiting for a human to stamp a form. They work around the clock, with exact precision. And they’re becoming a big deal in business. Companies use them for anything from tracking goods to issuing tickets for events.
“With smart contracts, trust is never an issue,” people often say. This trust comes from the blockchain. It’s a system that records every step. It’s like a witness that never forgets. So, when you agree to a smart contract, it’s set in stone.
In actual business use, smart contracts save time and money. And they’re not just for the big players. Even small businesses are finding smart contracts helpful. They cut down on errors and the time it takes to do stuff. It’s a win-win in the business world.
IoT and Cross-Chain Technology: Expanding Blockchain Use Cases
Now, let’s toss IoT into the mix. IoT stands for “Internet of Things.” This is all about connecting devices online so they can chat with each other. From your fridge to a factory sensor, they all join the talk.
Blockchain gives these talks a layer of safety. It makes sure the devices can trust each other. It’s perfect for when you don’t want leaks or hacks. Imagine your smartwatch paying for coffee, or a warehouse that orders more stock on its own. Blockchain and IoT make these things safer and smarter.
And here’s where cross-chain technology steps up. This lets different blockchains join hands and work together. Think of it like phone networks. You can call someone even if they’re not on the same service as you, right? Cross-chain tech does that for blockchains.
This teamwork paves the way for more uses. Your data can hop from one blockchain to another. Before, blockchains worked solo and kept things to themselves. Now, they share, making business smoother and giving customers more power.
In businesses, IoT and cross-chain are game-changers. They track goods from far away, manage supply chains like magic, and keep our stuff safe. They’re pioneering new ways to do business, and the future looks bright with them on board.
Blockchain is not just a buzzword; it’s changing how we do business. From smart contracts to talking gadgets, it’s making things faster, cheaper, and a whole lot safer. The more we use it, the more we realize its power. It’s leading the digital revolution, and we’re just getting started.
We’ve explored each key piece of blockchain’s design, from how it stores data to its unbreakable security. First, we saw how distributed ledgers work and the big ideas behind consensus methods like proof of work and proof of stake. Next, we looked at nodes and networks, and how they keep blockchain decentralized. We also covered why blockchain data is set in stone and how that helps you.
Then, we talked about making blockchain parts work together and keeping all transactions safe and sound. Lastly, we discussed real ways businesses are using blockchain today, like smart contracts that make deals easy and safe, and how blockchain plays well with the Internet of Things and connects different chains.
To wrap it up, blockchain is more than just tech talk—it’s a game-changer for secure, transparent deals all over the world. Whether it’s your own business or just your curiosity, knowing blockchain can really pay off. Keep an eye out, because blockchain is here to stay and will shape our digital future.
Q&A :
What is the Fundamental Structure of Blockchain Architecture?
Blockchain architecture comprises a decentralized network of nodes, each containing a complete copy of a ledger that records all transactions. The architecture is designed to be immutable and transparent, with transactions being verified by consensus algorithms before being added in chronological blocks to the chain.
How Do the Different Components of Blockchain Architecture Interact?
In blockchain architecture, components such as nodes, blocks, miners, and consensus mechanisms work in tandem. Nodes maintain and update copies of the ledger, miners validate and record transactions into new blocks, while consensus algorithms ensure that all nodes agree on the ledger’s state to maintain trust and security across the network.
What Role Does Cryptography Play in Blockchain Architecture?
Cryptography is a cornerstone of blockchain architecture, ensuring secure and trustworthy transactions. It is used to create digital signatures that verify a participant’s identity and to establish secure connections between nodes. Cryptography also underpins the ‘hashing’ process, which helps maintain the integrity and chronological order of the blockchain.
How Does Consensus Mechanism Influence Blockchain Architecture?
A consensus mechanism is critical to blockchain architecture as it provides a method for network participants to agree on the ledger’s state without the need for a central authority. Popular consensus mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), each with its own approach to validating transactions and achieving agreement across the network.
Can Blockchain Architecture Be Modified After Deployment?
Blockchain architecture is inherently resistant to modification; once data is recorded on the blockchain, it is difficult to alter. This ensures tamper-proof records. However, updates to the protocol can be made through various governance models, but they require a majority agreement from the network participants, often making the process challenging and requiring careful implementation to prevent forks.


RELATED POSTS
First Use Cases of Blockchain: Pioneering a Digital Revolution
Discover the genesis and early...
Platforms And Protocols For Connecting Different Blockchains: Interoperability Unlocked
Discover the Leading Interoperability Protocols...
Predictions For The Future Of Blockchain Technology: Trailblazing Tech Transformations Ahead
Blockchain technology is shaping the...
Ethereum Launch Unveiled: What’s New in the World of Crypto?
Discover the Launch of Ethereum...
Blockchain Showdown: Layer 1 vs Layer 2 Unraveled
Enhance transaction throughput with blockchain...
Blockchain Revolution: Blockchain Use Cases In Financial Services
Explore how blockchain is revolutionizing...
Advantages of Blockchain Transparency: Unveiling the Trust Revolution
Unlock the Advantages of Blockchain...
How does blockchain increase transparency: How Delivers Transparency
How does blockchain increase transparency?...
limitations of traditional systems in transparency: Unveiling the Gap
Limited transparency in old systems...
Blockchain For KYC/AML: Streamlining Compliance For The Future
Blockchain for KYC/AML: Revolutionizing compliance...
Predictions about the Future of Blockchain Security: Revolutionary Safeguards Ahead
Predictions about the future of...
Decentralized Systems Unveiled: Harnessing the Power of Collective Innovation
Unlocking the Benefits of Decentralized...
How does blockchain improve security: Enhancing Security in a Digital Age
How does blockchain improve security?...
What is a Bullish Run? Exploring Its Impact on Investment Strategies
What is a Bullish Run?...
Solayer Airdrop – Secrets to Maximizing Profits
To maximize profits from the...
Role of Blockchain Security Audits: Your Crypto Safe Haven?
Enhance Blockchain Security with Audits....