You’ve probably heard of blockchain—a tech buzzword nowadays. But dig deeper, and you hit the core: what is distributed ledger technology in blockchain? It isn’t just a trend; it’s a revolution. In this article, I’ll take you through the nuts and bolts of DLT, the unsung hero that makes blockchain tick. We’ll explore how it’s changing the face of digital transactions, and why businesses are scrambling to get on board. So, buckle up and get ready for a ride into the world of DLT!
Exploring the Fundamentals of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
What is Distributed Ledger Technology in Blockchain?
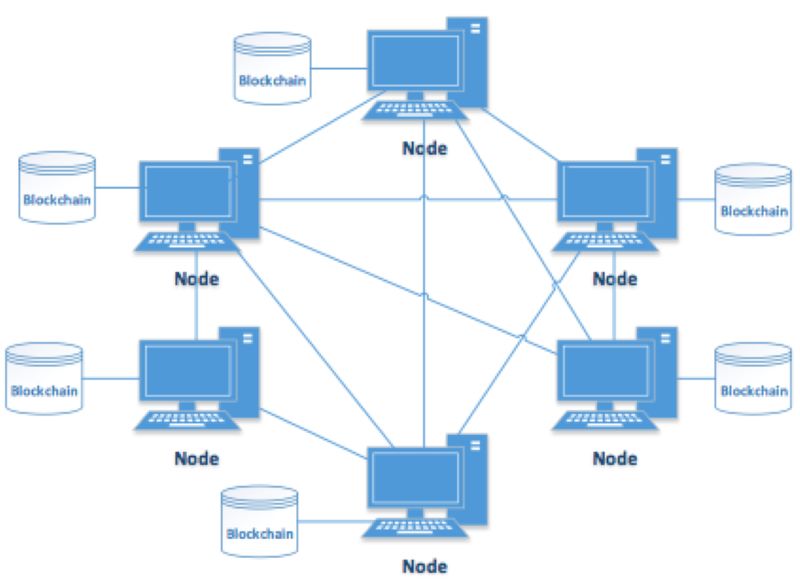
Let’s dive into how DLT works. Picture a ledger. It’s like a notebook filled with details of every transaction. Now, spread that notebook across a whole network. Every person owns a copy. When a new transaction happens, everyone updates their copy at the same time. This is DLT in action.
“Explain Distributed Ledger Technology.” It’s simple. DLT is a shared database. It lives across multiple places at once. Every part of the database talks to others. They all agree on what the data should look like. This trait is key. It makes sure every copy stays the same, all without a boss.
This is important for trust. When data lives in many places, changing it gets hard. If someone tries to cheat, the system spots it. The other parts won’t agree to the change. The record stays honest.
Now, imagine a chain of blocks. Each block holds a bunch of transactions. They’re linked together in order. This is blockchain, a type of DLT.
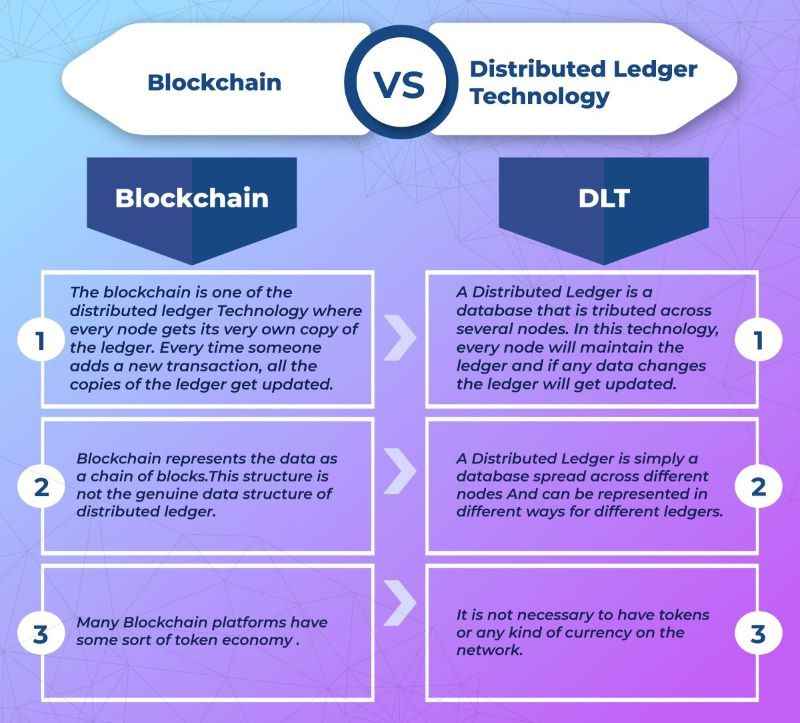
The Difference Between Blockchain vs. DLT
So, what’s the real difference between blockchain and DLT? Here it gets interesting. Not all DLTs are blockchains, but all blockchains are DLTs. Think of DLT as the big idea. Blockchain is a popular way to do it.
Blockchain is special because of how it groups transactions. They’re in blocks with a hash, like a unique fingerprint. This hash connects the blocks. It’s very secure and neat.
But other DLTs don’t use blocks. They can store data in many ways. Some are even faster than blockchains. They suit different needs, like voting or sharing power across a network.
In short, DLT is the big ocean. Blockchain is just one boat on it. Different boats have different uses. Some carry cargo. Others carry people. It all depends on what you need for your trip.
Understanding this can help us choose the right tool for the job. It’s like picking between a speedboat or a cruise ship. Both serve a purpose. With DLT, trust is key. It’s a game of everyone having the same story to tell.
Blockchain brought DLT into the light. It’s what runs Bitcoin and other digital money. DLT finds new ways to share data all the time. It’s changing how we think about online trust.
DLT doesn’t just stop with money. It’s great for keeping any records on track, like who owns a house or what’s in a product we buy. It’s a trusty hand in a world full of digital noise.
In summary, DLT spreads out data like cards on a table. Everyone can see and agree on the game being played. It’s fair and open. Getting to know DLT is like unlocking a door to a more honest online world. And that’s a place worth heading toward.
Consensus Mechanisms in Distributed Ledgers
How Consensus Works
Let’s delve into how the computers in a blockchain agree on the validity of transactions. Picture a classroom where students must reach a consensus on an answer. They discuss and debate until everyone agrees. This is similar to how DLT operates.
In a DLT network, every participant validates the information, ensuring security during transactions. The decentralized design means no single entity has control; instead, all computers work collaboratively. This consensus mechanism helps maintain the integrity of the data.
Each new transaction receives a unique code that’s difficult to replicate, ensuring that our information remains secure.
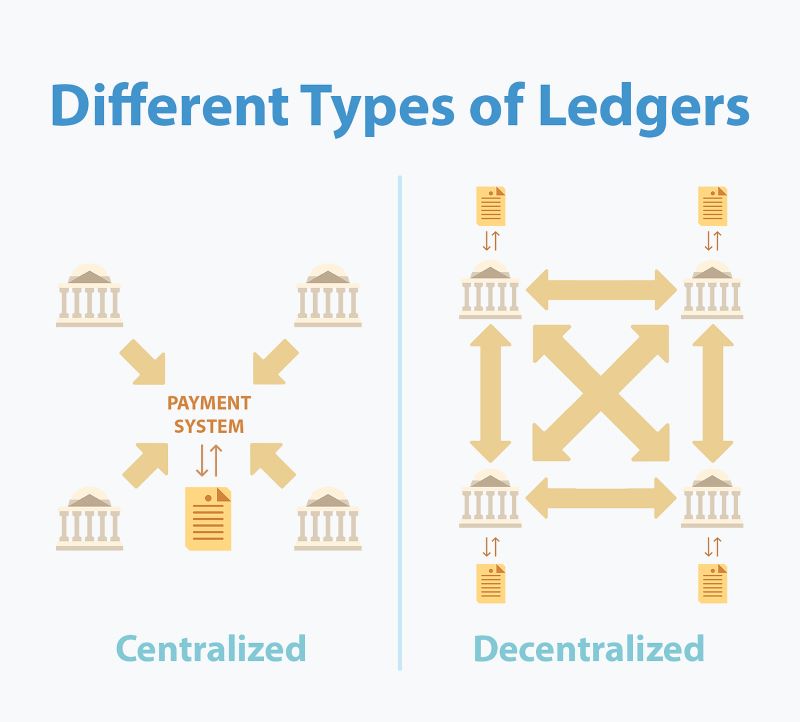
Types of Distributed Ledgers: Permissioned vs. Permissionless
There are two primary types of DLT:
- Permissioned Ledgers: These are like exclusive clubs, where only selected members can participate and make changes. This model is advantageous for businesses wanting to manage who accesses their network and keeps information private.
- Permissionless Ledgers: These function like public parks, open to anyone. This model supports cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, allowing users to join, send transactions, and view the entire transaction history.
Even in permissionless systems, transactions are secure. Each transaction is validated by computers across the globe, creating a robust trust framework.
The Role of DLT in Transforming Business Processes
Smart Contracts and Immutable Records
DLT has revolutionized how we manage data by allowing multiple parties to hold copies of a digital ledger, which are updated in real-time. This technology enhances security by ensuring that past data cannot be altered. Businesses are drawn to DLT for its reliability.
Additionally, DLT enables the use of “smart contracts.” These are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. Smart contracts automate processes, eliminating the need for intermediaries, which saves time and money. Industries are increasingly adopting smart contracts for a variety of applications.
Real-World Applications of DLT
DLT isn’t just a theoretical concept; it’s making significant impacts across various sectors. In supply chain management, DLT tracks products from manufacturer to consumer, enhancing transparency and accountability. It allows businesses to identify and resolve issues efficiently while ensuring product authenticity.
Beyond supply chains, DLT is transforming finance, healthcare, real estate, and more. For instance, in healthcare, it can safeguard patient records and streamline drug tracking. In finance, DLT can expedite cross-border payments.
Future-Proofing with Scalability Solutions and Robust Encryption Methods
Now, for the future. As more people use DLT, we need it to handle more action. This is scalability. We have to keep DLT fast as it grows. Imagine a road getting more lanes as more cars drive on it.
- DLT Scalability Solutions
What are we doing about scalability? We’re making DLT stretch like an elastic band. It can take on more trades, more users, without a sweat. We keep tweaking the tech and rules that make DLT work.
- Robust Encryption Methods
On top of that, we need iron-clad encryption. This is our digital lock to keep bad guys out. It turns data into secret codes. Even if they try, the bad guys can’t mess with these codes.
- Types of Distributed Ledgers
Did you know there are different types of DLT? Some are permissionless; anyone can join. Others are permissioned; these are like private clubs. Both have their uses, and both need to keep up with growth and security.
- Peer-to-Peer Networks and DLT
And let’s not forget, DLT runs on peer-to-peer networks. These are like teams where everyone plays a part. No single boss, everyone checks everyone else’s work. It gives power to the people and keeps the system fair and square.
To sum it up, DLT is about sharing and syncing data in a super-smart way. We want our DLT to pack a punch with speed and armor up with the best digital shields. We’re always after better ways to do this. And that’s what keeps things exciting in the world of DLT.
We’ve dug deep into how distributed ledger technology (DLT) shapes up and sets apart from blockchain. DLT’s smart design lets many users join in and keeps records straight without a boss. We’ve seen it’s not just one kind—it can be open to all or just some with permission.
Then we saw how it’s changing the game in business. Think smart contracts making deals smooth and the way it tracks stuff from start to end in supply chains.
But it’s not all smooth sailing. We’ve got to speed up transactions and lock down data tight to keep it safe and sound for the future. That’s where the real work is.
DLT’s cool and it’s got muscles to flex in our digital world. It’s changing things for the better, but we’ve got to keep our eyes peeled for the bumps. Let’s ride this wave smart!
Subscribe to our newsletter for insights, updates, and expert analysis on how DLT is transforming industries at here.
Q&A
- What is Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) in Blockchain?
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is a decentralized database that is managed by multiple participants across different locations. In the context of blockchain, DLT refers to the digital system for recording the transaction of assets in which the transactions and their details are recorded in multiple places at the same time. Unlike traditional databases, DLT has no central data store or administration functionality.
- How Does Distributed Ledger Technology Work in Blockchain?
DLT works by having a consensus mechanism that ensures all copies of the database are the same. This is essential in blockchain, as it is used to secure and synchronize all transactions. When a transaction is made, it is transmitted to a network of peer-to-peer nodes that validate the transaction. Once verified, the transaction is combined with other transactions to create a new block of data for the ledger, which is then added to the existing blockchain.
- What Are the Key Benefits of Distributed Ledger Technology in Blockchain?
The key benefits of using DLT in blockchain technology include enhanced security, transparency, and immutability. Security is improved because the data is decentralized, making it harder to tamper with. Transparency is achieved through the openness of the ledger, as all participants have access to the transaction history. Immutability ensures that once a transaction is entered in the ledger, it cannot be altered, creating a trustworthy and unchangeable record of transactions.
- Are Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology the Same Thing?
No, blockchain and DLT are not the same, though they are closely related. Blockchain is a type of DLT, where data is organized into blocks that are chained together. However, DLT can be structured in various other forms that do not necessarily follow a chain of blocks. All blockchains are DLTs, but not all DLTs are blockchains.
- What Are the Real-World Applications of DLT in Blockchain?
Real-world applications of DLT in blockchain encompass a wide range of industries, from finance and banking, where it’s used for secure and swift transactions, to healthcare, for maintaining patient records with improved confidentiality. In supply chain management, DLT offers transparent traceability of products from manufacturer to consumer. Additionally, DLT is used in voting systems, real estate, and legal services for secure and auditable transaction recording.

RELATED POSTS
Why Solana Layer 2 Sonic is the Key to High-Performance Gaming
Solana Layer 2 Sonic is...
Privacy Considerations: Navigating the Future of Student Data Management
Discover how to ensure privacy...
What is Data Tokenization? – The Key to Secure Data Management
What is Data Tokenization? This...
Crypto Currency on Futureverse – Breakthrough for the Future of Digital Finance
Crypto currency on Futureverse represents...
Impact of Consensus Algorithms: Bolstering or Breaking Security?
Explore the impact of consensus...
Why did Gama fail Crypto?
“Why did Gama fail crypto?”...
Blockchain in Education: Unlocking Cost-Saving Strategies for Students and Institutions
Educational cost reduction in schools...
Explanation of Proof of Work: How PoW Secures Blockchain Innovation
Explanation of Proof of Work...
The Unmatched Benefits of Blockchain in Education!
Unlocking Potential: How Blockchain Transforms...
Arch Network Airdrop: Detailed guide on how to participate
Arch Network is an innovative...
Gala Airdrop and 6 Tips to Maximize Gala Game Rewards
To maximize rewards from the...
Messari Crypto: A powerful tool for investors
In the world of cryptocurrency,...
Casper Crypto: Exploring and evaluating growth potential
As the cryptocurrency market continues...
Can You Rewrite Blockchain History? Exploring Data Immutability
Can you change data on...
Dunes Airdrop – Optimizing liquidity from resting assets
Dunes Airdrop brings a solution...
Decentralized Learning Unchained: Navigating the Blockchain Education Revolution
"How do decentralized learning platforms...