DAG Blockchain has become increasingly popular in the world of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology due to its remarkable advantages in transaction speed, scalability, and low cost. But what is DAG Blockchain? How does this technology work? In this article, we will explore DAG Blockchain in detail, how it differs from traditional blockchains, and its potential applications in the future.
What is DAG Blockchain?
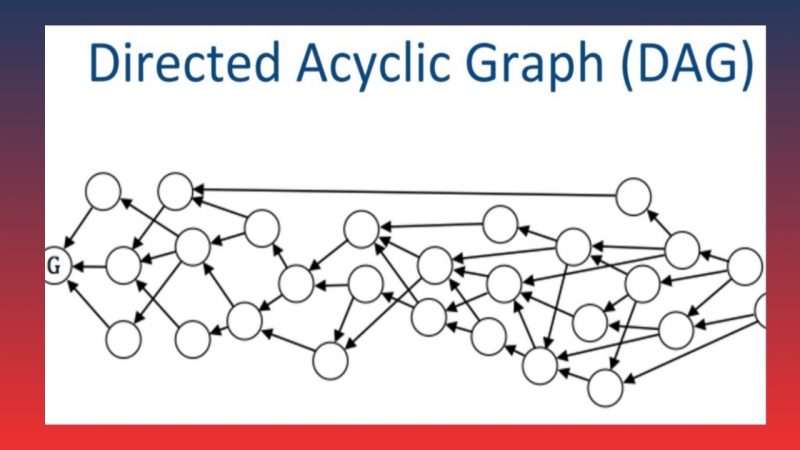
DAG Blockchain (Directed Acyclic Graph Blockchain) is a blockchain technology that replaces the traditional block structure with a directed acyclic graph (DAG). Instead of grouping transactions into blocks, like traditional blockchains such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, each transaction in DAG is recorded as a vertex in the graph and directly linked to previous transactions.
This means there are no specific blocks containing transactions. Instead, transactions are interconnected in a nonlinear chain. This structure eliminates the need for mining or consensus mechanisms (such as Proof of Work or Proof of Stake) required in traditional blockchain systems. Instead, DAG Blockchain validates transactions directly between transactions, reducing costs and speeding up transaction times. As a result, DAG can overcome the limitations of traditional blockchains, especially in terms of scalability and transaction performance.
With DAG, when a participant joins the network, they don’t have to wait for a new block to be created. Instead, they can create and validate transactions instantly, making DAG an ideal choice for applications requiring fast and continuous transaction processing.

How does DAG Blockchain work?
DAG Blockchain operates on the principle of a directed acyclic graph. Its mechanism is completely different from traditional blockchain systems, where transactions are grouped into blocks and must undergo validation through consensus algorithms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS).
In DAG Blockchain, each transaction is recorded as a vertex in the graph and does not need to be grouped into a block. New transactions are linked to previous transactions in the network, forming a continuous transaction chain. Transaction validation is done directly through the relationships between these transactions rather than through mining or consensus between miners.
One major advantage of DAG is its ability to eliminate network congestion, as there is no dependence on transaction blocks. In traditional blockchains, as the number of transactions increases, miners must process and validate each one, leading to congestion. However, in DAG Blockchain, transactions can be validated and processed in parallel without waiting for a new block’s confirmation. This improves the scalability and transaction speed of the network.
Advantages of DAG Blockchain
Fast and efficient transactions
One of the key advantages of DAG Blockchain is its ability to process transactions quickly and efficiently. While traditional blockchain systems like Bitcoin require waiting for a new block to be created and validated, DAG allows transactions to be validated immediately, avoiding congestion.
Thanks to its nonlinear mechanism and lack of blocks, DAG can process millions of transactions per second (TPS), far surpassing traditional blockchains. This is particularly crucial in financial and payment environments, where transaction speed is a decisive factor in the success of the system.
Cost and energy efficiency
DAG Blockchain does not require mining or the use of expensive consensus algorithms like Proof of Work (PoW). This not only reduces transaction costs but also saves energy. In traditional blockchains, mining requires complex calculations and consumes a significant amount of energy, raising costs and creating an environmentally unfriendly system.
In contrast, DAG eliminates this requirement by using a direct validation mechanism between transactions, reducing operational costs and minimizing environmental impact. This is especially important as global concerns over energy consumption and environmental protection continue to rise.
Superior scalability
Scalability is one of the greatest challenges of traditional blockchain systems. As the number of transactions increases, blockchain networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum are prone to congestion, causing longer validation times and higher costs. However, with DAG Blockchain, each transaction can be validated and processed in parallel without facing congestion issues. This allows DAG to scale better and process millions of transactions per second without compromising system performance.
This scalability makes DAG Blockchain an ideal choice for applications requiring fast and continuous transaction speeds, such as payment systems, the Internet of Things (IoT), and decentralized finance (DeFi) services.
Disadvantages of DAG Blockchain
Despite the many benefits of DAG Blockchain, there are some limitations to consider:
- Decentralization issues: One of the key features of traditional blockchains is decentralization. However, in some DAG systems, decentralization may be reduced. This happens when network nodes are not evenly distributed but are concentrated in certain regions or large organizations, increasing the risk of centralization of power.
- Spam attacks and security: DAG Blockchain may become a target for spam attacks, as it has low transaction costs and does not require mining. Fake transactions can be sent into the network to slow down or disrupt the system. Additionally, since DAG does not use consensus algorithms like Proof of Work, its security could be compromised if not protected by robust measures.
- Community and regulatory challenges: With the rapid development of DAG Blockchain technology, many organizations and investors are still not fully understanding or accepting this technology. This could make it challenging to build a user community and implement real-world applications. Furthermore, regulatory frameworks for this technology are still being developed.
Notable DAG Blockchain projects
DAG Blockchain is increasingly being applied in technology projects, especially in fields that require fast transaction speeds, large scalability, and low costs. Many blockchain projects use DAG to address the issues faced by traditional blockchain systems. Here are some notable projects utilizing DAG Blockchain technology:
IOTA
IOTA is a pioneering project that uses DAG Blockchain technology through a system called Tangle. Tangle differs from traditional blockchains by not using blocks and chains to store transactions. Instead, transactions in Tangle are organized as a directed acyclic graph (DAG), where each transaction validates two previous transactions, eliminating miners and transaction costs.
IOTA applications:
- Internet of Things (IoT): IOTA is designed to serve IoT, a field that requires high transaction speed and flexible scalability. IoT devices can communicate and transact without intermediaries, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
- Industries and Smart cities: IOTA has partnered with many large organizations to develop applications in smart cities, improving communication between devices and systems.
U2U Chain
U2U Chain is an emerging blockchain project that uses DAG technology to provide scalability solutions for decentralized networks in DePIN (Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks). U2U Chain uses DAG Blockchain to optimize transaction speeds and reduce costs in applications like IoT, decentralized storage, and GPU computing.
U2U Chain applications:
- DePIN (Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks): U2U Chain serves as the main platform for dApps in the DePIN space, using DAG technology to optimize the connection and data exchange between devices and users.
- IoT Networks and decentralized storage: U2U Chain has great potential to improve the performance of IoT networks and decentralized data storage systems, where transaction speed and scalability are crucial.
Nano
Nano is a notable project that applies DAG Blockchain, using a network structure called Block-Lattice instead of traditional blockchains. Each account in Nano has its own blockchain and can transact with other accounts without miners. This structure enhances scalability and reduces transaction fees.
Nano applications:
- Fast payments and transactions: Nano excels at processing real-time transactions with no transaction fees, making it an ideal choice for small transactions and fast payments.
- Payment service integration: Online payment platforms can integrate Nano for quick, cost-effective payment methods for users.
Constellation
Constellation is a DAG Blockchain platform designed to address scalability and transaction speed issues in traditional blockchain systems. Constellation uses Hypergraph technology to provide an efficient and decentralized transaction validation mechanism, allowing the system to handle large volumes of transactions without congestion.
Constellation Applications:
- Big data management: Constellation is designed to handle and analyze large volumes of data in applications like Big Data and Data Science. The system can efficiently store and retrieve distributed data.
- Finance and enterprise Blockchain: Constellation is applied in finance and enterprise sectors, where fast and secure transaction processing with low costs is essential.
Hedera Hashgraph
Hedera Hashgraph is a DAG Blockchain platform designed to provide a powerful, fast, and secure distributed solution. Hedera does not use Proof of Work or Proof of Stake but instead uses an algorithm called Gossip about Gossip and Virtual Voting to achieve consensus and validate transactions. This gives Hedera superior scalability while maintaining a high level of security.
Hedera hashgraph applications:
- Enterprise Blockchain: Hedera Hashgraph is an ideal platform for enterprise blockchain applications requiring scalability and high transaction speeds.
- Finance and smart contracts: Hedera is used in DeFi projects and Smart Contracts, offering a safe and fast environment for decentralized financial transactions.
- Supply chain management: With its ability to process transactions quickly and efficiently, Hedera Hashgraph is used in supply chain management, where transparency and efficiency are critical.
DAG Blockchain offers many superior advantages over traditional blockchain systems, particularly in terms of transaction speed, scalability, cost savings, and energy efficiency. With the ability to process millions of transactions per second and no need for mining, DAG presents a perfect solution for applications requiring high speed and low costs. Although there are challenges to overcome, especially regarding decentralization and security, DAG Blockchain remains a promising technology that could revolutionize how we conduct transactions and apply blockchain in the future.
We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights into “What is DAG Blockchain?” Stay tuned to Blockchain Global Network for more informative content every day.

RELATED POSTS
Impact of martial law in South Korea on the financial market
On December 3, 2024, South...
How Base L2 Sequencers are enabling the next generation of blockchain innovation
The evolution of blockchain technology...
How blockchain is revolutionizing the healthcare industry
The healthcare industry is grappling...
What is Data Tokenization? – The Key to Secure Data Management
What is Data Tokenization? This...
Trump Hosts Exclusive Dinner for Top $TRUMP Holders
On April 23, 2025, the...
Mushroom Warrior Bot Airdrop: Easy Tasks, Big Rewards
The Mushroom Warrior Bot Airdrop...
What are distributed systems? Bridging the Gap Between Efficiency and Complexity
In today’s digital age, the...
What is Airdrop in the Crypto World? Exploring Its Benefits and Risks
Curious about What is airdrop...
Top 3 Secrets behind Bitcoin Peak that you must know
The rise and fall of...
Rings Protocol Airdrop: How to Maximize Your Chances for Sonic Gems
Rings Protocol, a yield-bearing stablecoin...
How to add binance smart chain to metamask?
If you’ve been asking “How...
Stuart Alderoty: His role at Ripple
Discover Stuart Alderoty, Chief Legal...
WOO Network: A powerful DeFi financial platform
WOO Network (WOO) is a...
Moonwalk Fitness Airdrop – Guide to Participate and Receive Rewards
Moonwalk Fitness Airdrop offers a...
Remis Launches: A New Era in GameFi Innovation
On February 1, 2025, Remis...
Bitget integrates VietQR in Vietnam: Supporting VND Deposits and cryptocurrency trading
Bitget Integrates VietQR in Vietnam:...